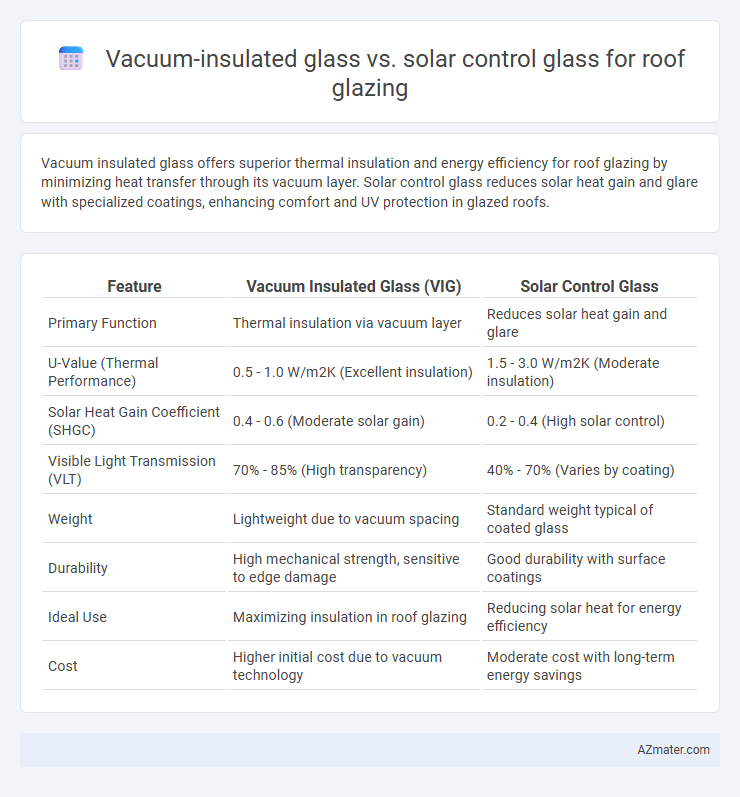
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for roof glazing by minimizing heat transfer through its vacuum layer. Solar control glass reduces solar heat gain and glare with specialized coatings, enhancing comfort and UV protection in glazed roofs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Solar Control Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermal insulation via vacuum layer | Reduces solar heat gain and glare |
| U-Value (Thermal Performance) | 0.5 - 1.0 W/m2K (Excellent insulation) | 1.5 - 3.0 W/m2K (Moderate insulation) |
| Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) | 0.4 - 0.6 (Moderate solar gain) | 0.2 - 0.4 (High solar control) |
| Visible Light Transmission (VLT) | 70% - 85% (High transparency) | 40% - 70% (Varies by coating) |
| Weight | Lightweight due to vacuum spacing | Standard weight typical of coated glass |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, sensitive to edge damage | Good durability with surface coatings |
| Ideal Use | Maximizing insulation in roof glazing | Reducing solar heat for energy efficiency |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to vacuum technology | Moderate cost with long-term energy savings |
Introduction to Roof Glazing Solutions
Roof glazing solutions enhance natural light and energy efficiency in buildings by selecting the right glass technology. Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation with minimal thickness, reducing heat loss and condensation under varied weather conditions. Solar control glass minimizes solar heat gain through specialized coatings, improving indoor comfort and reducing cooling loads in sun-exposed roofs.
Overview of Vacuum Insulated Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum, drastically reducing conductive and convective heat transfer, making it ideal for roof glazing where energy efficiency is critical. Its superior thermal insulation outperforms solar control glass, which primarily reduces solar heat gain by reflecting infrared radiation but offers less overall insulation. VIG enhances indoor temperature stability, minimizes condensation, and supports sustainable building certifications in high-performance roof glazing applications.
Understanding Solar Control Glass
Solar control glass for roof glazing is designed with coatings that reflect and absorb solar radiation, significantly reducing heat gain while maintaining high visible light transmission to enhance natural daylighting. Vacuum insulated glass (VIG), by contrast, emphasizes superior thermal insulation through a vacuum space between glass layers, minimizing conductive and convective heat transfer but offering limited solar heat regulation. Understanding solar control glass technology involves recognizing its role in controlling glare and solar heat, improving energy efficiency, and increasing occupant comfort in roof glazing applications.
Thermal Efficiency Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation for roof glazing by significantly reducing heat transfer through its airless space between glass layers, achieving U-values as low as 0.7 W/m2K, compared to solar control glass which typically has higher U-values around 2.5 W/m2K. Solar control glass primarily limits solar heat gain through selective coatings, reducing cooling loads but providing less overall insulation against conductive heat loss. For maximizing energy efficiency and maintaining stable indoor temperatures, vacuum insulated glass outperforms solar control glass in thermal performance of roof glazing systems.
Solar Heat Gain: Performance Differences
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior solar heat gain reduction by minimizing heat transfer through its vacuum layer, resulting in enhanced thermal insulation and lower interior temperatures for roof glazing applications. Solar control glass primarily reflects and absorbs infrared radiation, reducing solar heat gain but allowing slightly higher heat transmission compared to vacuum insulated glass. For optimal energy efficiency and indoor comfort, vacuum insulated glass provides a more effective solution in mitigating solar heat gain in roof glazing systems.
Energy Savings and Cost Implications
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation with U-values as low as 0.7 W/m2K, significantly reducing heat loss and improving energy savings compared to solar control glass, which primarily limits solar heat gain but has higher U-values around 1.1-2.8 W/m2K. Solar control glass can lower cooling costs by blocking up to 70% of solar radiation, making it cost-effective in hot climates, while VIG's higher upfront cost is offset by long-term savings on heating and cooling bills in varied climates. Choosing between VIG and solar control glass depends on balancing initial investment with targeted energy performance for specific roof glazing applications.
Daylight Transmission and Comfort
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer through its vacuum layer, resulting in enhanced indoor comfort while maintaining high daylight transmission levels ideal for roof glazing. Solar control glass reduces solar heat gain through specialized coatings that reflect infrared radiation, improving thermal comfort but often at the expense of lowered visible light transmission. Balancing daylight transmission and comfort, vacuum insulated glass is optimal for maximizing natural light without compromising energy efficiency, whereas solar control glass prioritizes heat reduction with moderate daylight allowance.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior durability for roof glazing due to its airtight sealed space that prevents moisture ingress and reduces thermal stress, significantly extending lifespan with minimal maintenance. Solar control glass, while effective at reducing solar heat gain, may require more frequent cleaning and inspection to maintain coating efficacy and prevent surface degradation from UV exposure. Choosing vacuum insulated glass minimizes long-term maintenance costs and enhances structural integrity in harsh weather conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) significantly reduces thermal transfer, enhancing energy efficiency and lowering heating and cooling demands in roof glazing applications, which minimizes overall carbon emissions. Solar control glass filters solar radiation, reducing heat gain and the need for air conditioning, promoting energy savings but often contains coatings that may complicate recycling processes. Choosing VIG supports long-term sustainability by extending building lifespan with superior insulation properties, while solar control glass contributes to immediate energy reduction, necessitating a balance based on environmental goals and operational performance.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Roof Glazing
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation with a U-value as low as 0.5 W/m2K, making it ideal for energy-efficient roof glazing by minimizing heat loss and condensation. Solar control glass enhances comfort by blocking up to 70% of solar heat gain while allowing high visible light transmission, effectively reducing cooling loads in sunny climates. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing insulation needs and solar heat control based on local climate, building orientation, and energy performance goals.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Solar control glass for Roof glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com