Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for heat-resistant tableware, while milk glass is favored for its opaque, decorative appearance and vintage charm in serving dishes. Choosing between the two depends on whether functionality or aesthetic appeal is the primary priority in tableware selection.
Table of Comparison
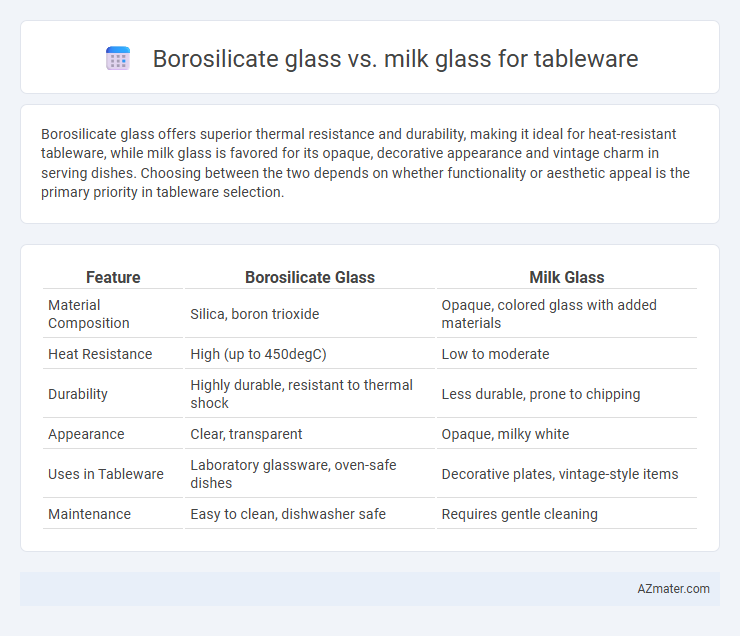
| Feature | Borosilicate Glass | Milk Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silica, boron trioxide | Opaque, colored glass with added materials |
| Heat Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Low to moderate |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to thermal shock | Less durable, prone to chipping |
| Appearance | Clear, transparent | Opaque, milky white |
| Uses in Tableware | Laboratory glassware, oven-safe dishes | Decorative plates, vintage-style items |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Requires gentle cleaning |
Introduction to Tableware Material Choices
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for heat-resistant tableware such as bakeware and drinkware. Milk glass, characterized by its opaque, milky white appearance, is prized for decorative table settings and vintage aesthetics but is more prone to chipping and less heat resistant. Choosing between borosilicate glass and milk glass depends on balancing functional performance with stylistic preferences in tableware applications.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its exceptional thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for tableware that can withstand sudden temperature changes. Composed primarily of silica and boron oxide, it offers superior strength compared to regular glass and resists chemical corrosion. Unlike milk glass, which is opaque and primarily decorative, borosilicate glass is transparent and practical for everyday use, especially in kitchens requiring heatproof and dishwasher-safe dishes.
What is Milk Glass?
Milk glass is a type of opaque or translucent white glass often used in tableware for its vintage aesthetic and durability. Unlike borosilicate glass, which is known for its thermal resistance and clarity, milk glass is prized for its decorative appeal and sturdy, non-transparent quality. Its composition includes calcium and magnesium silicates, making it less heat-resistant than borosilicate but favored for ornamental dishes and serving pieces.
Visual Aesthetics: Clarity vs. Opacity
Borosilicate glass offers exceptional clarity and brilliance, allowing vibrant colors and intricate designs beneath the surface to shine through with minimal distortion. Milk glass, characterized by its opaque and milky white appearance, provides a soft, diffuse glow that adds a vintage or classic charm to table settings. The choice between borosilicate and milk glass tableware depends on whether a transparent, modern look or a translucent, nostalgic aesthetic is preferred.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers exceptional durability and strength due to its low thermal expansion, making it resistant to thermal shock and less prone to cracking or breaking under temperature changes, ideal for everyday tableware use. Milk glass, while aesthetically appealing with its opaque and glossy finish, is more fragile and prone to chipping or breaking under impact or sudden temperature shifts. For long-lasting, resilient tableware, borosilicate glass outperforms milk glass significantly in terms of strength and durability.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Shock
Borosilicate glass exhibits exceptional heat resistance, tolerating temperatures up to 450degC and rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it ideal for oven-safe tableware. Milk glass, while visually appealing, has lower thermal tolerance and is prone to thermal shock when subjected to sudden temperature shifts, limiting its use in high-heat applications. For durability and safety under thermal stress, borosilicate glass outperforms milk glass in heat resistance and thermal shock resistance.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Borosilicate glass is highly resistant to thermal shock, making it safer for handling hot food and beverages without the risk of cracking or releasing harmful substances. Milk glass, although durable, lacks the same heat resistance and may be more prone to chipping or chemical leaching when exposed to acidic or hot foods. For food compatibility, borosilicate glass is non-porous and inert, ensuring no alteration in taste or contamination, whereas milk glass's opaque nature can sometimes hide defects and may contain lead or other compounds affecting food safety.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Borosilicate glass offers superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical damage, making it easier to clean with a variety of detergents without risk of scratches or clouding. Milk glass, being opaque and more porous, requires gentler cleaning methods to avoid surface damage and discoloration, often needing hand washing to maintain its aesthetic quality. Both materials benefit from avoiding abrasive cleaners, but borosilicate glass's durability allows for more versatile and low-maintenance cleaning options in tableware use.
Cost and Value Assessment
Borosilicate glass tableware offers superior durability and thermal resistance, justifying its higher initial cost by reducing replacement frequency and ensuring long-term value. Milk glass is more affordable upfront but tends to be less durable and more prone to chipping, which may increase replacement costs over time. Evaluating cost-effectiveness, borosilicate glass provides better value for households seeking longevity and resilience in everyday use.
Which is Best: Borosilicate Glass or Milk Glass for Tableware?
Borosilicate glass is best for tableware due to its high thermal resistance, durability, and clarity, making it ideal for both hot and cold foods. Milk glass, while aesthetically pleasing with its opaque, glossy finish, is more fragile and less resistant to temperature changes, limiting its practicality for everyday use. For durability and versatility in tableware, borosilicate glass outperforms milk glass significantly.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Milk glass for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com