Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light and heat control for skylights, reducing energy costs and enhancing comfort by automatically adjusting tint based on sunlight intensity. Laminated glass provides superior safety and sound insulation but lacks the adaptive shading features of electrochromic technology.
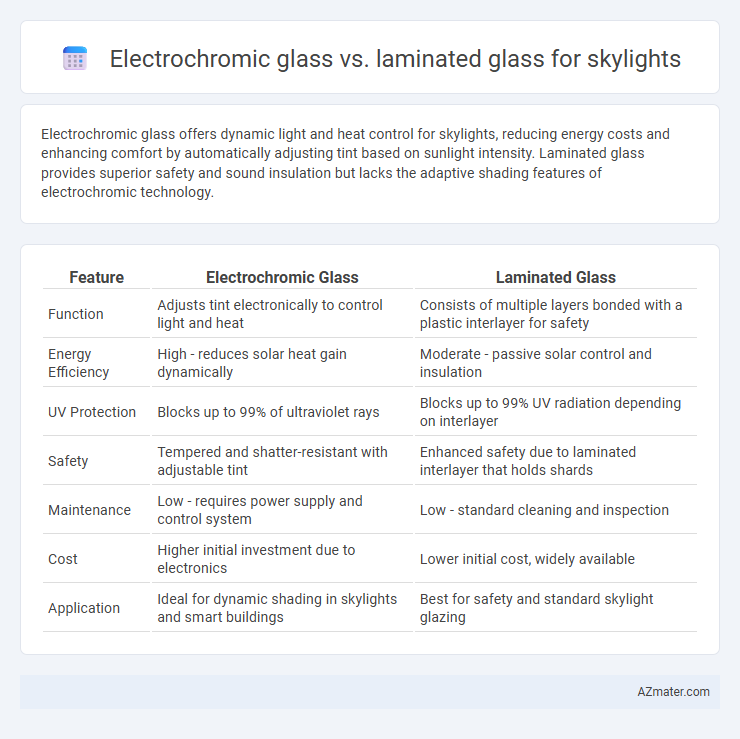
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Adjusts tint electronically to control light and heat | Consists of multiple layers bonded with a plastic interlayer for safety |
| Energy Efficiency | High - reduces solar heat gain dynamically | Moderate - passive solar control and insulation |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% of ultraviolet rays | Blocks up to 99% UV radiation depending on interlayer |
| Safety | Tempered and shatter-resistant with adjustable tint | Enhanced safety due to laminated interlayer that holds shards |
| Maintenance | Low - requires power supply and control system | Low - standard cleaning and inspection |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to electronics | Lower initial cost, widely available |
| Application | Ideal for dynamic shading in skylights and smart buildings | Best for safety and standard skylight glazing |
Introduction to Skylight Glass Options
Skylight glass options include electrochromic glass and laminated glass, each offering unique benefits for natural lighting and energy efficiency. Electrochromic glass dynamically adjusts tint to control solar heat gain and glare, enhancing comfort and reducing HVAC costs. Laminated glass provides superior strength and safety, with excellent UV protection and noise reduction, making it ideal for secure and durable skylight installations.
Overview of Electrochromic Glass
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control by adjusting its tint in response to electrical voltage, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in skylight applications. Unlike laminated glass, which primarily provides impact resistance and safety through layers of glass and interlayers, electrochromic glass actively regulates solar heat gain and glare without obstructing natural daylight. This smart glazing technology reduces reliance on blinds or shades, contributing to sustainable building design and improved indoor environmental quality.
Overview of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for skylights consists of two or more glass layers bonded with a durable interlayer, providing enhanced safety, impact resistance, and UV protection. Its ability to hold shattered glass fragments prevents falling hazards and improves structural integrity during storms. Laminated glass also offers acoustic insulation and reduces solar heat gain, making it a practical choice for energy-efficient and secure skylight installations.
Performance Comparison: Light Control
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control by allowing users to adjust the tint electronically, reducing glare and controlling solar heat gain effectively throughout the day. Laminated glass provides fixed light transmission with enhanced safety and UV protection but lacks the ability to modulate light intensity in real-time. For skylights, electrochromic glass outperforms laminated glass in adaptive daylight management, improving occupant comfort and energy efficiency.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Electrochromic glass for skylights offers dynamic energy efficiency by automatically adjusting tint to control solar heat gain and reduce cooling loads, significantly lowering HVAC energy consumption. Laminated glass provides superior insulation through its multiple layers, enhancing thermal resistance and reducing heat transfer, which improves overall energy conservation. Combining electrochromic technology with laminated glass can optimize both solar control and insulation, maximizing daylight management and indoor temperature stability.
Safety and Security Features
Electrochromic glass enhances skylight safety by enabling dynamic tint adjustment, reducing glare and heat while maintaining visibility and UV protection, which helps prevent interior damage and improves occupant comfort. Laminated glass provides superior security through its impact-resistant interlayer, preventing shattering and minimizing injury risks from breakage in extreme weather or accidents. Both technologies offer strong safety features, with electrochromic glass focusing on environmental control and laminated glass emphasizing structural integrity and protection against intrusion.
Durability and Maintenance
Electrochromic glass offers advanced durability with its multi-layered coating resistant to UV radiation, reducing degradation over time compared to laminated glass, which relies on a plastic interlayer that can delaminate under prolonged exposure to moisture and temperature fluctuations. Maintenance for electrochromic glass is minimal since it self-regulates light transmission, thereby reducing the need for frequent cleaning and protective treatments, whereas laminated glass often requires more regular inspection for interlayer integrity and possible surface damage. The longevity and performance stability of electrochromic glass make it a superior choice for skylights in environments with varying weather conditions.
Aesthetic Flexibility and Design
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic control over light transmission and tint, allowing seamless adjustment of brightness and privacy in skylight designs while maintaining a sleek, modern aesthetic. Laminated glass provides enhanced strength and safety with options for embedded interlayers or decorative films, enabling diverse textures and colors but lacking the active light modulation properties of electrochromic glass. Designers favor electrochromic glass for its innovative adaptability and clean appearance, whereas laminated glass is chosen for static design features combined with structural resilience.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Lifecycle
Electrochromic glass for skylights generally involves higher upfront installation costs due to its advanced smart technology and integration with automated controls, while laminated glass offers a more affordable initial investment with simpler installation requirements. Over the lifecycle, electrochromic glass can reduce energy expenses by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and glare, potentially offsetting its higher initial cost through energy savings and enhanced occupant comfort. Laminated glass, although less costly at installation, may incur additional costs over time due to limited energy efficiency and the potential need for replacements or upgrades to meet evolving building standards.
Best Use Cases and Recommendations
Electrochromic glass excels in skylights where dynamic light control and energy efficiency are priorities, allowing users to adjust transparency to reduce glare and solar heat gain throughout the day. Laminated glass is best suited for skylights requiring enhanced safety, impact resistance, and sound insulation, often preferred in areas prone to extreme weather or potential hazards. For smart buildings prioritizing occupant comfort and energy savings, electrochromic glass is recommended, while laminated glass is ideal for environments demanding robust protection and security.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Laminated glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com