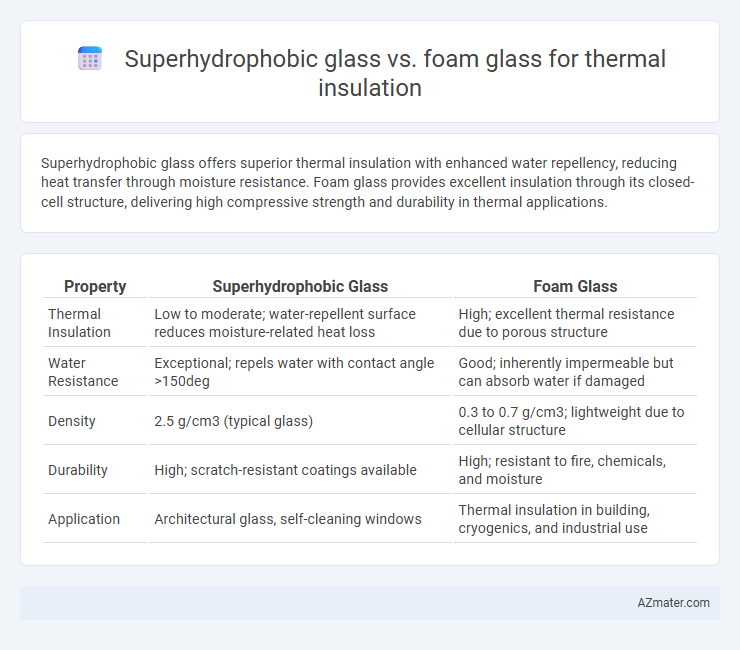
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior thermal insulation with enhanced water repellency, reducing heat transfer through moisture resistance. Foam glass provides excellent insulation through its closed-cell structure, delivering high compressive strength and durability in thermal applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Superhydrophobic Glass | Foam Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Low to moderate; water-repellent surface reduces moisture-related heat loss | High; excellent thermal resistance due to porous structure |
| Water Resistance | Exceptional; repels water with contact angle >150deg | Good; inherently impermeable but can absorb water if damaged |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 (typical glass) | 0.3 to 0.7 g/cm3; lightweight due to cellular structure |
| Durability | High; scratch-resistant coatings available | High; resistant to fire, chemicals, and moisture |
| Application | Architectural glass, self-cleaning windows | Thermal insulation in building, cryogenics, and industrial use |
Introduction to Advanced Thermal Insulation Materials
Superhydrophobic glass and foam glass are advanced thermal insulation materials utilized for energy efficiency and durability in construction. Superhydrophobic glass features a nanoscale coating that repels water and enhances thermal resistance, reducing heat transfer through windows and facades. Foam glass, composed of recycled glass with a cellular structure filled with air pockets, provides excellent thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and fire retardancy, making it suitable for industrial and residential applications.
Defining Superhydrophobic Glass
Superhydrophobic glass features a surface coating that repels water, preventing moisture absorption and enhancing thermal insulation efficiency by maintaining dry conditions. Foam glass, made from recycled glass powder, provides inherent thermal insulation through its cellular structure but is more prone to moisture retention compared to superhydrophobic glass. The advanced water-repellent properties of superhydrophobic glass reduce thermal conductivity degradation, making it a superior choice for sustainable insulation solutions in humid environments.
Understanding Foam Glass Properties
Foom glass, a lightweight and rigid material made from recycled glass, exhibits excellent thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, which minimizes heat transfer. It offers high compressive strength, moisture resistance, and long-term durability, making it suitable for extreme temperature environments. Compared to superhydrophobic glass, foam glass provides superior thermal barrier performance and enhanced fire resistance, ideal for construction and industrial applications.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Superhydrophobic glass typically exhibits thermal conductivity values around 0.8 to 1.0 W/m*K, making it less efficient for thermal insulation compared to foam glass, which has much lower thermal conductivity ranging from 0.03 to 0.06 W/m*K. Foam glass's cellular structure, filled with gas pockets, drastically reduces heat transfer, while superhydrophobic glass mainly offers water-repellent properties without significant insulation enhancement. For applications requiring superior thermal insulation, foam glass is preferred due to its substantially lower thermal conductivity.
Moisture Resistance: Superhydrophobic vs Foam Glass
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior moisture resistance due to its nanoscale surface texture that repels water, preventing moisture absorption and reducing the risk of condensation-related damage. Foam glass, while effective as a thermal insulator with its closed-cell structure, can allow some moisture ingress over time if the outer protective layer is compromised. The durability of superhydrophobic coatings ensures long-term moisture barrier performance, making it highly suitable for applications exposed to humid or wet environments.
Durability and Longevity in Building Environments
Superhydrophobic glass offers superior durability in building environments due to its water-repellent surface that resists dirt accumulation and reduces maintenance needs, extending its service life significantly compared to foam glass. Foam glass, while providing excellent thermal insulation with its closed-cell structure, may experience structural degradation and moisture ingress over time, potentially compromising its longevity in harsh conditions. The hydrophobic properties of superhydrophobic glass enhance resistance to environmental wear, making it a more durable and long-lasting choice for thermal insulation in demanding architectural applications.
Energy Efficiency Impact
Superhydrophobic glass enhances energy efficiency by significantly reducing heat transfer through its water-repellent, low-emissivity coating, which minimizes thermal bridging and moisture accumulation. Foam glass offers excellent thermal insulation with its closed-cell structure that traps air, providing low thermal conductivity and preventing heat loss in building envelopes. Comparing both, superhydrophobic glass excels in reducing condensation-related energy losses, while foam glass delivers superior overall insulation performance for sustainable energy conservation.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Superhydrophobic glass offers straightforward installation with lightweight panels that easily fit standard glazing systems, reducing labor time and minimizing structural modifications. Its self-cleaning properties significantly lower maintenance frequency and costs by repelling water and preventing dirt accumulation on surfaces. Foam glass insulation requires careful handling due to its rigidity and brittleness during installation, while maintenance involves periodic inspections for moisture penetration and potential cracking to maintain thermal performance.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Superhydrophobic glass offers outstanding durability and water repellency, reducing maintenance and extending lifespan, which supports sustainability by minimizing waste and resource use. Foam glass provides excellent thermal insulation with high resistance to fire and moisture, and is often made from recycled glass, making it a highly sustainable option with low environmental impact. Both materials contribute to energy efficiency, but foam glass's recycled content and non-toxic production process give it a distinct eco-friendly advantage for thermal insulation applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Optimal Thermal Insulation
Superhydrophobic glass offers exceptional water resistance and durability while maintaining transparency, making it ideal for applications requiring both thermal insulation and clarity. Foam glass provides superior thermal insulation performance due to its low thermal conductivity and lightweight, porous structure, suitable for high-efficiency insulating needs in construction and industrial settings. Selecting between superhydrophobic glass and foam glass depends on prioritizing factors such as moisture resistance, insulation R-value, mechanical strength, and specific environmental conditions to optimize thermal insulation effectiveness.
Infographic: Superhydrophobic glass vs Foam glass for Thermal insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com