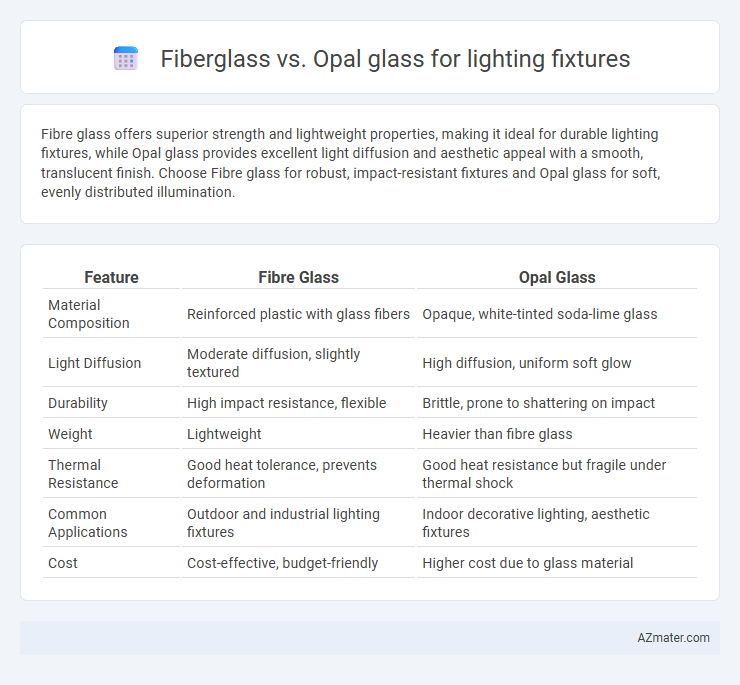
Fibre glass offers superior strength and lightweight properties, making it ideal for durable lighting fixtures, while Opal glass provides excellent light diffusion and aesthetic appeal with a smooth, translucent finish. Choose Fibre glass for robust, impact-resistant fixtures and Opal glass for soft, evenly distributed illumination.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fibre Glass | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Reinforced plastic with glass fibers | Opaque, white-tinted soda-lime glass |
| Light Diffusion | Moderate diffusion, slightly textured | High diffusion, uniform soft glow |
| Durability | High impact resistance, flexible | Brittle, prone to shattering on impact |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than fibre glass |
| Thermal Resistance | Good heat tolerance, prevents deformation | Good heat resistance but fragile under thermal shock |
| Common Applications | Outdoor and industrial lighting fixtures | Indoor decorative lighting, aesthetic fixtures |
| Cost | Cost-effective, budget-friendly | Higher cost due to glass material |
Introduction: The Importance of Glass Choice in Lighting Fixtures
Choosing between fiberglass and opal glass in lighting fixtures significantly impacts light diffusion, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Fiberglass offers lightweight strength and resistance to impact, making it ideal for high-traffic or outdoor environments. Opal glass provides superior light diffusion and a smooth, elegant finish, enhancing the quality and ambiance of indoor lighting.
What is Fibre Glass? Composition and Characteristics
Fiberglass is a composite material made from fine fibers of glass embedded in a resin matrix, commonly used in lighting fixtures for its durability and lightweight properties. Its composition includes silica-based glass fibers that provide high tensile strength, thermal stability, and resistance to moisture and corrosion. These characteristics make fiberglass an excellent choice for lighting fixtures requiring impact resistance and long-term performance in various environmental conditions.
What is Opal Glass? Composition and Characteristics
Opal glass is a type of glass used in lighting fixtures, characterized by its milky white, translucent appearance achieved by adding opacifiers such as tin oxide or bone ash during manufacturing. This composition diffuses light evenly, reducing glare and creating a soft, uniform illumination, making it ideal for decorative and functional lighting applications. Its durability, resistance to heat, and aesthetic appeal distinguish it from materials like fiberglass, which is more flexible but less visually refined.
Light Diffusion: Fibre Glass vs Opal Glass
Fibre glass offers excellent light diffusion with a textured surface that scatters light evenly, reducing glare and hotspots in lighting fixtures. Opal glass provides superior uniformity in light distribution due to its milky, translucent composition, creating a soft and consistent glow ideal for ambient lighting. Comparing the two, opal glass achieves smoother light diffusion with less translucency variation, while fibre glass excels in durability and lightweight applications with effective diffusion properties.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Fiberglass offers superior durability and strength for lighting fixtures due to its high tensile strength and resistance to impacts, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Opal glass, while aesthetically pleasing and providing excellent light diffusion, is more fragile and prone to cracking under stress or sudden impacts. Therefore, fiberglass outperforms opal glass in terms of longevity and robustness, especially in environments requiring high durability.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Fibre glass offers a textured, matte finish that enhances modern and industrial lighting designs with its robust and lightweight properties. Opal glass provides a smooth, translucent surface that diffuses light evenly, creating a soft, elegant glow ideal for classic and contemporary fixtures. Design flexibility with fibre glass allows for complex shapes and vibrant color options, while opal glass excels in achieving uniform light distribution and refined aesthetics.
Cost Effectiveness and Production Differences
Fiberglass lighting fixtures offer high cost-effectiveness due to lower raw material expenses and faster production time compared to opal glass, which requires more energy-intensive processes like melting and cooling. Production of fiberglass involves molding and curing techniques that enable mass customization and reduced labor costs, while opal glass demands precision in glass blowing or pressing, leading to higher skilled labor and machinery costs. The durability and lightweight nature of fiberglass also reduce transportation and installation expenses, enhancing overall economic advantages over opal glass in large-scale manufacturing.
Applications: Best Uses for Fibre Glass and Opal Glass
Fiberglass is ideal for outdoor lighting fixtures, industrial environments, and applications requiring high impact resistance and weather durability. Opal glass excels in indoor settings such as residential and commercial lighting where diffused, soft light distribution is essential for aesthetic ambiance and glare reduction. Fiberglass provides robust protection against moisture and chemicals, while opal glass enhances visual comfort through its translucent, uniform light diffusion.
Maintenance and Longevity
Fibre glass lighting fixtures offer superior durability and resistance to impact, reducing the need for frequent maintenance compared to Opal glass, which is more prone to cracks and breakage. Opal glass provides excellent light diffusion but requires careful handling and periodic cleaning to maintain its aesthetic clarity and performance over time. Fibre glass's resistance to corrosion and weathering ensures longer lifespan in harsh environments, making it a preferred choice for low-maintenance, long-lasting lighting solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Fibre glass lighting fixtures exhibit higher embodied energy due to energy-intensive production and non-biodegradable waste challenges, whereas opal glass offers greater recyclability and a lower carbon footprint through its natural silica composition. Opal glass's durability and inert chemical nature minimize environmental toxins, supporting sustainable lifecycle management compared to fibre glass, which often involves synthetic resins harmful to ecosystems. Selecting opal glass enhances sustainability goals by reducing landfill burden and promoting circular economy principles in lighting fixture manufacturing.
Infographic: Fibre glass vs Opal glass for Lighting fixture
 azmater.com
azmater.com