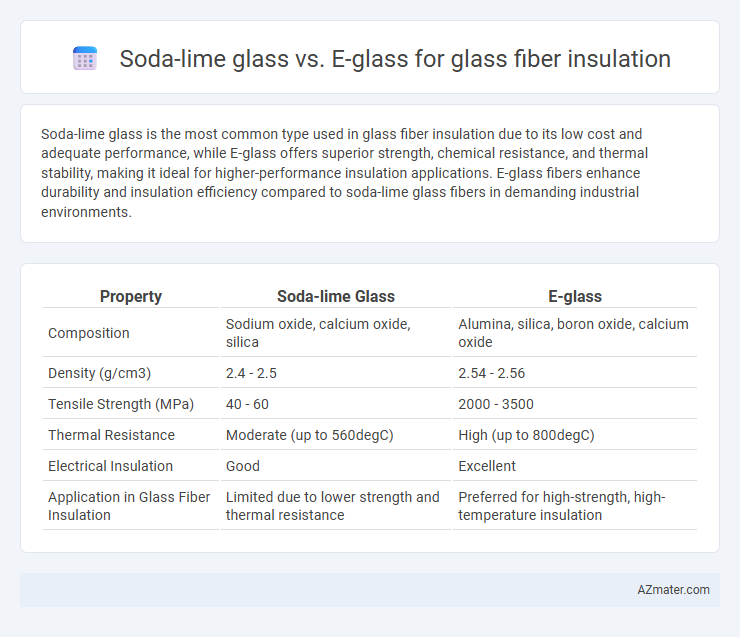
Soda-lime glass is the most common type used in glass fiber insulation due to its low cost and adequate performance, while E-glass offers superior strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for higher-performance insulation applications. E-glass fibers enhance durability and insulation efficiency compared to soda-lime glass fibers in demanding industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Soda-lime Glass | E-glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium oxide, calcium oxide, silica | Alumina, silica, boron oxide, calcium oxide |
| Density (g/cm3) | 2.4 - 2.5 | 2.54 - 2.56 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 40 - 60 | 2000 - 3500 |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate (up to 560degC) | High (up to 800degC) |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Excellent |
| Application in Glass Fiber Insulation | Limited due to lower strength and thermal resistance | Preferred for high-strength, high-temperature insulation |
Introduction to Glass Fiber Insulation
Glass fiber insulation primarily uses E-glass due to its superior electrical resistance, tensile strength, and thermal stability compared to soda-lime glass. Soda-lime glass, commonly used for windows and containers, lacks the specialized composition needed for efficient insulation performance. E-glass fibers offer enhanced durability and insulation efficiency, making them the preferred choice in construction and industrial applications.
Overview of Soda-Lime Glass
Soda-lime glass, the most common type of glass used in glass fiber insulation, primarily consists of silica (about 70-75%), sodium oxide (12-15%), and calcium oxide (10%). It offers good chemical durability, affordability, and ease of production compared to specialty glasses like E-glass. Despite lower mechanical strength and thermal resistance than E-glass, soda-lime glass remains widely used in insulation due to its cost-effectiveness and satisfactory performance in standard applications.
Overview of E-Glass
E-glass, or electrical grade glass, is the most commonly used fiber in glass fiber insulation due to its excellent strength, durability, and chemical resistance. It is composed primarily of silica (SiO2), alumina (Al2O3), and boron oxide (B2O3), which provide superior electrical insulating properties compared to soda-lime glass. The high tensile strength and thermal stability of E-glass fibers make them ideal for reinforcing composite materials and enhancing insulation performance in various industrial applications.
Chemical Composition Differences
Soda-lime glass primarily consists of silica (SiO2), sodium oxide (Na2O), and calcium oxide (CaO), making it less chemically resistant and suitable for general insulation applications. E-glass, or electrical glass, includes higher amounts of alumina (Al2O3) and boron oxide (B2O3) alongside silica, providing superior chemical durability and mechanical strength for glass fiber insulation. The enhanced chemical composition of E-glass results in improved resistance to moisture and alkaline environments compared to soda-lime glass.
Thermal Properties Comparison
Soda-lime glass fibers exhibit lower thermal resistance with a maximum operating temperature around 500degC, whereas E-glass fibers withstand higher temperatures up to approximately 700degC, making E-glass more suitable for high-temperature insulation applications. The thermal conductivity of E-glass typically ranges from 0.037 to 0.040 W/m*K, which is slightly lower than soda-lime glass, enhancing its insulation efficiency. E-glass also demonstrates superior dimensional stability and lower thermal expansion coefficient compared to soda-lime glass, contributing to better performance under thermal cycling conditions in insulation materials.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
E-glass exhibits higher mechanical strength and superior durability compared to soda-lime glass, making it more suitable for glass fiber insulation applications. The enhanced tensile strength and resistance to moisture and chemicals in E-glass result from its optimized alumina and silica composition. Soda-lime glass, while cost-effective, has lower fracture toughness and degrades faster under environmental stress, limiting its long-term performance in insulation materials.
Moisture and Corrosion Resistance
E-glass exhibits superior moisture and corrosion resistance compared to soda-lime glass, making it the preferred choice for glass fiber insulation in humid or chemically aggressive environments. The alkali-resistant composition of E-glass minimizes degradation and maintains mechanical integrity over time, enhancing durability. In contrast, soda-lime glass fibers are more susceptible to hydrolytic attack and corrosion, leading to reduced insulation performance and lifespan.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Soda-lime glass is the most economical raw material for glass fiber insulation due to its abundance and lower melting temperature, resulting in reduced energy consumption during manufacturing. E-glass offers superior mechanical properties and electrical resistance but comes at a higher production cost because of its specialized composition and more complex melting process. Choosing between soda-lime and E-glass fibers depends on balancing cost efficiency with performance requirements in insulation applications.
Typical Applications in Insulation
Soda-lime glass is commonly used in insulation applications such as fiberglass batts and blankets for residential and commercial buildings due to its cost-effectiveness and availability. E-glass fibers, known for their high tensile strength and electrical insulating properties, are preferred in industrial insulation, including high-temperature pipe wraps and electrical insulation components. The choice between soda-lime and E-glass depends on the specific thermal, mechanical, and electrical requirements of the insulation project.
Choosing the Right Glass Fiber for Insulation
Soda-lime glass and E-glass are primary types of glass fibers used in insulation, with E-glass preferred due to its superior strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. E-glass fibers offer better insulation performance and durability compared to soda-lime glass, which is more prone to corrosion and lower tensile strength. Selecting E-glass for glass fiber insulation ensures enhanced energy efficiency and longer-lasting material reliability in residential and industrial applications.
Infographic: Soda-lime glass vs E-glass for Glass fiber insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com