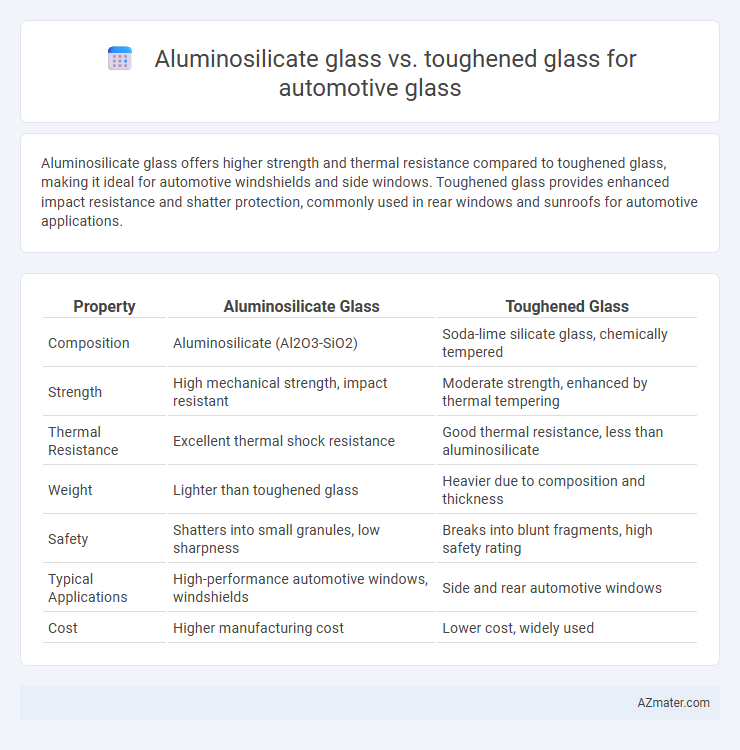
Aluminosilicate glass offers higher strength and thermal resistance compared to toughened glass, making it ideal for automotive windshields and side windows. Toughened glass provides enhanced impact resistance and shatter protection, commonly used in rear windows and sunroofs for automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminosilicate Glass | Toughened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate (Al2O3-SiO2) | Soda-lime silicate glass, chemically tempered |
| Strength | High mechanical strength, impact resistant | Moderate strength, enhanced by thermal tempering |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent thermal shock resistance | Good thermal resistance, less than aluminosilicate |
| Weight | Lighter than toughened glass | Heavier due to composition and thickness |
| Safety | Shatters into small granules, low sharpness | Breaks into blunt fragments, high safety rating |
| Typical Applications | High-performance automotive windows, windshields | Side and rear automotive windows |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely used |
Introduction to Automotive Glass Technologies
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior chemical durability and thermal resistance, making it ideal for automotive applications requiring high strength and scratch resistance. Toughened glass undergoes controlled thermal or chemical treatment to enhance impact resistance and shatter into small, blunt pieces for passenger safety in vehicle windows. Both glass types contribute to advanced automotive glass technologies by balancing strength, safety, and durability under varying environmental conditions.
Overview of Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass, composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, offers superior thermal stability and enhanced mechanical strength compared to traditional toughened glass used in automotive applications. This type of glass provides higher resistance to scratches, impacts, and thermal shocks, making it ideal for advanced automotive windshields and side windows that require durability and safety. Its lightweight nature also contributes to improved fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
Characteristics of Toughened (Tempered) Glass
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, offers high strength and safety for automotive applications due to its heat-treatment process that increases impact resistance up to four times compared to regular glass. It shatters into small, blunt granules rather than sharp shards, significantly reducing injury risk in accidents. Unlike aluminosilicate glass, which is chemically strengthened for scratch resistance and optical clarity, toughened glass prioritizes durability and safety under mechanical stress and thermal variations.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass, featuring a reinforced alumina and silica composition, offers superior scratch resistance and thermal stability compared to toughened glass commonly used in automotive applications. Toughened glass, produced through rapid cooling to induce compressive surface stress, excels in impact resistance and shatters into small, blunt fragments, enhancing passenger safety. In terms of long-term durability, aluminosilicate glass maintains structural integrity under extreme temperature fluctuations better than toughened glass, making it preferable for high-performance automotive windshields and windows.
Impact Resistance and Safety Features
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior impact resistance due to its chemical composition, making it highly resistant to cracks and shattering under stress, which enhances automotive safety by reducing the risk of sharp shards during collisions. Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, undergoes thermal treatment that increases strength and causes it to break into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, minimizing injury risks. Both materials improve safety features, but aluminosilicate glass delivers higher durability against impacts, while toughened glass excels in controlled breakage patterns crucial for occupant protection.
Weight and Fuel Efficiency Implications
Aluminosilicate glass offers a lighter alternative to traditional toughened glass in automotive applications, significantly reducing vehicle weight and enhancing fuel efficiency. The decreased mass of aluminosilicate glass contributes to lower rolling resistance and improved acceleration, resulting in measurable fuel savings over the vehicle's lifespan. Toughened glass, while providing high impact resistance, generally weighs more, thereby slightly diminishing potential fuel economy gains compared to aluminosilicate glass.
Thermal Stability and Weather Performance
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal stability due to its high resistance to thermal shock and ability to withstand sudden temperature changes without cracking, making it ideal for automotive applications exposed to extreme weather conditions. Toughened glass, while offering enhanced mechanical strength through a controlled tempering process, has lower thermal expansion tolerance compared to aluminosilicate, which can lead to stress fractures under rapid temperature fluctuations. In terms of weather performance, aluminosilicate glass maintains clarity and structural integrity during prolonged exposure to UV radiation and harsh environmental elements, whereas toughened glass may degrade faster under intense weathering conditions.
Repairability and Replacement Considerations
Aluminosilicate glass offers higher resistance to impact and thermal stress, reducing the frequency of repairs compared to toughened glass, which is more prone to shattering upon impact and often requires full replacement. Repairability is more feasible with aluminosilicate glass due to its enhanced durability and ability to withstand minor chips, whereas toughened glass typically cannot be repaired once damaged. Replacement considerations favor aluminosilicate glass for long-term cost efficiency and safety, while toughened glass may result in higher replacement costs and more frequent service intervals in automotive applications.
Cost Analysis and Manufacturing Differences
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal and chemical resistance compared to toughened glass, leading to higher manufacturing costs due to advanced processing techniques like ion exchange strengthening. Toughened glass, produced through controlled thermal tempering, provides a cost-effective solution with enhanced mechanical strength but lower resistance to environmental factors. Cost analysis reveals aluminosilicate glass commands a premium price, justified by its longer lifespan and reduced replacement frequency in automotive applications.
Future Trends in Automotive Glass Selection
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal and chemical resistance, making it ideal for advanced automotive applications like electric vehicles with high battery safety requirements. Toughened glass provides enhanced impact resistance and shatterproof protection, remaining a cost-effective choice for standard vehicle windows. Future trends emphasize hybrid solutions combining aluminosilicate's durability with toughened glass's strength to meet evolving safety and energy efficiency standards in automotive glass selection.
Infographic: Aluminosilicate glass vs Toughened glass for Automotive glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com