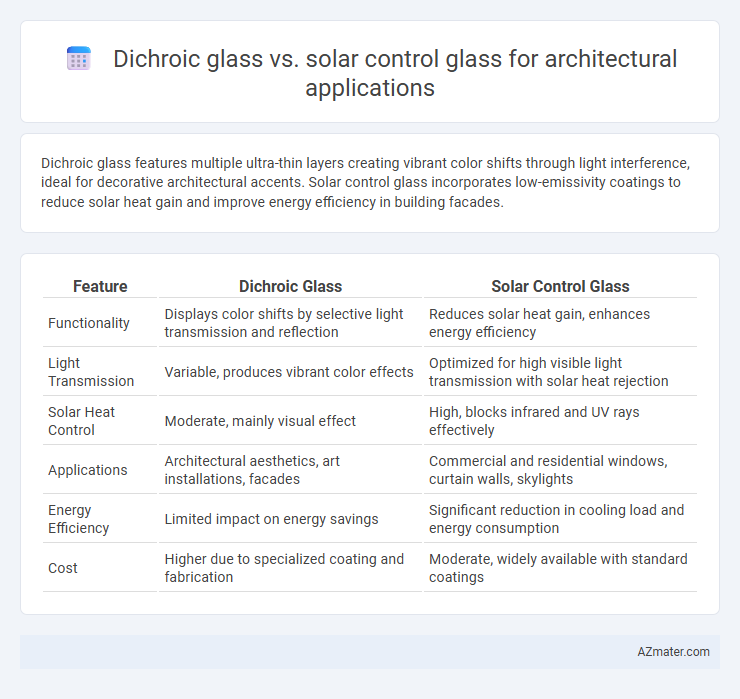
Dichroic glass features multiple ultra-thin layers creating vibrant color shifts through light interference, ideal for decorative architectural accents. Solar control glass incorporates low-emissivity coatings to reduce solar heat gain and improve energy efficiency in building facades.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dichroic Glass | Solar Control Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Displays color shifts by selective light transmission and reflection | Reduces solar heat gain, enhances energy efficiency |
| Light Transmission | Variable, produces vibrant color effects | Optimized for high visible light transmission with solar heat rejection |
| Solar Heat Control | Moderate, mainly visual effect | High, blocks infrared and UV rays effectively |
| Applications | Architectural aesthetics, art installations, facades | Commercial and residential windows, curtain walls, skylights |
| Energy Efficiency | Limited impact on energy savings | Significant reduction in cooling load and energy consumption |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized coating and fabrication | Moderate, widely available with standard coatings |
Understanding Dichroic Glass: Composition and Aesthetics
Dichroic glass consists of multiple ultra-thin layers of metal oxides deposited on the glass surface, creating a unique optical effect with color shifts depending on the viewing angle and light conditions. This glass type enhances architectural aesthetics by producing vibrant, iridescent hues, making it ideal for decorative facades and interior design elements. In contrast, solar control glass primarily focuses on energy efficiency, employing coatings that reduce solar heat gain and improve building thermal performance without significantly altering visual appearance.
Solar Control Glass: Technology and Performance
Solar control glass employs advanced coatings that selectively reflect and absorb solar radiation, significantly reducing heat gain while maintaining natural daylight transmission. Its performance metrics include high solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) reduction and visible light transmittance (VLT) optimization, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Compared to dichroic glass, solar control glass prioritizes thermal regulation and UV protection, making it ideal for architectural applications focused on sustainability and occupant comfort.
Visual Impact: Color and Light Transmission Differences
Dichroic glass creates dynamic color effects by reflecting and transmitting different hues depending on the viewing angle and lighting conditions, enhancing architectural aesthetics with vibrant, shifting visuals. Solar control glass primarily focuses on reducing solar heat gain and glare while maintaining neutral or subtle tinting, offering consistent light transmission without significant color change. The visual impact of dichroic glass is more pronounced and artistic, whereas solar control glass aims for functional clarity and comfort by optimizing light and heat management.
Energy Efficiency: Comparing Heat and UV Control
Dichroic glass offers dynamic light filtering by reflecting and transmitting specific wavelengths, reducing solar heat gain while enhancing natural daylight with minimal color distortion, which can contribute to moderate energy savings in buildings. Solar control glass is engineered with coatings that significantly reduce infrared heat transmission and block up to 99% of UV rays, providing superior thermal insulation and protecting interior furnishings from UV degradation, resulting in higher overall energy efficiency. In terms of energy performance, solar control glass typically outperforms dichroic glass by maintaining lower indoor temperatures and reducing cooling loads more effectively in various climatic conditions.
Architectural Applications: Where Each Glass Excels
Dichroic glass excels in architectural applications that require dynamic aesthetic effects, such as facades and interior partitions, due to its unique ability to refract and reflect light in multiple colors, creating vibrant visual interest. Solar control glass is ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes, effectively reducing solar heat gain and glare while maintaining natural daylight, making it perfect for windows, skylights, and curtain walls in commercial and residential buildings. Each glass type enhances architectural design through either artistic expression with dichroic glass or functional energy performance with solar control glass.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Dichroic glass offers high durability with its multi-layered thin film coating that resists fading and degradation, requiring minimal maintenance to preserve its vibrant color shifts. Solar control glass features advanced coatings that enhance resistance to weathering and UV radiation, reducing wear while needing regular cleaning to maintain optimal solar performance. Both types ensure long-lasting architectural applications, but solar control glass may demand more frequent upkeep to sustain its energy efficiency capabilities.
Cost Comparison: Investment and Long-Term Savings
Dichroic glass typically involves higher upfront costs due to its complex manufacturing process and specialized coatings that create vivid color effects. Solar control glass, while often less expensive initially, provides significant long-term savings by reducing energy consumption through superior heat rejection and UV protection. Evaluating total investment requires balancing the aesthetic value of dichroic glass against the predictable energy cost reductions offered by solar control glass in architectural applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Dichroic glass enhances energy efficiency by selectively filtering light and reducing heat gain, leading to lower cooling demands and reduced carbon emissions in buildings. Solar control glass minimizes ultraviolet and infrared radiation transmission, decreasing reliance on artificial cooling systems and promoting sustainable energy consumption. Both types contribute to green building certifications by improving thermal performance and supporting environmental sustainability in architectural designs.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Dichroic glass offers exceptional customization through its unique color-shifting properties, enabling architects to create dynamic visual effects that change with lighting and viewing angles. Solar control glass prioritizes performance, providing customizable coatings that optimize energy efficiency by selectively filtering solar radiation while maintaining transparency. Combining design flexibility with functional benefits, both materials cater to tailored architectural applications but differ fundamentally in aesthetic impact versus thermal regulation.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Architectural Project
Dichroic glass offers vibrant color-shifting effects and dynamic aesthetics, making it ideal for artistic facades and interior features where visual impact is paramount. Solar control glass excels in reducing solar heat gain and glare while maintaining high visible light transmittance, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in commercial buildings. Selecting the right glass depends on the project's primary goals--opting for dichroic glass to create striking visual statements or choosing solar control glass to optimize thermal performance and sustainability.
Infographic: Dichroic glass vs Solar control glass for Architectural glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com