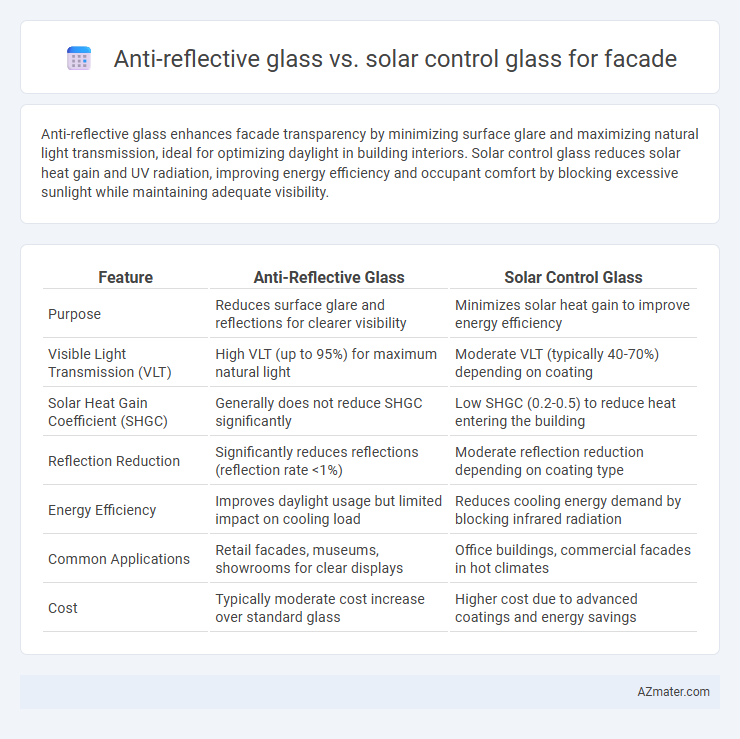
Anti-reflective glass enhances facade transparency by minimizing surface glare and maximizing natural light transmission, ideal for optimizing daylight in building interiors. Solar control glass reduces solar heat gain and UV radiation, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort by blocking excessive sunlight while maintaining adequate visibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Reflective Glass | Solar Control Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces surface glare and reflections for clearer visibility | Minimizes solar heat gain to improve energy efficiency |
| Visible Light Transmission (VLT) | High VLT (up to 95%) for maximum natural light | Moderate VLT (typically 40-70%) depending on coating |
| Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) | Generally does not reduce SHGC significantly | Low SHGC (0.2-0.5) to reduce heat entering the building |
| Reflection Reduction | Significantly reduces reflections (reflection rate <1%) | Moderate reflection reduction depending on coating type |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves daylight usage but limited impact on cooling load | Reduces cooling energy demand by blocking infrared radiation |
| Common Applications | Retail facades, museums, showrooms for clear displays | Office buildings, commercial facades in hot climates |
| Cost | Typically moderate cost increase over standard glass | Higher cost due to advanced coatings and energy savings |
Introduction to Modern Facade Glazing Solutions
Anti-reflective glass enhances facade transparency by minimizing glare and improving visual clarity, making it ideal for modern architectural designs seeking natural light optimization. Solar control glass effectively reduces solar heat gain and UV radiation, providing superior energy efficiency and occupant comfort in building facades exposed to intense sunlight. Both glazing solutions contribute to sustainable facade systems, with anti-reflective glass maximizing daylight use and solar control glass balancing thermal regulation in contemporary building envelopes.
What is Anti-Reflective Glass?
Anti-reflective glass is engineered with special coatings that minimize surface reflections, enhancing light transmission and visibility through building facades. This type of glass improves visual clarity by reducing glare and unwanted reflections from the sun or artificial lighting. In facade applications, anti-reflective glass is ideal for maximizing natural daylight while maintaining aesthetic transparency and reducing visual distractions.
What is Solar Control Glass?
Solar control glass is designed to reduce heat gain by reflecting and absorbing solar radiation while allowing natural light to pass through, improving energy efficiency in building facades. Unlike anti-reflective glass that minimizes surface reflections to enhance transparency and visibility, solar control glass incorporates special coatings or tints to control solar heat and glare. This technology helps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures and reduces reliance on air conditioning in commercial and residential buildings.
Key Differences Between Anti-Reflective and Solar Control Glass
Anti-reflective glass reduces surface glare and enhances natural light transmission by minimizing reflections, making it ideal for improving visibility and aesthetic appeal in building facades. Solar control glass, on the other hand, is designed to limit solar heat gain through selective coating, thus improving energy efficiency by reducing cooling loads in buildings. The key difference lies in their primary function: anti-reflective glass optimizes light clarity, while solar control glass prioritizes thermal regulation and energy savings.
Light Transmission and Visual Clarity
Anti-reflective glass enhances facade performance by maximizing light transmission, reducing surface reflections to improve visual clarity and daylight penetration. Solar control glass minimizes solar heat gain through selective coatings, filtering infrared radiation while maintaining moderate light transmission levels to reduce glare. Choosing between them depends on the balance needed between natural light optimization and thermal regulation for building facades.
Solar Heat Gain and Energy Efficiency
Anti-reflective glass minimizes surface glare by enhancing visible light transmission but does not significantly reduce solar heat gain, often leading to higher cooling demands in facade applications. Solar control glass incorporates special coatings or tints that effectively block infrared radiation, reducing solar heat gain and improving energy efficiency by lowering air conditioning loads. For facades, solar control glass offers superior performance in managing thermal comfort and energy consumption compared to anti-reflective glass.
Aesthetic Impact on Building Exteriors
Anti-reflective glass enhances facade aesthetics by minimizing glare and reflections, resulting in clearer views and a sleek, modern appearance. Solar control glass offers tinted or coated surfaces that reduce heat gain while providing a distinctive, colored facade that can complement architectural styles. Choosing between these glasses depends on whether the priority is maximizing transparency for an open look or achieving energy efficiency with a visually impactful, shaded exterior.
Cost Comparison and Long-Term Value
Anti-reflective glass typically costs more upfront due to its specialized coatings that reduce glare and enhance visibility, while solar control glass offers moderate initial pricing with integrated UV and infrared light rejection properties. Over the long term, solar control glass provides greater energy savings by minimizing heat gain and reducing cooling costs, enhancing overall facade performance and occupant comfort. Despite higher initial expenses, anti-reflective glass can deliver superior aesthetic value and daylight optimization, potentially increasing building value and occupant productivity.
Suitable Applications for Each Glass Type
Anti-reflective glass is ideal for commercial building facades and retail storefronts where maximizing natural light and enhancing visibility are critical, reducing glare while maintaining clarity. Solar control glass suits office buildings and residential facades in hot climates by minimizing solar heat gain and improving energy efficiency through its reflective and absorptive coatings. Choosing between these glass types depends on balancing transparency requirements with thermal performance needs in specific architectural applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Facade Project
Anti-reflective glass enhances natural light transmission and reduces glare, making it ideal for facades where clarity and visibility are paramount. Solar control glass minimizes solar heat gain by reflecting infrared rays while maintaining transparency, crucial for energy efficiency and thermal comfort in sunny climates. Selecting the right facade glass involves balancing visual aesthetics, energy performance, and environmental conditions to optimize building functionality and occupant comfort.
Infographic: Anti-reflective glass vs Solar control glass for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com