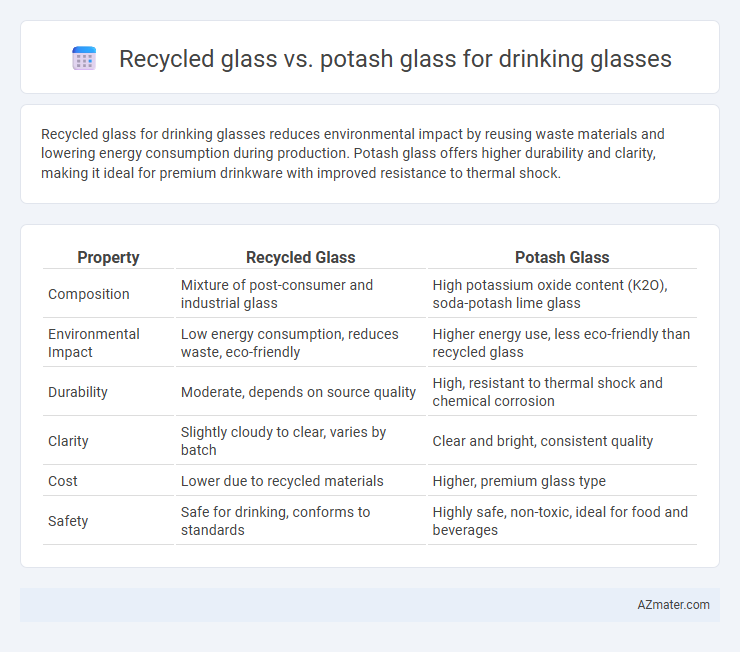
Recycled glass for drinking glasses reduces environmental impact by reusing waste materials and lowering energy consumption during production. Potash glass offers higher durability and clarity, making it ideal for premium drinkware with improved resistance to thermal shock.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Glass | Potash Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Mixture of post-consumer and industrial glass | High potassium oxide content (K2O), soda-potash lime glass |
| Environmental Impact | Low energy consumption, reduces waste, eco-friendly | Higher energy use, less eco-friendly than recycled glass |
| Durability | Moderate, depends on source quality | High, resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion |
| Clarity | Slightly cloudy to clear, varies by batch | Clear and bright, consistent quality |
| Cost | Lower due to recycled materials | Higher, premium glass type |
| Safety | Safe for drinking, conforms to standards | Highly safe, non-toxic, ideal for food and beverages |
Overview: Recycled Glass vs Potash Glass
Recycled glass drinking glasses leverage post-consumer or industrial glass waste, reducing environmental impact through sustainable material reuse and energy-efficient manufacturing. Potash glass, containing potassium oxide, offers enhanced clarity and chemical durability, making it resistant to watermarks and etching compared to soda-lime or recycled glass variants. While recycled glass prioritizes eco-friendly properties, potash glass emphasizes superior optical quality and resilience, balancing sustainability with performance in glassware production.
Material Sources and Sustainability
Recycled glass for drinking glasses is sourced from post-consumer and industrial glass waste, significantly reducing raw material extraction and energy consumption compared to potash glass, which primarily relies on mined potash and sand. The use of recycled glass minimizes landfill waste and lowers carbon emissions, enhancing sustainability in production processes. Potash glass, while durable, involves resource-intensive mining that impacts ecosystems and contributes to higher environmental footprints relative to recycled glass.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Recycled glass drinking glasses utilize crushed post-consumer glass, melted at lower temperatures to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint, promoting sustainability in manufacturing. Potash glass, containing potassium oxide, requires higher melting points and longer processing times, offering superior clarity and chemical resistance but increasing production costs and energy use. The manufacturing process of recycled glass emphasizes eco-friendly practices, while potash glass prioritizes enhanced physical properties through more intensive processing.
Environmental Impact
Recycled glass drinking glasses reduce landfill waste and lower energy consumption by requiring less raw material and melting temperature compared to potash glass. Potash glass production involves mining potash salts, which can lead to habitat disruption and higher carbon emissions during processing. Choosing recycled glass supports circular economy principles by minimizing resource extraction and greenhouse gas emissions.
Chemical Properties and Composition
Recycled glass and potash glass differ significantly in chemical composition, impacting their suitability for drinking glasses. Recycled glass typically consists of soda-lime silica with varying levels of impurities and metal oxides, which can affect durability and clarity. Potash glass, enriched with potassium oxide, offers higher chemical resistance, greater hardness, and improved thermal stability, making it a preferred material for premium drinking glasses.
Durability and Longevity
Recycled glass drinking glasses often exhibit slightly reduced durability due to the presence of impurities and variations in melting temperatures during production, which can lead to increased brittleness or microfractures. Potash glass, known for its high potassium oxide content, provides greater resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, enhancing overall longevity and maintaining clarity over time. Consumers seeking long-lasting drinking glasses typically prefer potash glass for its superior strength and consistent durability compared to recycled glass alternatives.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Options
Recycled glass drinking glasses offer unique, eco-friendly aesthetics characterized by subtle color variations and occasional air bubbles, giving each piece a handcrafted, rustic appeal that enhances artisanal design options. Potash glass provides a clear, brilliant finish with excellent clarity and smooth texture, allowing for sleek, modern designs and intricate etching or embossing that maintain long-term brilliance. Both materials support diverse design possibilities, but recycled glass emphasizes sustainability with organic patterns, while potash glass prioritizes elegance and refined transparency.
Safety and Health Considerations
Recycled glass for drinking glasses is often free from harmful chemicals, reducing exposure to toxins like lead and cadmium commonly found in some potash glass formulations. Potash glass, known for its durability and clarity, sometimes contains higher levels of alkali content, which may leach under acidic conditions, potentially posing health risks. Choosing recycled glass ensures better compliance with safety standards and minimizes chemical migration, promoting healthier consumption habits.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Recycled glass drinking glasses offer significant cost efficiency due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during manufacturing, making them more affordable for mass production compared to potash glass. Potash glass, while known for its clarity and durability, tends to be pricier due to the use of potassium carbonate and less widespread manufacturing processes. Market availability of recycled glass products is rapidly growing as sustainability drives consumer demand, whereas potash glass remains a niche option primarily found in premium or specialty drinkware collections.
Best Uses and Consumer Recommendations
Recycled glass is ideal for eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable drinking options with a unique, rustic appearance and moderate durability suitable for everyday use. Potash glass offers superior clarity, brilliance, and chemical resistance, making it preferred for high-end drinkware and prolonged contact with acidic beverages like citrus-based drinks. Consumers aiming for a balance of environmental impact and durability may choose recycled glass, whereas those prioritizing luxury and longevity often opt for potash glass in premium settings.
Infographic: Recycled glass vs Potash glass for Drinking glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com