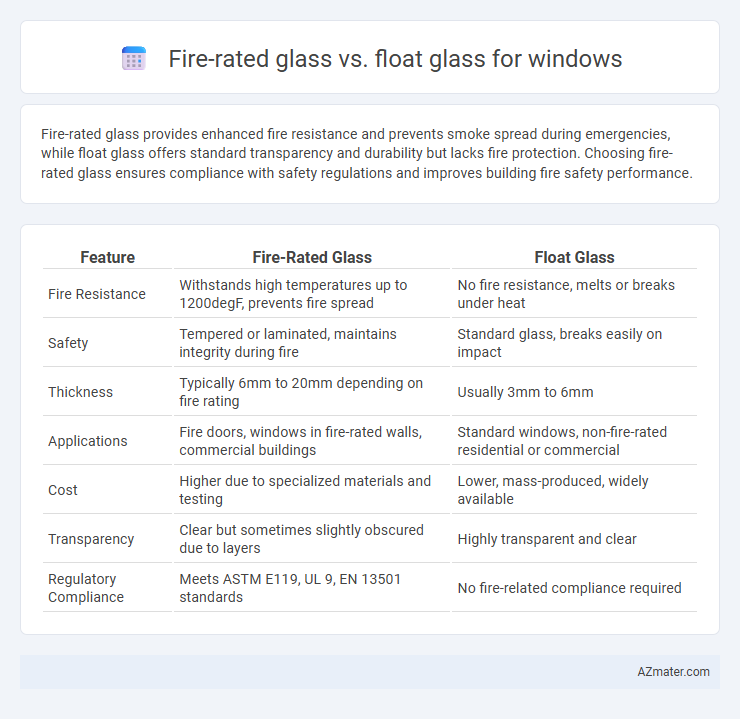
Fire-rated glass provides enhanced fire resistance and prevents smoke spread during emergencies, while float glass offers standard transparency and durability but lacks fire protection. Choosing fire-rated glass ensures compliance with safety regulations and improves building fire safety performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Rated Glass | Float Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Withstands high temperatures up to 1200degF, prevents fire spread | No fire resistance, melts or breaks under heat |
| Safety | Tempered or laminated, maintains integrity during fire | Standard glass, breaks easily on impact |
| Thickness | Typically 6mm to 20mm depending on fire rating | Usually 3mm to 6mm |
| Applications | Fire doors, windows in fire-rated walls, commercial buildings | Standard windows, non-fire-rated residential or commercial |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials and testing | Lower, mass-produced, widely available |
| Transparency | Clear but sometimes slightly obscured due to layers | Highly transparent and clear |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets ASTM E119, UL 9, EN 13501 standards | No fire-related compliance required |
Introduction to Fire-Rated Glass and Float Glass
Fire-rated glass is specially engineered to resist high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke, making it essential for safety in commercial and residential buildings. Float glass, produced by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, offers clarity and durability but lacks fire-resistant properties. Choosing between fire-rated and float glass depends on regulatory requirements and the need for fire protection in window applications.
Understanding Fire-Rated Glass: Key Features
Fire-rated glass offers superior heat resistance and prevents the spread of flames and smoke, making it essential for building safety and compliance with fire codes. Its multi-layered structure and special coatings enable it to maintain integrity under high temperatures, unlike standard float glass which lacks such protective features. Fire-rated glass enhances occupant protection in emergency situations by providing a critical barrier against fire hazards.
Overview of Float Glass: Characteristics and Uses
Float glass is a type of flat glass known for its smooth, uniform surface and excellent optical clarity, produced by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, typically tin. It is widely used in windows, doors, and facades due to its affordability, versatility, and ease of fabrication, but it lacks inherent fire-resistant properties. Float glass is commonly found in residential and commercial applications where standard glazing is sufficient, unlike fire-rated glass that is engineered to withstand extreme heat and prevent flame spread.
Safety and Fire Protection Capabilities
Fire-rated glass provides superior safety and fire protection capabilities compared to float glass, as it is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke for a specified duration, often 30 to 120 minutes. It incorporates intumescent layers or special coatings that maintain integrity under extreme heat, ensuring safe egress routes and protection for occupants in case of fire emergencies. In contrast, float glass lacks these fire-resistant properties and can shatter or fail quickly under exposure to flames, making it unsuitable for applications requiring fire safety compliance.
Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency
Fire-rated glass significantly outperforms float glass in thermal performance by withstanding high temperatures up to 1,200degF while maintaining structural integrity, essential for fire safety in buildings. Its ability to insulate against heat transfer reduces energy consumption during temperature fluctuations, enhancing overall energy efficiency. Float glass, lacking such fire-resistant properties, offers lower thermal insulation, making it less effective for energy-saving applications in windows.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Fire-rated glass offers enhanced safety while supporting versatile design flexibility, allowing architects to incorporate sleek, modern aesthetics without compromising on protection. Unlike traditional float glass, fire-rated glass can be customized with various thicknesses, tints, and finishes to meet both stringent fire codes and aesthetic requirements. This combination of functionality and style makes fire-rated glass ideal for contemporary window designs requiring both safety and visual appeal.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Fire-rated glass offers superior durability and strength compared to float glass, as it is specifically engineered to withstand extreme heat and prevent fire spread. Its multi-layered construction with intumescent interlayers enhances impact resistance and maintains structural integrity under high temperatures. In contrast, float glass, made through a continuous molten glass floating process, lacks fire-resistant properties and is more prone to breakage under thermal stress or impact.
Regulatory Compliance and Building Codes
Fire-rated glass meets strict regulatory compliance requirements outlined in international building codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) and NFPA 80, ensuring it can withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread for specified durations. Float glass, while commonly used for standard windows due to its clarity and cost-effectiveness, does not comply with fire protection standards and fails to provide the necessary fire resistance in emergency situations. Compliance with building codes mandates the use of fire-rated glass in fire-rated assemblies to enhance occupant safety and enable safe egress during fires.
Cost Considerations: Fire-Rated vs Float Glass
Fire-rated glass typically costs significantly more than float glass due to its specialized manufacturing process and fire-resistant properties, which are critical for enhancing building safety and meeting regulatory standards. Float glass, being a standard, non-fire-resistant option, offers a more budget-friendly choice for general window installations without fire protection requirements. When considering long-term investment, fire-rated glass may lead to cost savings by reducing potential fire damage and complying with insurance and building code mandates.
Choosing the Best Glass for Your Windows
Fire-rated glass offers crucial protection by withstanding high temperatures and preventing fire spread, making it ideal for safety-focused window installations in commercial and residential buildings. Float glass, while less resistant to heat, provides affordable clarity and is suitable for standard window applications where fire resistance is not a priority. Selecting the best glass involves assessing the specific fire safety requirements, building codes, and thermal performance needed for your windows.
Infographic: Fire-rated glass vs Float glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com