Glass ceramic offers superior thermal stability and lower thermal expansion compared to fused silica glass, making it ideal for high-precision optical lenses. Fused silica glass provides exceptional UV transparency and excellent optical homogeneity, benefiting applications requiring high purity and minimal light distortion.
Table of Comparison
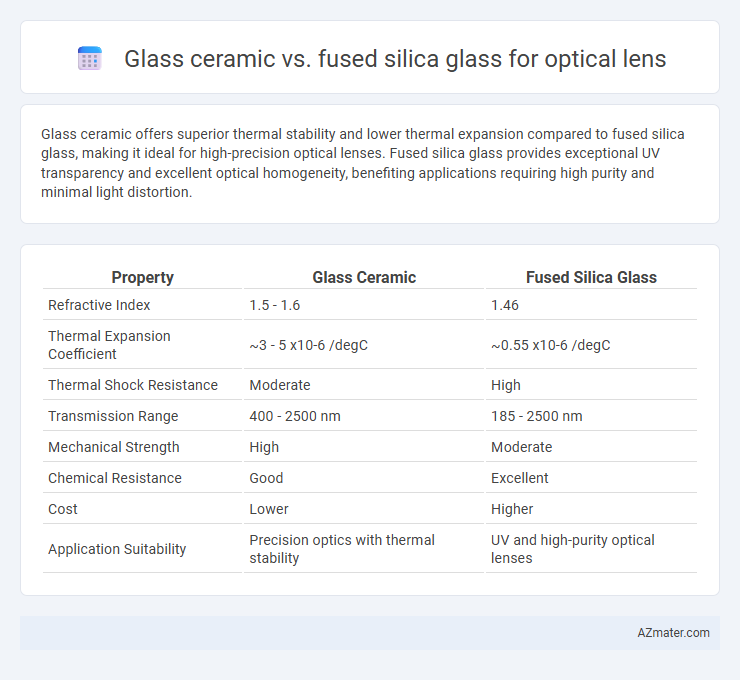
| Property | Glass Ceramic | Fused Silica Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Refractive Index | 1.5 - 1.6 | 1.46 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | ~3 - 5 x10-6 /degC | ~0.55 x10-6 /degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Transmission Range | 400 - 2500 nm | 185 - 2500 nm |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application Suitability | Precision optics with thermal stability | UV and high-purity optical lenses |
Introduction to Optical Lens Materials
Glass ceramic and fused silica glass represent two prominent materials used in optical lens manufacturing, each offering distinct properties tailored to specific applications. Glass ceramic provides excellent thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for lenses subjected to temperature fluctuations. Fused silica glass boasts superior optical clarity and ultraviolet transparency, along with high resistance to radiation and chemical corrosion, making it preferred for precision lenses in high-performance optical systems.
Overview of Glass Ceramic
Glass ceramic for optical lenses offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to fused silica glass, making it ideal for high-precision applications. Its unique microstructure combines the benefits of both glass and crystalline materials, resulting in low thermal expansion and excellent resistance to thermal shock. This material provides enhanced durability and optical clarity, suitable for demanding environments in laser systems and aerospace optics.
Overview of Fused Silica Glass
Fused silica glass is a high-purity, non-crystalline form of silicon dioxide renowned for its exceptional optical clarity, low thermal expansion coefficient, and superior resistance to thermal shock. It offers excellent transmission in the ultraviolet to near-infrared wavelength range, making it ideal for precision optical lenses used in laser systems, spectroscopy, and high-performance imaging. Compared to glass ceramics, fused silica provides superior homogeneity and minimal birefringence, ensuring high-quality optical performance in demanding environments.
Optical Properties Comparison
Glass ceramic lenses exhibit higher refractive indices and improved thermal stability compared to fused silica glass, enhancing image resolution and reducing chromatic aberration. Fused silica glass offers superior UV transparency and lower birefringence, making it ideal for high-precision optical applications requiring minimal light distortion. The choice depends on balancing durability with optical clarity, where glass ceramics provide better mechanical strength, while fused silica excels in wavelength transmission and optical purity.
Thermal Stability and Expansion
Glass ceramic exhibits superior thermal stability and significantly lower thermal expansion compared to fused silica glass, making it highly resistant to deformation under fluctuating temperatures. Fused silica glass offers excellent thermal stability but has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion, which can lead to slight dimensional changes impacting optical precision. The choice between glass ceramic and fused silica glass for optical lenses depends on the application's sensitivity to thermal stress and dimensional integrity requirements.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Glass ceramic exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to fused silica glass, making it more resistant to scratches and impacts in optical lens applications. Its enhanced durability ensures longer lifespan under harsh environmental conditions, including thermal cycling and mechanical stress. Fused silica glass offers excellent thermal stability but is comparatively more fragile, limiting its use in high-stress optical systems where robustness is critical.
Transmission Range and Clarity
Glass ceramic lenses feature a broad transmission range typically spanning from ultraviolet (UV) to near-infrared (NIR) wavelengths, with excellent thermal and mechanical stability that maintains optical clarity under varying conditions. Fused silica glass offers superior transmission in the deep UV range down to 180 nm and extends into the infrared up to about 3.5 microns, providing exceptional clarity and low absorption critical for high-precision optical applications. Both materials exhibit high optical clarity, but fused silica's lower impurity levels and minimal scattering make it the preferred choice for applications demanding the highest transmission quality and minimal distortion.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Glass ceramic offers cost-effective manufacturing due to lower melting temperatures and easier molding processes compared to fused silica glass, which requires high-temperature processing and more complex fabrication steps. Fused silica glass provides superior optical clarity and thermal stability but involves higher production costs driven by energy consumption and precision machining requirements. Manufacturers must balance budget constraints with performance needs, as fused silica lenses deliver exceptional durability and low thermal expansion at a premium price.
Applications in Optical Systems
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-precision optical lens applications in aerospace and laser systems. Fused silica glass provides excellent UV transparency and high damage threshold, preferred in spectroscopy, lithography, and UV laser optics. Both materials excel in different optical systems, with glass ceramic suited for dimensional stability and fused silica prioritized for spectral purity and laser resilience.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-precision optical lenses exposed to varying temperatures. Fused silica glass excels in optical clarity and UV transparency, with extremely low thermal expansion suitable for applications requiring minimal distortion. The choice depends on specific needs: glass ceramic suits durable, temperature-variable environments, while fused silica glass best fits high-precision, low-distortion optics.
Infographic: Glass ceramic vs Fused silica glass for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com