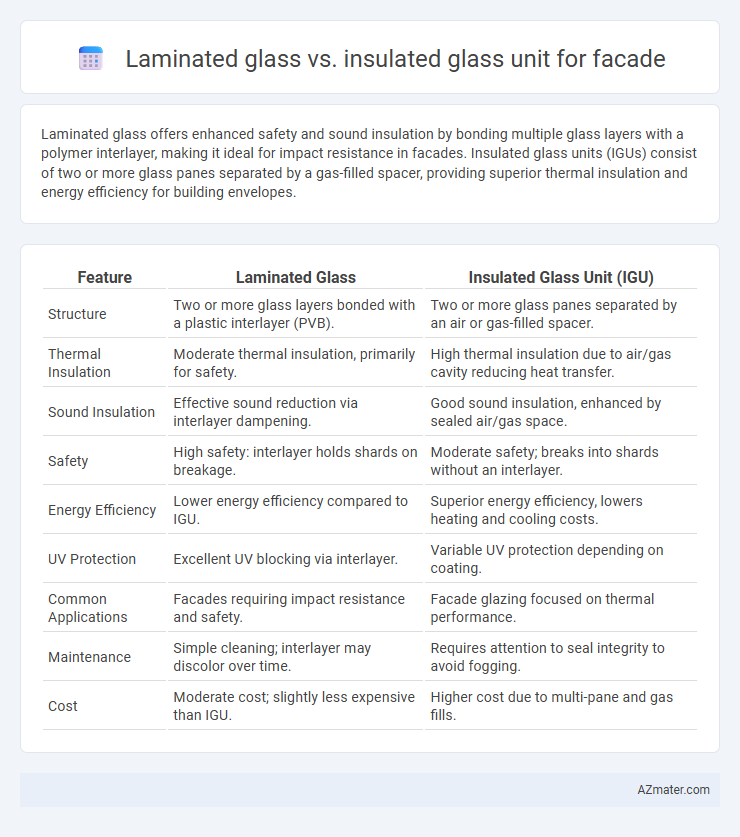
Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and sound insulation by bonding multiple glass layers with a polymer interlayer, making it ideal for impact resistance in facades. Insulated glass units (IGUs) consist of two or more glass panes separated by a gas-filled spacer, providing superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for building envelopes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Insulated Glass Unit (IGU) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer (PVB). | Two or more glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled spacer. |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate thermal insulation, primarily for safety. | High thermal insulation due to air/gas cavity reducing heat transfer. |
| Sound Insulation | Effective sound reduction via interlayer dampening. | Good sound insulation, enhanced by sealed air/gas space. |
| Safety | High safety: interlayer holds shards on breakage. | Moderate safety; breaks into shards without an interlayer. |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower energy efficiency compared to IGU. | Superior energy efficiency, lowers heating and cooling costs. |
| UV Protection | Excellent UV blocking via interlayer. | Variable UV protection depending on coating. |
| Common Applications | Facades requiring impact resistance and safety. | Facade glazing focused on thermal performance. |
| Maintenance | Simple cleaning; interlayer may discolor over time. | Requires attention to seal integrity to avoid fogging. |
| Cost | Moderate cost; slightly less expensive than IGU. | Higher cost due to multi-pane and gas fills. |
Introduction to Laminated Glass and Insulated Glass Units
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety, sound insulation, and UV protection for building facades. Insulated glass units (IGUs) are composed of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer and sealed to create an air or gas-filled cavity that improves thermal performance and energy efficiency. Both types are essential for modern facades, with laminated glass excelling in impact resistance and IGUs offering superior insulation.
Defining Key Differences: Laminated Glass vs Insulated Glass Unit
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety, sound insulation, and UV protection, making it ideal for facades requiring impact resistance and security. Insulated glass units (IGUs) feature two or more glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled spacer, optimizing thermal insulation and energy efficiency for building envelopes. The key difference lies in laminated glass's focus on durability and safety, while IGUs prioritize thermal performance and energy savings in facade applications.
Structural Performance in Facade Applications
Laminated glass offers superior structural performance in facade applications due to its multi-layer composition, which enhances impact resistance and maintains integrity upon breakage, providing increased safety and security. Insulated glass units (IGUs) primarily improve thermal performance but rely on the strength of individual glass panes, making them less effective in resisting structural loads compared to laminated glass. Selecting laminated glass for facades ensures improved durability against wind pressure, seismic forces, and accidental impacts, critical for building envelope resilience.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency Comparison
Laminated glass features multiple bonded layers providing sound attenuation and safety but offers limited thermal insulation compared to insulated glass units (IGUs), which contain multiple panes separated by gas-filled spacers, significantly reducing heat transfer. IGUs enhance energy efficiency by utilizing low-emissivity coatings and argon or krypton gas fills, resulting in superior U-values and solar heat gain coefficients that reduce HVAC costs. While laminated glass excels in impact resistance and security, IGUs are the preferred choice for facade applications prioritizing thermal performance and energy savings.
Sound Insulation: Acoustic Performance Analysis
Laminated glass features a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that significantly enhances sound insulation by dampening sound waves, making it highly effective for noise reduction in facades. Insulated glass units (IGUs), composed of two or more glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled space, improve acoustic performance by creating a sound barrier with variable pane thickness and gas fills such as argon or krypton. Studies show laminated glass generally outperforms single-pane IGUs in low-frequency noise reduction, while multi-pane IGUs excel in high-frequency sound attenuation, making combination laminated IGUs optimal for superior facade acoustic performance.
Safety and Security: Which Glass Offers More Protection?
Laminated glass offers superior safety by holding shattered pieces together due to its interlayer, preventing dangerous glass shards during impact or breakage. Insulated glass units (IGUs) primarily provide thermal insulation but do not enhance security or impact resistance as effectively as laminated glass. For facades requiring robust protection against forced entry or accidents, laminated glass is the preferred choice due to its durability and ability to maintain structural integrity upon impact.
Aesthetic Flexibility and Design Options
Laminated glass offers superior aesthetic flexibility with its ability to incorporate various colors, patterns, and interlayers, enhancing design creativity for facades. Insulated glass units (IGUs) provide versatile design options by combining multiple glass panes with gas fills and coatings to optimize energy efficiency without compromising visual clarity. Both laminated glass and IGUs can be customized in thickness and finish, enabling tailored solutions for modern architectural facades.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Laminated glass offers superior durability for facades due to its interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, reducing breakage risks and enhancing safety. Insulated glass units (IGUs) provide excellent thermal insulation but may require more maintenance to address potential seal failures and moisture ingress over time. Choosing laminated glass minimizes repair frequency and extends facade lifespan, while IGUs demand careful upkeep to preserve energy efficiency and prevent condensation issues.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Long-Term Investments
Laminated glass typically incurs a lower initial cost compared to insulated glass units (IGUs) due to simpler manufacturing processes and fewer materials involved. However, IGUs offer superior thermal insulation, which can significantly reduce long-term energy expenses, leading to better return on investment for facade applications. Maintenance costs tend to be lower for laminated glass, but the enhanced durability and energy efficiency of insulated glass units often justify their higher upfront price in commercial and high-performance building projects.
Best Practices for Facade Glass Selection
Laminated glass offers superior safety and security for facades by holding shards together upon impact, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and hurricane-prone regions. Insulated glass units (IGUs) enhance thermal performance with multiple panes separated by air or gas-filled spaces, reducing energy costs and improving occupant comfort in commercial buildings. Best practices for facade glass selection involve balancing safety, sound insulation, energy efficiency, and local climate conditions to optimize building performance and occupant well-being.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Insulated glass unit for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com