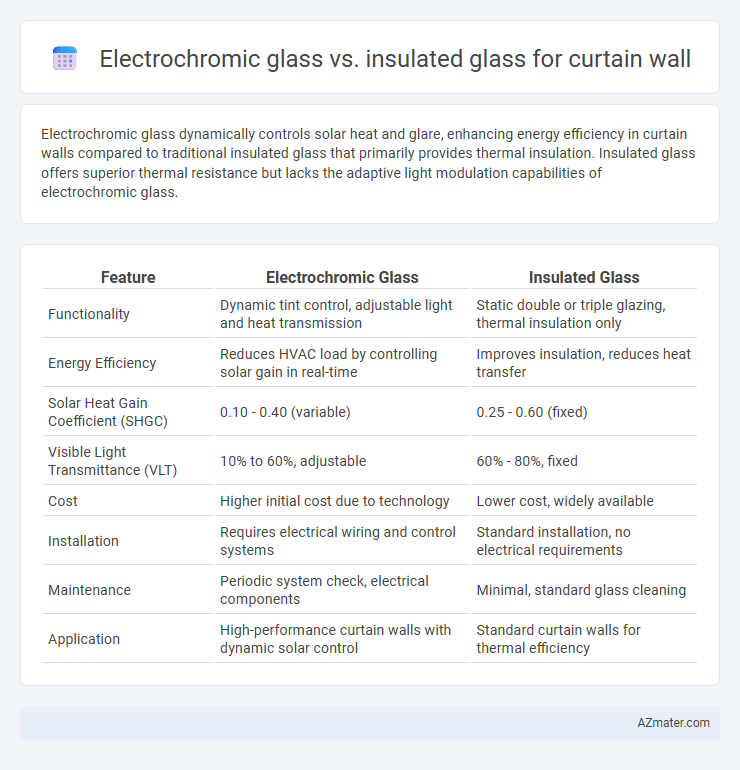
Electrochromic glass dynamically controls solar heat and glare, enhancing energy efficiency in curtain walls compared to traditional insulated glass that primarily provides thermal insulation. Insulated glass offers superior thermal resistance but lacks the adaptive light modulation capabilities of electrochromic glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Insulated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Dynamic tint control, adjustable light and heat transmission | Static double or triple glazing, thermal insulation only |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces HVAC load by controlling solar gain in real-time | Improves insulation, reduces heat transfer |
| Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) | 0.10 - 0.40 (variable) | 0.25 - 0.60 (fixed) |
| Visible Light Transmittance (VLT) | 10% to 60%, adjustable | 60% - 80%, fixed |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to technology | Lower cost, widely available |
| Installation | Requires electrical wiring and control systems | Standard installation, no electrical requirements |
| Maintenance | Periodic system check, electrical components | Minimal, standard glass cleaning |
| Application | High-performance curtain walls with dynamic solar control | Standard curtain walls for thermal efficiency |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glazing Options
Curtain wall glazing options primarily include Electrochromic glass and Insulated glass, each offering distinct performance benefits for building facades. Electrochromic glass provides dynamic solar control by adjusting tint levels electronically, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Insulated glass, typically composed of double or triple panes with gas fills, excels in thermal insulation and noise reduction for curtain walls.
What is Electrochromic Glass?
Electrochromic glass is a type of smart glass that changes its tint in response to an electrical voltage, allowing dynamic control of light and heat transmission in curtain wall systems. Unlike insulated glass, which primarily provides static thermal insulation and soundproofing through multiple glass layers and gas fills, electrochromic glass actively modulates solar heat gain and glare while maintaining transparency. This technology enhances energy efficiency and occupant comfort by reducing reliance on blinds or HVAC systems in commercial building facades.
Understanding Insulated Glass Units (IGUs)
Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) consist of two or more glass panes separated by a spacer and sealed to create an air or gas-filled cavity, enhancing thermal insulation and reducing energy loss in curtain wall applications. Electrochromic glass integrated into IGUs offers dynamic light and heat control by changing tint in response to electrical stimulus, improving occupant comfort and energy efficiency. Compared to standard insulated glass, electrochromic IGUs optimize solar heat gain and glare without sacrificing daylight, making them a superior choice for sustainable building facades.
Key Performance Differences
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic solar control by electronically tinting to reduce glare and heat gain, enhancing energy efficiency in curtain wall systems. Insulated glass primarily provides thermal insulation with fixed transparency, minimizing heat transfer but lacking adaptable shading capabilities. Key performance differences include electrochromic glass's ability to modulate light and solar heat gain in real-time versus insulated glass's superior static thermal resistance and sound insulation.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Electrochromic glass significantly enhances energy efficiency in curtain walls by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and visible light transmission, reducing reliance on HVAC systems compared to insulated glass, which offers static thermal insulation. Insulated glass primarily minimizes heat transfer through its double or triple glazing layers filled with inert gases but lacks adaptive solar control, leading to higher cooling or heating demands in varying weather conditions. Implementing electrochromic glass can result in up to 20-30% energy savings over insulated glass by optimizing daylight use and reducing glare while maintaining thermal comfort.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic tinting capabilities, providing architects with enhanced control over natural light, glare reduction, and privacy, thereby enabling sleek, adaptive curtain wall designs that respond to environmental changes. This technology supports seamless integration into modern facades with minimal framework, preserving clean aesthetics while reducing reliance on blinds or shading devices. Insulated glass, while excellent for thermal performance and noise reduction, typically lacks the variable transparency and color-shifting properties, limiting design flexibility and aesthetic innovation in curtain wall applications.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Electrochromic glass commands higher upfront costs compared to traditional insulated glass due to advanced technology and installation complexity, but offers substantial energy savings by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and reducing HVAC loads. Insulated glass, with lower initial expenses, delivers consistent thermal insulation but lacks smart shading capabilities that optimize daylight and reduce glare. The ROI for electrochromic glass improves markedly in climates with high solar exposure or stringent energy codes, potentially offsetting initial investments within 5 to 7 years through reduced energy bills and improved occupant comfort.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Electrochromic glass for curtain walls requires specialized electrical wiring and control systems during installation, adding complexity compared to insulated glass, which involves straightforward glazing techniques. Maintenance of electrochromic glass includes periodic inspection of electronic components and potential software updates to ensure functionality, whereas insulated glass primarily demands routine cleaning and seal integrity checks. The higher initial installation expertise for electrochromic systems often results in longer setup times but offers dynamic light and heat control, contrasting with the passive insulation efficiency of traditional insulated glass.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Electrochromic glass in curtain walls significantly reduces energy consumption by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and natural light, leading to lower HVAC loads and decreased carbon emissions compared to insulated glass. Its ability to switch tint levels on demand enhances building occupant comfort while minimizing reliance on artificial lighting, further supporting sustainability goals. Insulated glass offers thermal insulation benefits but lacks the adaptive control of solar radiation, resulting in less optimized energy efficiency and environmental performance.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic control over light and heat transmission, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in curtain wall applications. Insulated glass provides superior thermal insulation and soundproofing, making it a cost-effective solution for projects prioritizing durability and static performance. Selecting between electrochromic and insulated glass depends on project-specific needs such as energy savings, aesthetic flexibility, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Insulated glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com