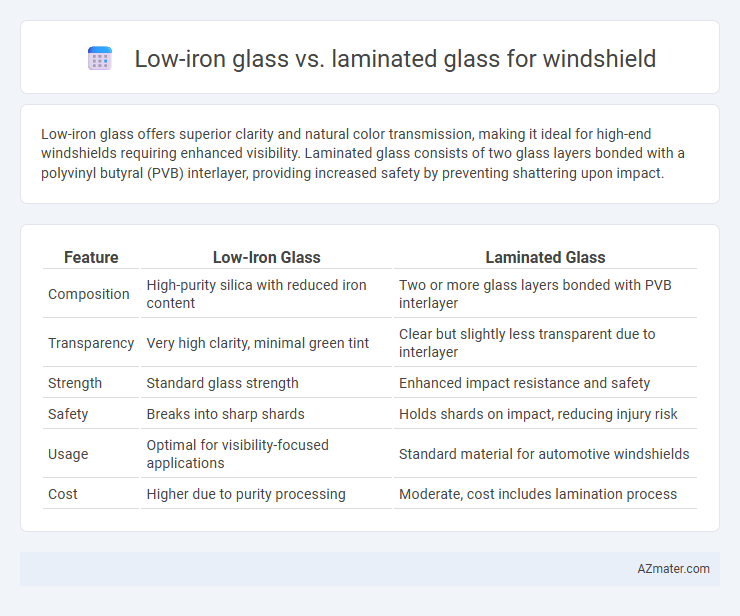
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and natural color transmission, making it ideal for high-end windshields requiring enhanced visibility. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing increased safety by preventing shattering upon impact.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Low-Iron Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High-purity silica with reduced iron content | Two or more glass layers bonded with PVB interlayer |
| Transparency | Very high clarity, minimal green tint | Clear but slightly less transparent due to interlayer |
| Strength | Standard glass strength | Enhanced impact resistance and safety |
| Safety | Breaks into sharp shards | Holds shards on impact, reducing injury risk |
| Usage | Optimal for visibility-focused applications | Standard material for automotive windshields |
| Cost | Higher due to purity processing | Moderate, cost includes lamination process |
Introduction to Automotive Glass Types
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and enhanced visibility in automotive windshields due to its reduced iron content, minimizing the greenish tint common in standard glass. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing increased safety by preventing shattering upon impact. Both types are critical in automotive applications, balancing clarity, durability, and occupant protection.
What is Low-Iron Glass?
Low-iron glass is a type of high-purity glass with reduced iron content, offering superior clarity and light transmission compared to standard automotive glass. This transparent glass enhances visibility by minimizing the greenish tint typically found in conventional laminated glass used for windshields. In contrast, laminated glass integrates a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) layer for safety, while low-iron glass primarily focuses on optical performance without compromising structural integrity.
Understanding Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for windshields consists of two layers of glass bonded together with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing enhanced safety by preventing shattering upon impact. Low-iron glass, while offering superior clarity and light transmission due to reduced iron content, lacks the structural integrity and impact resistance found in laminated glass. Understanding laminated glass highlights its critical role in automotive safety, as it maintains windshield integrity during collisions and protects occupants from debris.
Key Differences Between Low-Iron and Laminated Glass
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and enhanced light transmission compared to standard glass due to its reduced iron content, making it ideal for applications requiring high optical precision. Laminated glass, composed of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, provides increased safety by holding shards together upon impact, which is essential for windshields. While low-iron glass emphasizes visual clarity and aesthetics, laminated glass prioritizes impact resistance and occupant protection, marking the primary functional distinction between the two.
Optical Clarity: Low-Iron vs Laminated Glass
Low-iron glass offers superior optical clarity compared to laminated glass due to its reduced iron content, minimizing the greenish tint typically found in standard glass. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers with an interlayer, tends to exhibit slightly lower transparency and can create minor distortion under certain lighting. For windshields, using low-iron glass enhances visibility and visual accuracy, critical for driver safety and comfort.
Safety Performance: Which Glass Offers Better Protection?
Laminated glass offers superior safety performance for windshields due to its multi-layer construction, which holds shards together upon impact and prevents glass from dispersing, reducing injury risk during collisions. Low-iron glass, while providing higher clarity and visual aesthetics, lacks the integral safety benefits of laminated glass since it is typically a single layer and more prone to shattering. The enhanced impact resistance and structural integrity of laminated glass make it the better choice for optimal protection in automotive applications.
UV and Heat Resistance Comparison
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and enhanced UV protection due to its reduced iron content, making it beneficial for minimizing ultraviolet damage inside the vehicle. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers including a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides excellent UV blocking and significantly better heat resistance by reducing solar energy transmission. When comparing UV and heat resistance for windshields, laminated glass excels in thermal insulation and safety, while low-iron glass prioritizes optical clarity with moderate UV filtering capabilities.
Cost Analysis: Low-Iron Glass vs Laminated Glass
Low-iron glass typically costs 20-30% more than standard laminated glass due to its higher purity and clarity, making it preferred for luxury vehicles despite the price premium. Laminated glass, widely used in windshields, offers superior safety and durability at a more economical price point, with cost variations influenced by thickness and interlayer materials. Evaluating total expenses involves considering installation, long-term maintenance, and potential replacement costs alongside initial material prices.
Durability and Maintenance Factors
Low-iron glass offers enhanced clarity and aesthetic appeal but is less resistant to impacts and scratches compared to laminated glass, which is specifically designed for durability in automotive windshields. Laminated glass consists of multiple layers, including a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing superior resistance to shattering and improved safety during collisions. Maintenance-wise, laminated glass typically requires less frequent replacement and offers better long-term performance under stress, while low-iron glass may necessitate more careful handling to prevent damage.
Choosing the Right Windshield: Which Glass is Best for You?
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and light transmission, enhancing visibility and safety for drivers seeking a clearer view. Laminated glass provides robust impact resistance and holds together upon breakage, making it ideal for durability and occupant protection. Choosing between low-iron and laminated glass depends on prioritizing visual clarity versus enhanced safety features for your vehicle's windshield.
Infographic: Low-iron glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com