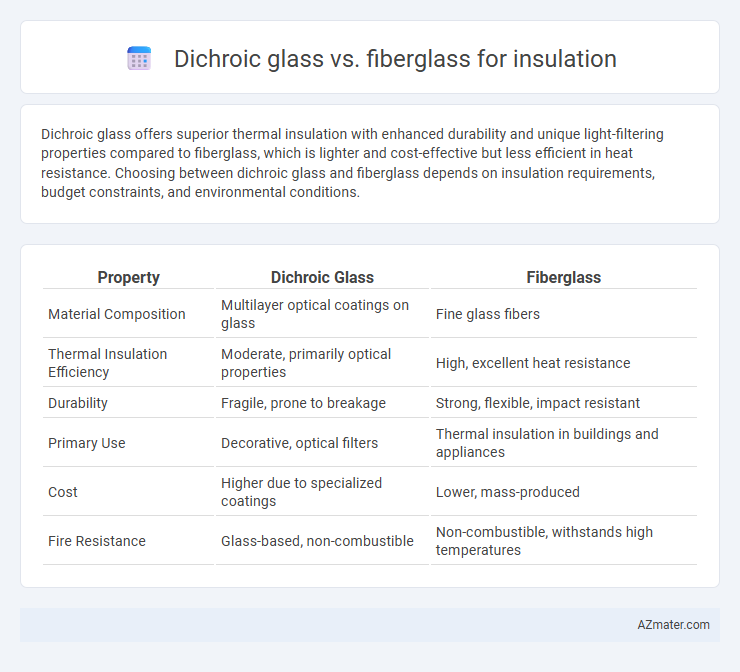
Dichroic glass offers superior thermal insulation with enhanced durability and unique light-filtering properties compared to fiberglass, which is lighter and cost-effective but less efficient in heat resistance. Choosing between dichroic glass and fiberglass depends on insulation requirements, budget constraints, and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dichroic Glass | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Multilayer optical coatings on glass | Fine glass fibers |
| Thermal Insulation Efficiency | Moderate, primarily optical properties | High, excellent heat resistance |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to breakage | Strong, flexible, impact resistant |
| Primary Use | Decorative, optical filters | Thermal insulation in buildings and appliances |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized coatings | Lower, mass-produced |
| Fire Resistance | Glass-based, non-combustible | Non-combustible, withstands high temperatures |
Introduction to Dichroic Glass and Fiberglass Insulation
Dichroic glass features multiple ultra-thin layers of metal oxides, creating unique optical properties that selectively reflect and transmit light in vibrant colors. Fiberglass insulation consists of fine glass fibers woven into a mat, providing thermal resistance by trapping air and reducing heat transfer in buildings. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with dichroic glass used primarily in decorative and optical applications, while fiberglass is widely implemented for thermal and acoustic insulation in construction.
Composition and Material Properties
Dichroic glass consists of multiple ultra-thin layers of metal oxides deposited on glass, offering unique optical properties like color-shifting and high durability but limited thermal insulation capabilities. Fiberglass insulation is made from fine glass fibers spun into a wool-like material, providing excellent thermal resistance and low thermal conductivity crucial for energy efficiency. While dichroic glass emphasizes optical performance and aesthetic applications, fiberglass excels in thermal insulation due to its fibrous composition and high R-value.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Dichroic glass offers limited thermal insulation due to its thin, layered structure primarily designed for optical properties, whereas fiberglass excels in thermal insulation through its dense, fibrous composition that traps air and reduces heat transfer. Fiberglass insulation typically achieves R-values between R-2.2 to R-4.3 per inch, making it highly effective for temperature regulation in buildings. Dichroic glass's main function is not insulation but light filtration, so its thermal resistance is significantly lower compared to the specialized thermal barrier properties of fiberglass materials.
Heat Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Dichroic glass exhibits superior heat resistance due to its ability to withstand temperatures up to approximately 1100degC, making it ideal for applications involving intense thermal exposure. Fiberglass insulation typically tolerates temperatures ranging from 230degC to 540degC depending on the binder used, offering reliable performance in moderate heat environments. When prioritizing temperature tolerance for insulation, dichroic glass outperforms fiberglass by maintaining structural integrity under higher thermal stress.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Dichroic glass exhibits superior energy efficiency by selectively reflecting and transmitting specific wavelengths of light, reducing heat gain while allowing natural daylight, which minimizes cooling and lighting energy demands. Fiberglass insulation primarily limits heat transfer through its thermal resistance, effectively reducing heating and cooling costs but does not contribute to daylight management. Integrating dichroic glass with fiberglass insulation can optimize overall energy performance by combining spectral solar control with high R-values for thermal resistance.
Installation Process and Ease
Dichroic glass is primarily used for decorative purposes and requires specialized installation techniques involving precise cutting and secure mounting to handle its delicate, reflective surface. Fiberglass insulation is widely preferred for thermal and acoustic insulation due to its straightforward installation process, involving cutting batts or rolls to fit spaces and using adhesives or fasteners for secure placement. Easier handling and adaptability make fiberglass more suitable for most insulation projects, while dichroic glass demands expert installation for aesthetic applications.
Durability and Longevity
Dichroic glass offers excellent durability with high resistance to UV radiation, chemical corrosion, and thermal stress, making it suitable for long-term architectural applications. Fiberglass insulation, while cost-effective and lightweight, can degrade over time due to moisture absorption and mechanical wear, potentially reducing its insulating properties and lifespan. For applications demanding prolonged durability and minimal maintenance, dichroic glass outperforms fiberglass by maintaining structural integrity and insulation efficiency over decades.
Cost and Budget Considerations
Dichroic glass insulation is significantly more expensive than fiberglass due to its specialized manufacturing process, making it less feasible for budget-conscious projects. Fiberglass offers a cost-effective solution with widespread availability and lower installation expenses, ideal for large-scale insulation needs. Budget planning should prioritize fiberglass when minimizing upfront costs is critical, while dichroic glass may be reserved for niche applications requiring higher thermal performance despite higher investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Dichroic glass offers limited environmental benefits in insulation compared to fiberglass, as its production involves rare earth metals and energy-intensive processes leading to higher carbon footprints. Fiberglass insulation, widely recycled and manufactured with abundant materials like sand and recycled glass, typically provides better sustainability through lower embodied energy and improved recyclability. Assessing life cycle impacts, fiberglass's widespread use in energy-efficient building applications contributes to reduced environmental harm over time, whereas dichroic glass remains niche with less proven ecological advantages.
Choosing the Right Insulation: Dichroic Glass vs Fiberglass
Choosing the right insulation requires understanding the unique properties of dichroic glass and fiberglass. Dichroic glass offers superior thermal resistance and aesthetic appeal through its color-shifting capabilities, making it ideal for design-focused applications. Fiberglass provides excellent soundproofing and cost-effective thermal insulation, commonly used in residential and commercial buildings for energy efficiency.
Infographic: Dichroic glass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com