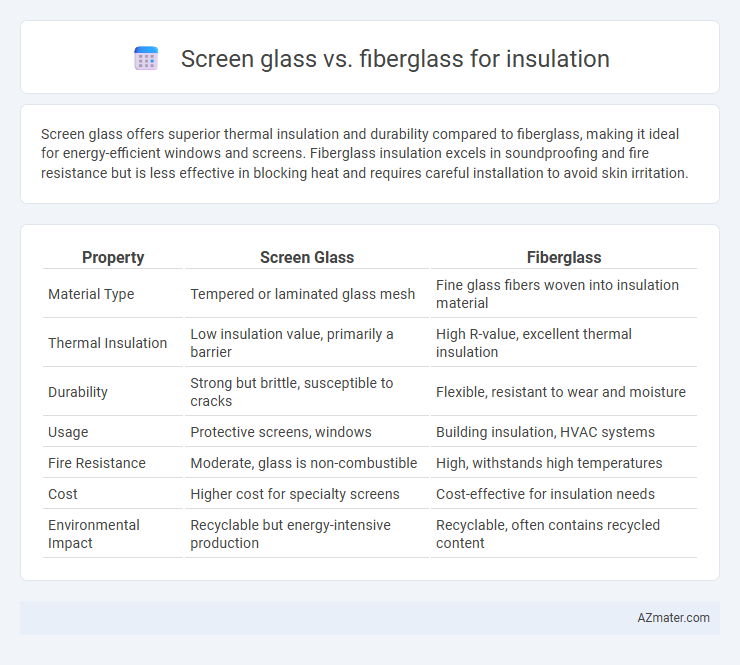
Screen glass offers superior thermal insulation and durability compared to fiberglass, making it ideal for energy-efficient windows and screens. Fiberglass insulation excels in soundproofing and fire resistance but is less effective in blocking heat and requires careful installation to avoid skin irritation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Screen Glass | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Tempered or laminated glass mesh | Fine glass fibers woven into insulation material |
| Thermal Insulation | Low insulation value, primarily a barrier | High R-value, excellent thermal insulation |
| Durability | Strong but brittle, susceptible to cracks | Flexible, resistant to wear and moisture |
| Usage | Protective screens, windows | Building insulation, HVAC systems |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate, glass is non-combustible | High, withstands high temperatures |
| Cost | Higher cost for specialty screens | Cost-effective for insulation needs |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but energy-intensive production | Recyclable, often contains recycled content |
Understanding Screen Glass and Fiberglass Insulation
Screen glass insulation uses fine glass fibers woven into a mesh that blocks airflow and reduces heat transfer, offering durability and resistance to moisture. Fiberglass insulation consists of loose or batt fibers designed to trap air within the material, providing high thermal resistance (R-value) and sound absorption. Both materials leverage glass fibers but differ in structure and application, impacting their effectiveness in insulation and energy efficiency.
Composition and Material Differences
Screen glass insulation primarily consists of silica-based glass fibers woven into a mesh that provides lightweight, transparent coverage with moderate thermal resistance. Fiberglass insulation is composed of fine strands of glass fibers bound with resins, forming dense batts or loose-fill materials designed for high thermal and acoustic insulation efficiency. The key material difference lies in screen glass's thin, flexible mesh structure versus fiberglass's denser, bulkier fiber composition tailored for maximum heat retention and soundproofing.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Fiberglass insulation offers superior thermal resistance with R-values typically ranging from R-2.2 to R-3.8 per inch, making it highly effective at reducing heat transfer in walls and attics. Screen glass, primarily used for windows, provides limited thermal insulation and relies on coatings or multiple panes to improve energy efficiency, but cannot match the insulating capabilities of fiberglass. For optimal thermal insulation performance in building envelopes, fiberglass remains the preferred choice due to its higher R-value and better ability to minimize heat loss and gain.
Soundproofing Capabilities
Fiberglass insulation provides superior soundproofing capabilities compared to screen glass, effectively reducing airborne noise due to its dense mat structure that absorbs sound waves. Screen glass offers minimal soundproofing benefits since its primary function is visual transparency and not acoustic insulation. For optimal noise reduction in building applications, fiberglass insulation remains the preferred material, significantly enhancing soundproofing performance in walls and ceilings.
Durability and Lifespan
Fiberglass insulation offers high durability with resistance to moisture, mold, and pests, maintaining effectiveness for up to 80 years when properly installed. Screen glass insulation, while less common, provides moderate durability but may degrade faster under UV exposure and physical damage, reducing its lifespan to around 20-30 years. For long-term performance, fiberglass is preferred due to its superior resilience and extended lifespan in various environmental conditions.
Fire Resistance Comparison
Screen glass offers superior fire resistance compared to fiberglass insulation due to its non-combustible nature and ability to withstand temperatures exceeding 700degF without degradation. Fiberglass, while resistant to heat, can lose structural integrity and emit toxic fumes when exposed to high temperatures during a fire event. Choosing screen glass enhances building safety by providing a more resilient barrier against fire hazards in insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Screen glass insulation offers superior recyclability as it is made from abundant natural silica and can be remelted indefinitely, reducing landfill waste and energy consumption during production. Fiberglass insulation, while also recyclable, relies on energy-intensive manufacturing processes and often incorporates synthetic resins that complicate reuse and disposal. Choosing screen glass enhances sustainability by minimizing carbon footprint and promoting circular economy principles in building materials.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Screen glass insulation offers a straightforward installation process with lightweight panels that can be easily cut and fitted into irregular spaces, making it ideal for DIY projects and quick applications. Fiberglass insulation requires more careful handling due to its irritating fibers and often needs protective gear during installation, along with precise measurements to avoid gaps that reduce thermal performance. The flexibility of fiberglass allows it to conform tightly to wall cavities and around obstacles, whereas screen glass provides rigid structure but excels in ease of fitting and minimal settling over time.
Cost Analysis: Screen Glass vs Fiberglass
Screen glass insulation generally exhibits a higher upfront cost compared to fiberglass due to its advanced manufacturing process and enhanced durability. Fiberglass offers a more budget-friendly solution with widespread availability, making it popular for large-scale projects aiming to minimize initial expenses. Long-term cost benefits of screen glass include superior energy efficiency and reduced maintenance, which can offset the initial investment over the lifespan of the insulation.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Screen glass offers superior transparency and weather resistance, making it ideal for window insulation in residential and commercial buildings where natural light and durability are prioritized. Fiberglass insulation boasts high thermal resistance (R-value) and soundproofing qualities, best suited for walls, attics, and HVAC systems to improve energy efficiency and noise reduction. In environments requiring both insulation and visibility, combining screen glass with fiberglass panels can optimize performance across temperature control and light transmission.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com