Low-iron glass offers superior light transmission and clarity, enhancing natural daylight in curtain walls while maintaining structural strength. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort in building facades.
Table of Comparison
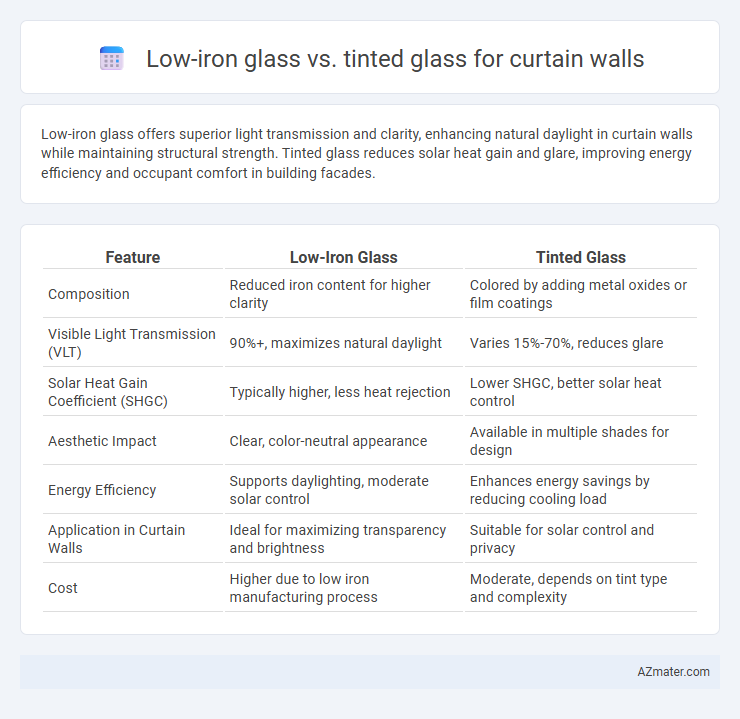
| Feature | Low-Iron Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Reduced iron content for higher clarity | Colored by adding metal oxides or film coatings |
| Visible Light Transmission (VLT) | 90%+, maximizes natural daylight | Varies 15%-70%, reduces glare |
| Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) | Typically higher, less heat rejection | Lower SHGC, better solar heat control |
| Aesthetic Impact | Clear, color-neutral appearance | Available in multiple shades for design |
| Energy Efficiency | Supports daylighting, moderate solar control | Enhances energy savings by reducing cooling load |
| Application in Curtain Walls | Ideal for maximizing transparency and brightness | Suitable for solar control and privacy |
| Cost | Higher due to low iron manufacturing process | Moderate, depends on tint type and complexity |
Introduction to Low-Iron and Tinted Glass in Curtain Walls
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and enhanced light transmission, making it ideal for curtain wall applications where natural daylighting and aesthetic transparency are prioritized. Tinted glass incorporates metal oxides or other colorants to reduce solar heat gain and glare, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in building facades. Both low-iron and tinted glass provide unique performance benefits essential for optimizing the functionality and visual appeal of modern curtain wall systems.
Key Properties of Low-Iron Glass
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and light transmission compared to tinted glass, making it ideal for curtain walls that require maximum natural daylight and vibrant colors. Its reduced iron content minimizes the greenish tint found in standard glass, enhancing aesthetic appeal and visual transparency in architectural applications. Low-iron glass also provides excellent UV resistance and durability, ensuring long-lasting performance in building envelopes.
Key Properties of Tinted Glass
Tinted glass for curtain walls offers superior solar control, reducing glare and heat gain by absorbing a portion of sunlight, which enhances energy efficiency in buildings. It typically exhibits a darker appearance compared to low-iron glass, providing increased privacy without compromising natural light. With higher thermal performance and UV protection, tinted glass effectively contributes to occupant comfort and glass unit durability in commercial facades.
Light Transmission Differences
Low-iron glass offers higher light transmission rates, typically around 90%, allowing more natural daylight to enter curtain walls compared to tinted glass, which generally transmits between 30% to 70% depending on the tint level. The enhanced clarity and reduced greenish hue of low-iron glass improve visual comfort and color accuracy within interior spaces. Tinted glass, designed to reduce solar heat gain, decreases light transmission deliberately, balancing daylight control with energy efficiency in building facades.
Color Clarity and Visual Impact
Low-iron glass offers superior color clarity with minimal green tint, enhancing natural light transmission and providing a true-to-color view in curtain wall applications. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare but can alter the exterior appearance with a colored hue that impacts the building's visual uniformity. Choosing low-iron glass improves aesthetic brightness and transparency, while tinted glass emphasizes energy efficiency and shading performance in facade design.
Energy Efficiency and Solar Control
Low-iron glass offers higher visible light transmittance than tinted glass, enhancing natural daylight penetration in curtain wall systems without compromising energy efficiency. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain by absorbing and reflecting infrared radiation, which improves solar control but can also lower daylight levels, potentially increasing artificial lighting needs. Selecting between low-iron and tinted glass involves balancing daylight quality with solar heat gain reduction to optimize energy performance in building facades.
Applications and Design Flexibility
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and natural light transmission, making it ideal for curtain walls in high-end commercial buildings where aesthetics and daylighting are crucial. Tinted glass provides enhanced solar control and energy efficiency by reducing glare and heat gain, suitable for buildings in hot climates requiring thermal management. Design flexibility is greater with low-iron glass due to its neutral color and ability to pair with various coatings, while tinted glass often limits color options but excels in balancing daylight and privacy.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Low-iron glass typically incurs higher upfront costs due to its enhanced clarity and reduced green tint, making it a premium option for curtain walls that demand visual performance. Tinted glass offers a more budget-friendly alternative, providing solar control benefits while maintaining a lower price point suitable for cost-sensitive projects. When evaluating curtain wall budgets, low-iron glass is ideal for high-end developments prioritizing aesthetics, whereas tinted glass aligns with projects emphasizing energy efficiency and cost efficiency.
Environmental and Sustainability Aspects
Low-iron glass, with its higher light transmission and clarity, enhances natural daylighting, reducing the need for artificial lighting and lowering energy consumption in curtain wall systems. Tinted glass, while reducing solar heat gain and cooling loads, can limit natural light penetration, potentially increasing indoor lighting demands. Both options impact sustainability differently: low-iron glass supports visual comfort and daylight utilization, whereas tinted glass primarily contributes to thermal performance and energy efficiency in building envelopes.
Choosing the Right Glass for Curtain Wall Systems
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and high light transmission, making it ideal for curtain wall systems that prioritize natural daylight and transparency. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in buildings located in hot climates. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing aesthetic goals, energy performance requirements, and environmental factors specific to the building's location.
Infographic: Low-iron glass vs Tinted glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com