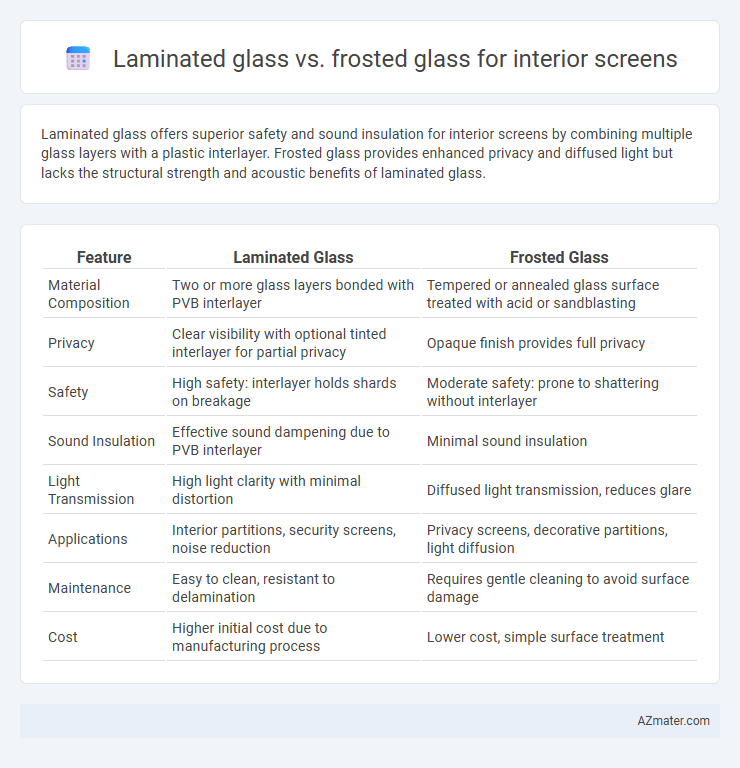
Laminated glass offers superior safety and sound insulation for interior screens by combining multiple glass layers with a plastic interlayer. Frosted glass provides enhanced privacy and diffused light but lacks the structural strength and acoustic benefits of laminated glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Frosted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with PVB interlayer | Tempered or annealed glass surface treated with acid or sandblasting |
| Privacy | Clear visibility with optional tinted interlayer for partial privacy | Opaque finish provides full privacy |
| Safety | High safety: interlayer holds shards on breakage | Moderate safety: prone to shattering without interlayer |
| Sound Insulation | Effective sound dampening due to PVB interlayer | Minimal sound insulation |
| Light Transmission | High light clarity with minimal distortion | Diffused light transmission, reduces glare |
| Applications | Interior partitions, security screens, noise reduction | Privacy screens, decorative partitions, light diffusion |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, resistant to delamination | Requires gentle cleaning to avoid surface damage |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to manufacturing process | Lower cost, simple surface treatment |
Introduction to Laminated and Frosted Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety, sound insulation, and UV protection for interior screens. Frosted glass is treated with acid etching or sandblasting to create a translucent surface that offers privacy while allowing light to pass through. Both materials serve distinct aesthetic and functional purposes in interior design, with laminated glass emphasizing durability and security, and frosted glass focusing on privacy and light diffusion.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Laminated glass is composed of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), manufactured through heat and pressure lamination to enhance safety and durability. Frosted glass is produced by either sandblasting or acid etching the surface of a single glass pane, creating a translucent finish that diffuses light while maintaining privacy. The manufacturing process for laminated glass involves complex lamination and curing, whereas frosted glass requires surface treatment techniques that alter texture without compromising structural integrity.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Versatility
Laminated glass offers a sleek, clear appearance with the option to incorporate decorative interlayers, enhancing both safety and visual interest for interior screens. Frosted glass provides a matte, translucent finish that diffuses light softly, creating privacy while adding a subtle texture ideal for minimalist or modern designs. Both materials deliver distinct aesthetic appeal and design versatility, allowing customization to suit various interior styles and functional needs.
Light Transmission and Privacy Levels
Laminated glass offers high light transmission, typically around 70-90%, ensuring clear visibility while providing enhanced safety and sound insulation for interior screens. Frosted glass reduces light transmission significantly, often to 40-60%, diffusing light to create a softer glow and increasing privacy by obscuring detailed views. Choosing between laminated and frosted glass depends on balancing the need for maximum natural light with the desired level of privacy in interior spaces.
Safety and Security Features
Laminated glass offers superior safety and security for interior screens due to its multi-layered composition, which holds shards together upon impact, reducing injury risk and preventing easy break-ins. Frosted glass, while providing privacy by obscuring visibility, lacks the same shatter-resistant properties and can break into sharp pieces, posing higher safety hazards. Choosing laminated glass enhances protection against accidents and forced entry while maintaining aesthetic appeal in interior design.
Acoustic Performance Comparison
Laminated glass provides superior acoustic performance for interior screens due to its ability to reduce noise transmission through the interlayer that dampens sound vibrations. Frosted glass, while effective for privacy and light diffusion, offers limited sound insulation as its surface texture does not significantly impede sound waves. For environments demanding enhanced noise control, laminated glass is the preferred choice because it combines clarity with effective acoustic dampening.
Maintenance and Durability
Laminated glass offers superior durability due to its multi-layer construction, which holds together even when shattered, reducing maintenance costs related to cracks or breakage. Frosted glass, while aesthetically pleasing and providing privacy, is more prone to scratches and surface wear, requiring more frequent cleaning and potential replacement. The maintenance of laminated glass is generally lower over time, as it resists impacts and environmental damage better than frosted glass, making it a more durable choice for interior screens.
Cost Considerations
Laminated glass typically incurs higher costs than frosted glass due to its multiple layers and safety features, making it a durable choice for interior screens. Frosted glass offers a budget-friendly option with its simple acid-etching or sandblasting process that provides privacy without the added structural benefits. Budget constraints and the desired level of security and aesthetics are critical factors when choosing between laminated and frosted glass for interior applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Laminated glass offers superior durability and enhanced safety due to its bonded layers, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. Frosted glass, while providing privacy and diffuse light, typically requires chemical treatments that can have a higher environmental footprint during production. Choosing laminated glass for interior screens promotes sustainability through extended lifespan and recyclability, aligning with eco-friendly building practices.
Choosing the Right Glass for Interior Screens
Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and durability for interior screens, featuring a plastic interlayer that holds shards in place upon breakage, making it ideal for high-traffic areas requiring impact resistance. Frosted glass provides privacy and aesthetic appeal by diffusing light while obscuring visibility, suitable for spaces that prioritize confidentiality without sacrificing natural light. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing safety needs with design preferences, where laminated glass excels in security and frost glass in privacy enhancement.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Frosted glass for Interior screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com