Screen glass is typically designed for scratch resistance and impact protection in electronic displays, while optical glass used in lenses offers superior light transmission, minimal distortion, and precise refractive properties essential for high-quality imaging. Optical glass contains specific formulations to enhance clarity and focus, whereas screen glass prioritizes durability and surface hardness over optical performance.
Table of Comparison
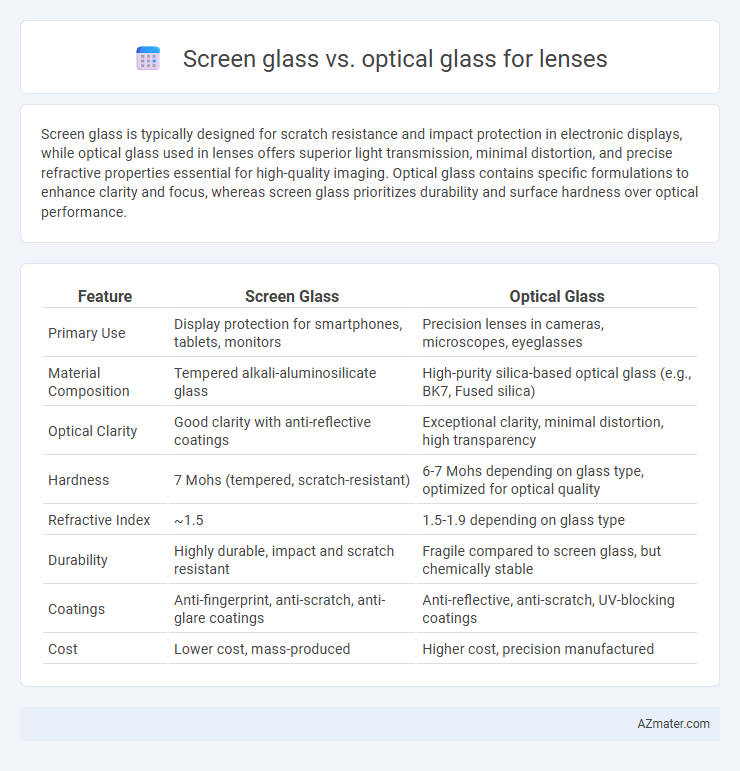
| Feature | Screen Glass | Optical Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Display protection for smartphones, tablets, monitors | Precision lenses in cameras, microscopes, eyeglasses |
| Material Composition | Tempered alkali-aluminosilicate glass | High-purity silica-based optical glass (e.g., BK7, Fused silica) |
| Optical Clarity | Good clarity with anti-reflective coatings | Exceptional clarity, minimal distortion, high transparency |
| Hardness | 7 Mohs (tempered, scratch-resistant) | 6-7 Mohs depending on glass type, optimized for optical quality |
| Refractive Index | ~1.5 | 1.5-1.9 depending on glass type |
| Durability | Highly durable, impact and scratch resistant | Fragile compared to screen glass, but chemically stable |
| Coatings | Anti-fingerprint, anti-scratch, anti-glare coatings | Anti-reflective, anti-scratch, UV-blocking coatings |
| Cost | Lower cost, mass-produced | Higher cost, precision manufactured |
Introduction to Screen Glass and Optical Glass
Screen glass, commonly used in display technologies, offers high transparency and durability to enhance visual clarity and touch sensitivity, making it ideal for smartphones, tablets, and monitors. Optical glass, engineered with precise refractive indices and low dispersion properties, is essential for lenses to achieve accurate light refraction and minimal aberrations in cameras, microscopes, and telescopes. Both materials are tailored for specific optical performance, with screen glass emphasizing surface protection and visibility, while optical glass prioritizes precise light control and image quality.
Key Differences Between Screen Glass and Optical Glass
Screen glass typically refers to protective covers used for electronic device displays, prioritizing durability and scratch resistance, while optical glass is specifically engineered for lens applications with precise control over refractive indices and minimal light distortion. Optical glass possesses superior clarity, low dispersion, and consistent optical properties essential for image quality in lenses, whereas screen glass is optimized for impact resistance and touch responsiveness. The key differences lie in their material composition, light transmission efficiency, and functional purpose in either safeguarding screens or enhancing optical performance in lenses.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Screen glass typically consists of alkali-aluminosilicate materials with high durability and scratch resistance, optimized for flat display surfaces, while optical glass for lenses is composed of carefully formulated silica-based compounds with varying refractive indices to enhance light transmission and minimize aberrations. Manufacturing screen glass involves processes like fusion draw or float glass methods to achieve uniform thickness and strength, whereas optical glass undergoes precise melting, mixing, and controlled annealing to ensure homogeneity and optical clarity. The critical difference lies in optical glass's stringent quality control for refractive properties versus screen glass's focus on mechanical robustness and surface hardness.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Optical glass offers superior optical clarity and higher light transmission compared to screen glass, making it ideal for precision lenses in cameras and scientific instruments. Its carefully controlled refractive index and low dispersion minimize light distortion and maximize image sharpness. Screen glass typically exhibits lower optical performance due to impurities and less uniformity, resulting in reduced clarity and light transmission efficiency.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Screen glass, typically made from tempered or chemically strengthened glass, offers high scratch resistance and durability suitable for touchscreens and protective covers, but lacks the optical precision required for lens applications. Optical glass, designed with specific refractive properties and superior clarity, balances moderate scratch resistance with enhanced durability, making it ideal for high-performance lenses in cameras, microscopes, and optical instruments. When prioritizing scratch resistance and durability for lenses, optical glass often incorporates specialized coatings to improve hardness and longevity without compromising optical quality.
Performance in Camera Lenses and Optical Devices
Screen glass in camera lenses often offers basic protection and scratch resistance but lacks the precision and clarity of optical glass. Optical glass is engineered with high refractive index and low dispersion, enhancing light transmission, reducing chromatic aberration, and delivering superior image sharpness and color fidelity in optical devices. Performance in camera lenses is significantly improved with optical glass due to its specialized coatings and material properties designed for precise light manipulation and minimal distortion.
Cost Comparison: Screen Glass vs Optical Glass
Screen glass generally costs less than optical glass due to its lower manufacturing precision and material quality requirements. Optical glass demands high purity and precise refractive index control, driving up production expenses and resulting in higher prices. For applications requiring superior clarity and minimal distortion, the increased cost of optical glass is justified compared to the more budget-friendly screen glass options.
Applications in Consumer Electronics
Screen glass in consumer electronics primarily serves as a protective layer for displays, offering scratch resistance and impact durability, essential for smartphones, tablets, and laptops. Optical glass used in lenses enhances image clarity and precision in cameras, VR devices, and augmented reality systems by minimizing distortion and improving light transmission. The choice between screen glass and optical glass depends on the device's need for protection versus optical performance in imaging applications.
Pros and Cons of Each Glass Type
Screen glass offers durability and scratch resistance, making it ideal for protective lens covers, but it generally sacrifices optical clarity and light transmission compared to optical glass. Optical glass provides superior image quality with high refractive index and minimal distortion, essential for precision lenses, yet it tends to be more fragile and costly. While screen glass enhances impact resistance and reduces glare, optical glass ensures excellent color accuracy and sharpness crucial for professional imaging applications.
How to Choose the Right Glass for Your Lens
Selecting the right glass for your lens depends on balancing optical clarity, durability, and cost. Optical glass offers superior light transmission and minimal distortion, ideal for high-precision lenses in photography or scientific instruments. Screen glass provides adequate clarity with enhanced scratch resistance and affordability, making it suitable for less demanding applications like smartphone or tablet lenses.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Optical glass for Lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com