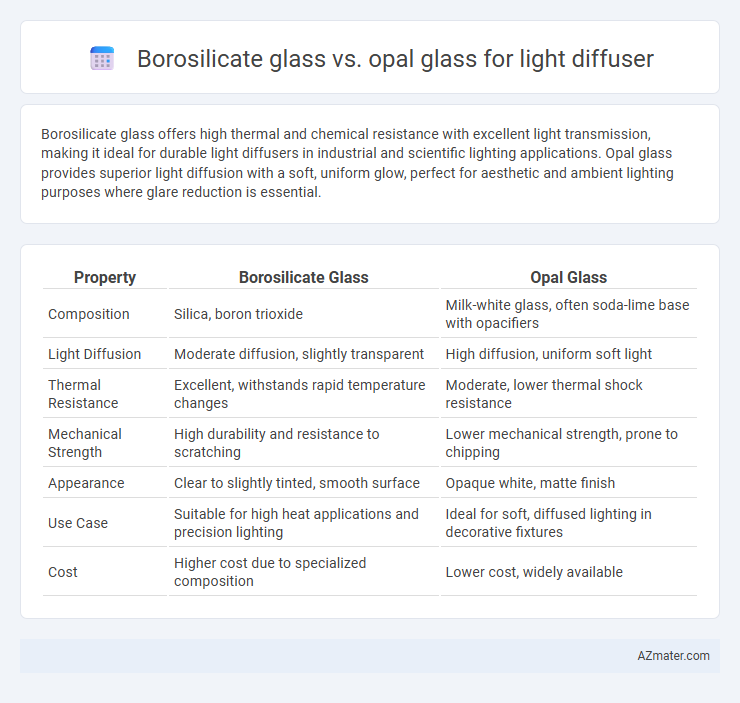
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal and chemical resistance with excellent light transmission, making it ideal for durable light diffusers in industrial and scientific lighting applications. Opal glass provides superior light diffusion with a soft, uniform glow, perfect for aesthetic and ambient lighting purposes where glare reduction is essential.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, boron trioxide | Milk-white glass, often soda-lime base with opacifiers |
| Light Diffusion | Moderate diffusion, slightly transparent | High diffusion, uniform soft light |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent, withstands rapid temperature changes | Moderate, lower thermal shock resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High durability and resistance to scratching | Lower mechanical strength, prone to chipping |
| Appearance | Clear to slightly tinted, smooth surface | Opaque white, matte finish |
| Use Case | Suitable for high heat applications and precision lighting | Ideal for soft, diffused lighting in decorative fixtures |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized composition | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Light Diffuser Materials
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for light diffusers requiring long-lasting performance and resistance to heat-induced stress. Opal glass provides a smooth, translucent surface that evenly diffuses light, reducing glare and creating a soft illumination effect favored in decorative and ambient lighting. Choosing between borosilicate and opal glass depends on the specific application's need for thermal stability versus diffusion quality.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its high resistance to thermal shock, chemical corrosion, and mechanical stress, making it ideal for use in light diffusers where durability and clarity are essential. It consists mainly of silica and boron trioxide, which give it a low coefficient of thermal expansion, preventing cracks and breakage under temperature fluctuations. Compared to opal glass, borosilicate offers superior transparency and longevity, ensuring consistent light diffusion in lighting applications.
What is Opal Glass?
Opal glass is a type of glass specifically designed for light diffusion, characterized by its milky white, translucent appearance that evenly scatters light to reduce glare and create soft illumination. Unlike borosilicate glass, which is known for its high thermal and chemical resistance, opal glass prioritizes aesthetic diffusion properties, making it ideal for applications in lighting fixtures and covers. The light-scattering quality of opal glass enhances visual comfort, while borosilicate glass excels in durability and heat tolerance but offers less effective light diffusion.
Optical Properties: Borosilicate vs Opal Glass
Borosilicate glass offers high transparency with minimal light distortion, making it ideal for applications requiring clear and precise light diffusion. Opal glass features a milky, translucent quality that scatters light more evenly, reducing glare and creating a softer illumination. While borosilicate excels in optical clarity and thermal resistance, opal glass prioritizes uniform light diffusion and aesthetic softness in lighting fixtures.
Light Transmission and Diffusion Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers high light transmission, typically around 90%, ensuring minimal light loss and clear illumination, while opal glass diffuses light more effectively by scattering it evenly, reducing glare and creating a softer glow. The microstructure of opal glass diffuses light through a milky or frosted appearance, leading to a transmission rate often between 60-80%, ideal for uniform light distribution in fixtures. Borosilicate is preferred for applications requiring clarity and thermal resistance, whereas opal glass excels in environments prioritizing balanced diffusion and aesthetic light softening.
Durability and Resistance to Heat
Borosilicate glass offers superior durability and thermal resistance due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and suitable for harsh environments. Opal glass, while aesthetically pleasing and effective at diffusing light, generally has lower heat resistance and is more prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Choosing borosilicate glass for light diffusers ensures enhanced longevity and performance in high-temperature applications.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Borosilicate glass offers a sleek, transparent aesthetic with high clarity and subtle color tones, enhancing modern and minimalist lighting designs. Opal glass, characterized by its milky white finish, provides a soft, diffused glow that eliminates glare and creates a warm, inviting ambiance ideal for contemporary and classic interiors. Designers often choose borosilicate glass for precision and durability in fixtures, while opal glass is favored for evenly diffused light and a visually soothing effect in pendant lamps, wall sconces, and chandeliers.
Cost and Availability Differences
Borosilicate glass typically costs more than opal glass due to its superior thermal resistance and durability, making it a premium choice for light diffusers. Opal glass is more readily available and cheaper, often used in mass-produced lighting fixtures where cost efficiency is a priority. Manufacturers prefer opal glass for its ease of production and cost-effectiveness, while borosilicate glass is chosen for specialized applications requiring higher performance despite higher expenses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it highly recyclable and reducing waste in light diffuser applications. Opal glass, while providing excellent diffusion properties, typically requires more energy-intensive manufacturing processes and may incorporate additives that challenge recycling efforts. Choosing borosilicate glass supports environmental sustainability through its longer lifecycle and reduced ecological footprint in production and disposal.
Choosing the Right Glass for Light Diffusers
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for light diffusers in environments with fluctuating temperatures or intense heat sources. Opal glass provides superior diffusion and soft, uniform light output due to its milky appearance, enhancing visual comfort in residential and commercial lighting applications. Selecting between borosilicate and opal glass depends on prioritizing heat resistance and strength versus optimal light diffusion and aesthetic softness.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Opal glass for Light diffuser
 azmater.com
azmater.com