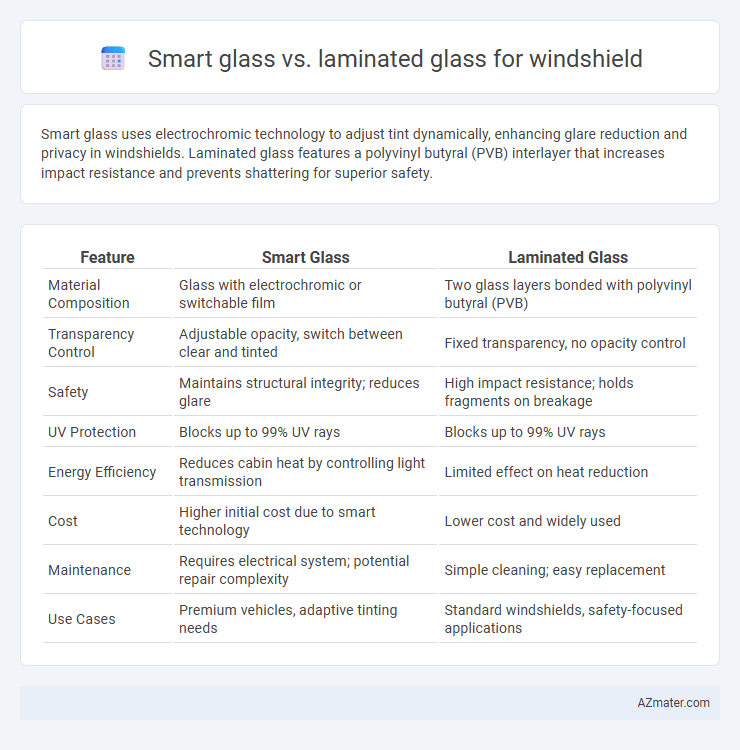
Smart glass uses electrochromic technology to adjust tint dynamically, enhancing glare reduction and privacy in windshields. Laminated glass features a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that increases impact resistance and prevents shattering for superior safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass with electrochromic or switchable film | Two glass layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) |
| Transparency Control | Adjustable opacity, switch between clear and tinted | Fixed transparency, no opacity control |
| Safety | Maintains structural integrity; reduces glare | High impact resistance; holds fragments on breakage |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% UV rays | Blocks up to 99% UV rays |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces cabin heat by controlling light transmission | Limited effect on heat reduction |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to smart technology | Lower cost and widely used |
| Maintenance | Requires electrical system; potential repair complexity | Simple cleaning; easy replacement |
| Use Cases | Premium vehicles, adaptive tinting needs | Standard windshields, safety-focused applications |
Introduction to Smart Glass and Laminated Glass
Smart glass for windshields uses electrochromic technology to dynamically control light transmission, enhancing driver comfort and reducing glare. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers with a durable interlayer, offering superior safety by preventing shattering upon impact. Both materials improve visibility but differ in functionality, with smart glass providing adaptive tinting and laminated glass focusing on structural integrity.
How Smart Glass Technology Works
Smart glass technology uses electrochromic or photochromic materials that change opacity or tint in response to electrical voltage or light exposure, allowing dynamic control of light and heat transmission through the windshield. This adaptive feature enhances driver comfort and visibility by reducing glare and heat buildup without sacrificing clarity, unlike laminated glass which primarily offers static protection with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer for impact resistance and shatter prevention. Smart glass integrates sensors and control systems to modulate transparency in real-time, providing energy efficiency and improved safety over traditional laminated windshields.
Composition of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for windshields consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together by an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances impact resistance and prevents shattering. This composition ensures safety by holding glass fragments in place during collisions, reducing injury risk. In contrast, smart glass integrates electronically controlled layers that adjust transparency, prioritizing visibility and comfort rather than structural safety.
Key Differences Between Smart and Laminated Windshields
Smart windshields incorporate electrochromic or suspended particle technology, allowing users to adjust transparency for glare reduction and privacy, while laminated windshields consist of two glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, enhancing impact resistance and preventing shattering. Smart glass excels in dynamic light control and energy efficiency, whereas laminated glass prioritizes safety by holding shards together during collisions. The choice depends on whether adaptive comfort or structural integrity is the primary concern in automotive applications.
Safety Features: Smart Glass vs Laminated Glass
Smart glass enhances windshield safety by dynamically tinting to reduce glare and UV exposure, improving driver visibility and minimizing eye strain. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides superior impact resistance and prevents shattering, ensuring passenger protection during collisions. Both technologies prioritize safety, but smart glass offers adaptive light control, while laminated glass excels in structural integrity and occupant retention.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection Comparison
Smart glass windshields offer superior energy efficiency by dynamically controlling light and heat transmission, significantly reducing cabin temperature and minimizing the need for air conditioning. Laminated glass provides effective UV protection through its polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays to protect occupants and interior materials. While laminated glass excels in consistent UV blocking, smart glass enhances overall energy savings by adjusting transparency based on sunlight intensity, contributing to improved fuel economy and passenger comfort.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Smart glass windshields typically cost significantly more upfront due to advanced technology and specialized installation requirements compared to laminated glass, which remains the economical standard. Installation of smart glass demands expert calibration and sometimes specialized equipment, increasing labor expenses, whereas laminated glass installation is straightforward and widely supported by most repair shops. Maintenance for smart glass can incur higher costs because of the complex internal systems prone to malfunction, while laminated glass maintenance generally involves simple crack repair or replacement, making it more cost-effective over time.
Durability and Longevity Considerations
Smart glass for windshields offers advanced durability through its dynamic tinting technology, which helps reduce UV damage and heat buildup, extending the lifespan of the glass. Laminated glass, composed of two or more layers of glass with a durable interlayer, excels in impact resistance and maintains structural integrity even when cracked, providing long-term safety and durability. Choosing between smart glass and laminated glass depends on balancing the benefits of innovative functionality against proven toughness and longevity in automotive applications.
Customization and Aesthetic Options
Smart glass offers advanced customization options for windshields, including adjustable tint levels and privacy settings that enhance driver comfort and vehicle aesthetics. Laminated glass provides traditional safety benefits with options for embedded UV protection and acoustic interlayers but is limited in aesthetic versatility compared to smart glass. The ability of smart glass to dynamically alter transparency and colors presents a modern, stylish alternative for personalized windshield design.
Choosing the Right Windshield: Factors to Consider
When choosing between smart glass and laminated glass for a windshield, prioritize factors such as visibility, durability, and safety standards. Laminated glass offers superior shatter resistance and UV protection, making it a reliable choice for impact safety and long-term use. Smart glass provides adjustable tint and glare reduction, enhancing comfort in varying light conditions, but may come at a higher cost and require specialized maintenance.
Infographic: Smart glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com