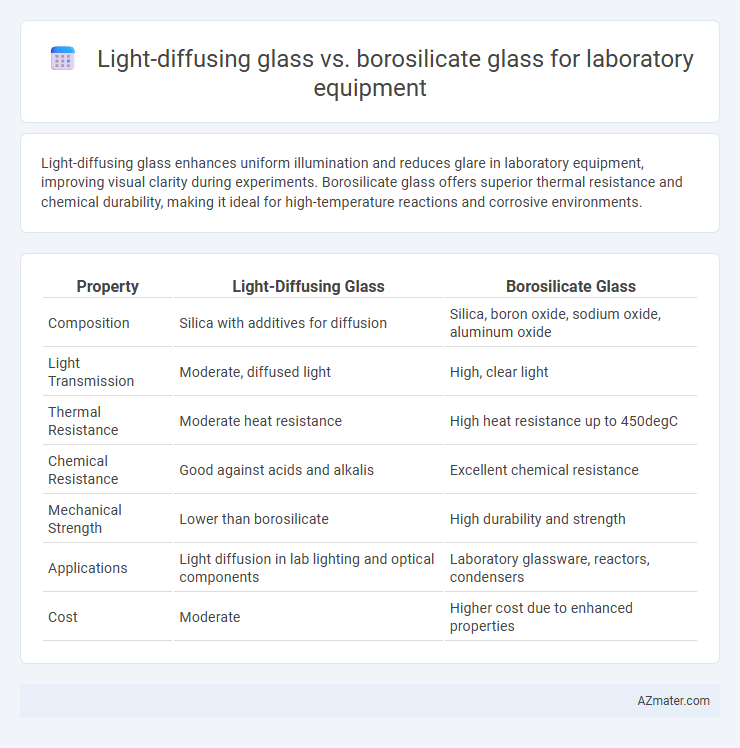
Light-diffusing glass enhances uniform illumination and reduces glare in laboratory equipment, improving visual clarity during experiments. Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for high-temperature reactions and corrosive environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Light-Diffusing Glass | Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica with additives for diffusion | Silica, boron oxide, sodium oxide, aluminum oxide |
| Light Transmission | Moderate, diffused light | High, clear light |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | High heat resistance up to 450degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower than borosilicate | High durability and strength |
| Applications | Light diffusion in lab lighting and optical components | Laboratory glassware, reactors, condensers |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Laboratory Glassware Materials
Laboratory glassware materials primarily include light-diffusing glass and borosilicate glass, each offering unique properties for scientific applications. Light-diffusing glass enhances visibility by scattering light, ideal for imaging and photometric measurements, while borosilicate glass is prized for its exceptional thermal resistance, chemical durability, and low thermal expansion, making it the standard choice for most laboratory apparatus. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the specific experimental requirements, balancing optical clarity and resistance to heat or chemical reactions.
What is Light-Diffusing Glass?
Light-diffusing glass is a specialized material designed to scatter light evenly, reducing glare and enhancing visibility in laboratory settings. Unlike borosilicate glass, which is prized for its thermal resistance and chemical durability, light-diffusing glass optimizes light dispersion to improve observation of reactions and measurements. This glass is particularly useful in instruments requiring uniform illumination, ensuring precise and consistent results in experimental procedures.
Understanding Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass is a highly durable and heat-resistant material commonly used in laboratory equipment due to its low thermal expansion and excellent chemical stability. Unlike light-diffusing glass, which is designed to scatter light and reduce glare, borosilicate glass maintains optical clarity while withstanding harsh temperature changes and chemical exposure. This makes borosilicate glass ideal for precise scientific applications such as beakers, test tubes, and reaction vessels where strength and transparency are critical.
Key Properties Comparison: Light-Diffusing vs Borosilicate Glass
Light-diffusing glass offers enhanced light scattering properties, improving uniform illumination in optical experiments, while borosilicate glass is prized for its exceptional thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for high-temperature lab processes. Borosilicate glass features low thermal expansion (approximately 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC), reducing the risk of cracking under thermal stress, whereas light-diffusing glass may have higher thermal expansion but excels in minimizing glare and enhancing light distribution. Both materials provide chemical resistance, but borosilicate glass is more suitable for corrosive chemicals and thermal cycling, whereas light-diffusing glass is specialized for optical clarity and light manipulation in laboratory settings.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior chemical resistance, with excellent tolerance to acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for laboratory equipment subjected to harsh chemical environments. Light-diffusing glass, while offering unique optical properties for reducing glare and enhancing light uniformity, typically lacks the robust durability and chemical stability of borosilicate glass. The thermal shock resistance of borosilicate glass also surpasses that of light-diffusing glass, ensuring greater longevity and reliability under rapid temperature changes common in lab settings.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Shock Resistance
Light-diffusing glass for laboratory equipment typically has moderate temperature tolerance but excels in evenly distributing heat, minimizing localized thermal stress. Borosilicate glass offers superior temperature tolerance up to approximately 450degC and outstanding thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for rapid temperature changes in lab experiments. These properties make borosilicate glass more reliable for applications involving extreme temperature fluctuations compared to light-diffusing glass.
Optical Performance and Light Transmission
Light-diffusing glass enhances uniform light distribution by scattering light waves, reducing glare and hot spots, which benefits imaging and spectroscopic applications in laboratories. Borosilicate glass offers superior optical clarity with high transparency and minimal light distortion, making it ideal for precise optical measurements and chemical resistance under thermal stress. While light-diffusing glass sacrifices some light transmission for diffusion effect, borosilicate glass maintains high transmittance, typically above 90%, ensuring accurate visual and photometric analysis.
Common Applications in Laboratory Equipment
Light-diffusing glass is commonly used in laboratory equipment requiring uniform illumination and minimized glare, such as light sources for microscopy and photometric devices. Borosilicate glass is favored for its excellent thermal resistance and chemical durability in applications like reaction vessels, condensers, and volumetric flasks. Both materials serve distinct roles, with light-diffusing glass enhancing optical performance and borosilicate glass providing reliable structural integrity under harsh laboratory conditions.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Light-diffusing glass generally incurs higher costs due to specialized manufacturing processes and limited suppliers, making it less readily available compared to borosilicate glass. Borosilicate glass dominates the laboratory equipment market with widespread availability and lower prices, driven by its robust chemical resistance and thermal stability. Laboratories often prefer borosilicate glass for cost efficiency and ease of procurement, especially in large-scale or routine applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Laboratory Needs
Light-diffusing glass offers enhanced visibility by scattering light, making it ideal for laboratory applications requiring uniform illumination and reducing glare on instruments. Borosilicate glass provides superior chemical resistance, thermal durability, and mechanical strength, making it the preferred choice for handling aggressive chemicals and high-temperature processes. Selecting the right glass depends on prioritizing optical clarity and lighting conditions with light-diffusing glass, or demanding robustness and chemical stability with borosilicate glass for laboratory equipment.
Infographic: Light-diffusing glass vs Borosilicate glass for Laboratory equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com