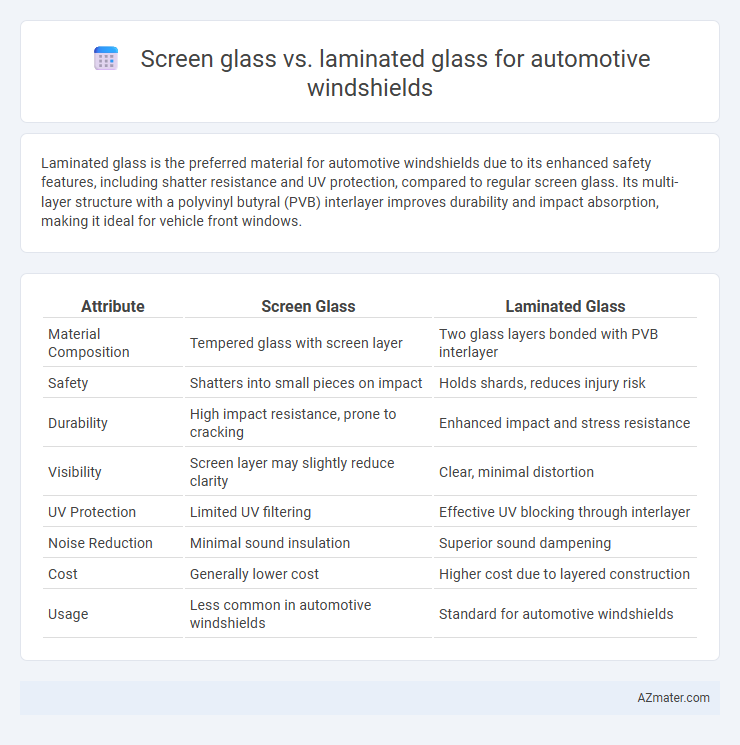
Laminated glass is the preferred material for automotive windshields due to its enhanced safety features, including shatter resistance and UV protection, compared to regular screen glass. Its multi-layer structure with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer improves durability and impact absorption, making it ideal for vehicle front windows.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Screen Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Tempered glass with screen layer | Two glass layers bonded with PVB interlayer |
| Safety | Shatters into small pieces on impact | Holds shards, reduces injury risk |
| Durability | High impact resistance, prone to cracking | Enhanced impact and stress resistance |
| Visibility | Screen layer may slightly reduce clarity | Clear, minimal distortion |
| UV Protection | Limited UV filtering | Effective UV blocking through interlayer |
| Noise Reduction | Minimal sound insulation | Superior sound dampening |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to layered construction |
| Usage | Less common in automotive windshields | Standard for automotive windshields |
Introduction to Automotive Windshields
Automotive windshields play a crucial role in vehicle safety, providing clear visibility while protecting occupants from debris and impact. Screen glass, often used in display and infotainment systems, differs significantly from laminated glass, which consists of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer to enhance strength and reduce shattering risks during collisions. Laminated glass is the industry standard for windshields due to its ability to absorb impact, maintain integrity upon breaking, and comply with safety regulations like FMVSS 205 in the automotive sector.
What is Screen Glass?
Screen glass in automotive windshields refers to a specialized tempered glass layer embedded with a conductive or protective mesh designed to support heads-up displays (HUD) and enhance optical clarity. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of multiple layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) for safety and impact resistance, screen glass incorporates electronic components for interactive functionalities. This integration allows screen glass windshields to offer advanced display features while maintaining structural integrity and visibility for drivers.
Understanding Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for automotive windshields consists of two glass layers bonded by a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering into sharp pieces. This structure improves safety by maintaining windshield integrity during collisions and reduces the risk of occupant ejection. Compared to standard screen glass, laminated glass offers superior noise reduction, UV protection, and durability against environmental stressors, making it the preferred choice for automotive windshields.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Screen glass in automotive windshields is typically produced through a precise tempering process that enhances strength by heating and rapidly cooling the glass, resulting in safety features like controlled shattering. Laminated glass manufacturing involves sandwiching a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) interlayer between two glass sheets, then undergoing heat and pressure lamination to create impact resistance and prevent glass from dispersing upon breakage. The key difference in manufacturing lies in tempering for screen glass, which enhances durability and heat resistance, versus lamination for laminated glass, providing superior safety and acoustic insulation in automotive applications.
Safety Features and Impact Resistance
Screen glass used in automotive windshields offers basic protection with moderate impact resistance but tends to shatter into sharp fragments upon collision, posing safety risks. Laminated glass consists of two layers of glass bonded by a durable polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, which maintains windshield integrity by preventing shattering and enhancing occupant protection during accidents. The laminated glass's superior impact resistance and ability to absorb energy make it the preferred choice for modern automotive safety standards.
Durability and Longevity
Screen glass for automotive windshields offers high impact resistance but typically lacks the structural integrity and longevity found in laminated glass. Laminated glass consists of two layers of glass bonded with an inner polyvinyl butyral (PVB) layer that enhances durability by preventing shattering and maintaining windshield integrity upon impact. This construction significantly extends the lifespan of the windshield by reducing the risk of cracks and damage from environmental stressors, making laminated glass the preferred choice for long-term automotive safety and performance.
Cost Differences and Value
Screen glass for automotive windshields generally costs less upfront compared to laminated glass, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. Laminated glass offers superior safety benefits by preventing shattering upon impact, which can reduce long-term repair costs and enhance occupant protection. Despite higher initial expenses, laminated glass provides better value through durability, noise reduction, and UV protection, contributing to overall vehicle longevity and comfort.
Visibility and Optical Clarity
Screen glass in automotive windshields offers moderate visibility with basic optical clarity suitable for standard driving conditions, but it may suffer from minor distortions due to its manufacturing process. Laminated glass provides superior optical clarity and enhanced visibility by combining multiple layers, including a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that reduces glare and minimizes distortion. The laminated structure also improves safety by preventing glass shards from scattering during impact while maintaining clear, unobstructed vision in various lighting conditions.
Repairability and Replacement
Screen glass for automotive windshields offers easier and more cost-effective repairability due to its simpler laminated structure, allowing minor chips and cracks to be fixed without full replacement. Laminated glass, comprised of multiple layers bonded by an interlayer, boasts superior strength and safety but often requires complete windshield replacement when damaged, increasing repair costs and downtime. Choosing between screen glass and laminated glass hinges on balancing quick, affordable repairs against enhanced durability and safety standards.
Which is Best for Automotive Windshields?
Laminated glass is the best choice for automotive windshields due to its superior safety features, consisting of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer that prevents shattering upon impact. Screen glass, often used in certain display applications, lacks the structural integrity and impact resistance required for automotive safety standards. Laminated windshields offer enhanced protection against accidents, UV rays, and noise reduction, making them essential for vehicle safety and performance.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Laminated glass for Automotive windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com