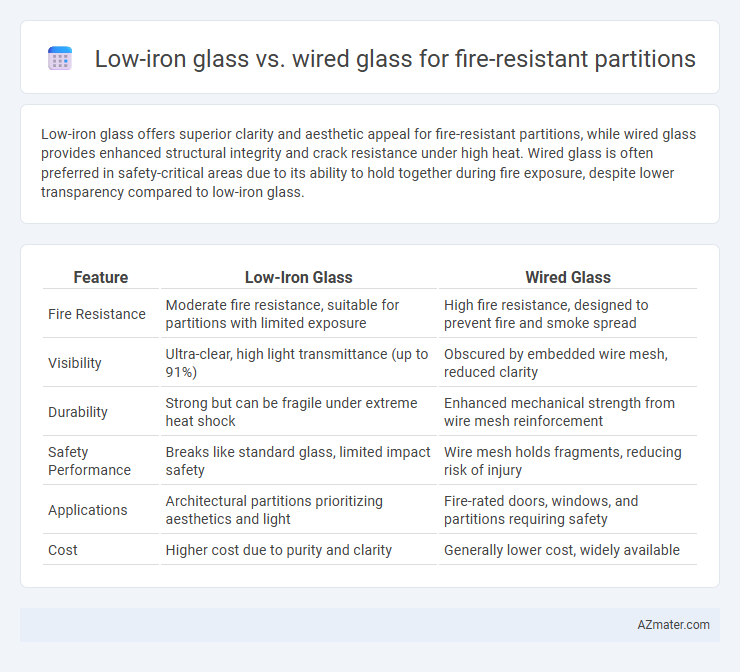
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and aesthetic appeal for fire-resistant partitions, while wired glass provides enhanced structural integrity and crack resistance under high heat. Wired glass is often preferred in safety-critical areas due to its ability to hold together during fire exposure, despite lower transparency compared to low-iron glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Low-Iron Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Moderate fire resistance, suitable for partitions with limited exposure | High fire resistance, designed to prevent fire and smoke spread |
| Visibility | Ultra-clear, high light transmittance (up to 91%) | Obscured by embedded wire mesh, reduced clarity |
| Durability | Strong but can be fragile under extreme heat shock | Enhanced mechanical strength from wire mesh reinforcement |
| Safety Performance | Breaks like standard glass, limited impact safety | Wire mesh holds fragments, reducing risk of injury |
| Applications | Architectural partitions prioritizing aesthetics and light | Fire-rated doors, windows, and partitions requiring safety |
| Cost | Higher cost due to purity and clarity | Generally lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Partitions
Fire-resistant partitions play a critical role in enhancing building safety by containing fire and smoke, limiting structural damage, and providing safe evacuation routes. Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and aesthetic appeal while maintaining fire resistance, ideal for visible partition applications in commercial spaces. Wired glass, characterized by its embedded metal mesh, provides robust fire protection and impact resistance, making it suitable for high-risk areas requiring enhanced structural integrity.
What is Low-Iron Glass?
Low-iron glass is a type of fire-resistant partition glass characterized by its high clarity and minimal green tint, achieved by reducing iron content during manufacturing. It provides superior optical quality compared to wired glass, enhancing visibility and aesthetic appeal in fire-rated applications. Low-iron glass also meets stringent fire safety standards while maintaining structural integrity under high temperatures.
Understanding Wired Glass
Wired glass is a fire-resistant partition material embedded with a mesh of steel wires that holds glass shards together during high heat, preventing breakage and maintaining barrier integrity. Unlike low-iron glass, wired glass prioritizes fire containment with enhanced structural stability rather than clarity, as its wired mesh reduces transparency. This makes wired glass ideal for fire-rated partitions where safety and code compliance are critical, despite sacrificing some aesthetic appeal compared to low-iron glass.
Fire Resistance Properties: Low-Iron vs Wired Glass
Low-iron glass offers enhanced clarity and aesthetic appeal but generally has lower fire resistance compared to wired glass, which is embedded with a metal mesh to maintain integrity under high heat and prevent shattering. Wired glass can withstand temperatures up to 1,200degF (649degC) and is often rated for up to 90 minutes of fire protection, making it suitable for fire-resistant partitions requiring strict fire ratings. In contrast, low-iron glass typically lacks the embedded reinforcement necessary for prolonged fire exposure, limiting its effectiveness in fire-resistive applications despite superior visibility.
Strength and Safety Comparison
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and aesthetic appeal but generally has lower impact resistance compared to wired glass, which incorporates embedded metal mesh for enhanced shatter resistance and fire containment. Wired glass maintains structural integrity under fire exposure by preventing glass breakage and limiting the spread of flames and smoke, providing higher safety in fire-resistant partitions. While low-iron glass excels in visibility and design flexibility, wired glass prioritizes strength and safety, making it the preferred choice for critical fire-resistant applications.
Optical Clarity and Aesthetics
Low-iron glass offers superior optical clarity with enhanced light transmission and minimal green tint, making it an excellent choice for fire-resistant partitions where visual transparency and aesthetics are paramount. Wired glass, while providing structural integrity and fire resistance, typically exhibits reduced clarity due to its embedded wire mesh, resulting in a more obscured view. For applications prioritizing clean, unobstructed sightlines and contemporary design, low-iron glass outperforms wired glass in both transparency and aesthetic appeal.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for fire-resistant partitions in high-end commercial spaces, showrooms, and architectural designs where visual transparency is critical. Wired glass provides enhanced safety and structural integrity, commonly used in industrial buildings, schools, and healthcare facilities where fire resistance and compliance with safety regulations are prioritized. Both materials meet fire rating standards, but selection depends on balancing aesthetic requirements with functional safety needs.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Low-iron glass typically costs more than wired glass due to its higher clarity and advanced manufacturing processes, impacting budget decisions for fire-resistant partitions. Installation of low-iron glass requires careful handling and specialized equipment to preserve its aesthetic qualities, resulting in potentially higher labor costs compared to the more robust, traditional wired glass. Wired glass offers easier and quicker installation with lower upfront costs but may involve trade-offs in visual appeal and modern building code requirements.
Maintenance and Durability
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and requires minimal maintenance due to its resistance to discoloration and corrosion, ensuring long-lasting aesthetics in fire-resistant partitions. Wired glass, while highly durable and shatter-resistant due to its embedded wire mesh, demands regular inspections to check for potential rust or wire mesh deterioration that can compromise its fire-resistance. Both materials provide strong fire protection, but low-iron glass excels in maintenance ease and long-term visual performance, whereas wired glass prioritizes structural integrity and impact resistance.
Choosing the Right Glass for Fire-Rated Partitions
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and enhances visibility in fire-rated partitions, making it ideal for applications where aesthetics and natural light are priorities. Wired glass provides reliable fire resistance by embedding a wire mesh that helps prevent glass shattering during a fire, ensuring safety in high-risk areas. Selecting the right glass for fire-rated partitions depends on balancing performance requirements, safety standards like ASTM E119, and design preferences.
Infographic: Low-iron glass vs Wired glass for Fire-resistant partition
 azmater.com
azmater.com