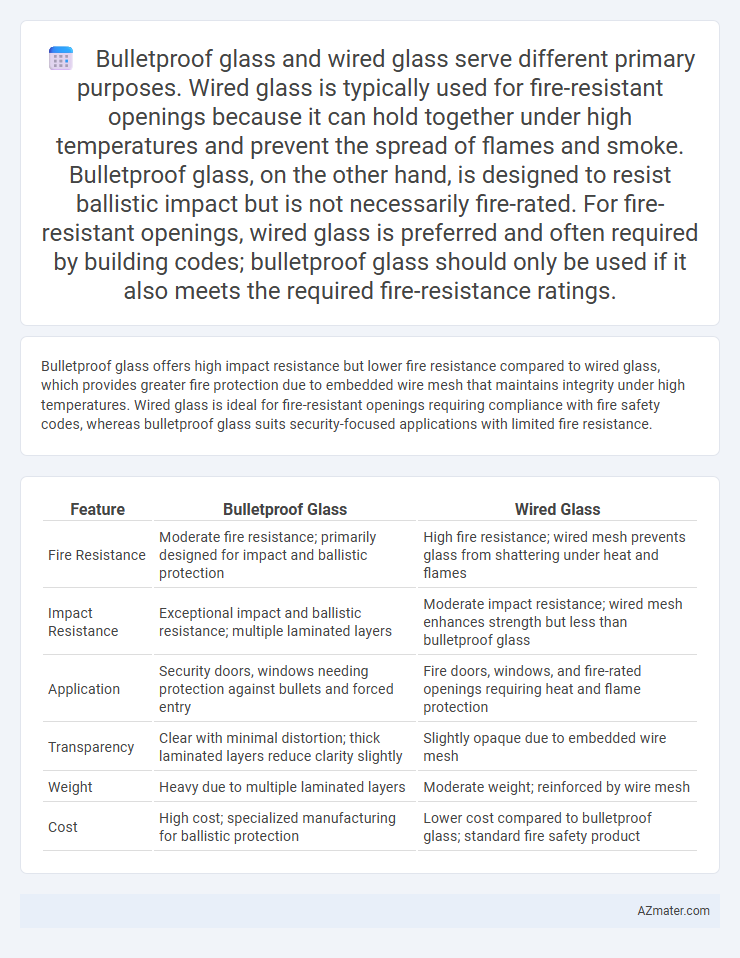
Bulletproof glass offers high impact resistance but lower fire resistance compared to wired glass, which provides greater fire protection due to embedded wire mesh that maintains integrity under high temperatures. Wired glass is ideal for fire-resistant openings requiring compliance with fire safety codes, whereas bulletproof glass suits security-focused applications with limited fire resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bulletproof Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Moderate fire resistance; primarily designed for impact and ballistic protection | High fire resistance; wired mesh prevents glass from shattering under heat and flames |
| Impact Resistance | Exceptional impact and ballistic resistance; multiple laminated layers | Moderate impact resistance; wired mesh enhances strength but less than bulletproof glass |
| Application | Security doors, windows needing protection against bullets and forced entry | Fire doors, windows, and fire-rated openings requiring heat and flame protection |
| Transparency | Clear with minimal distortion; thick laminated layers reduce clarity slightly | Slightly opaque due to embedded wire mesh |
| Weight | Heavy due to multiple laminated layers | Moderate weight; reinforced by wire mesh |
| Cost | High cost; specialized manufacturing for ballistic protection | Lower cost compared to bulletproof glass; standard fire safety product |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Glazing
Fire-resistant glazing, including bulletproof glass and wired glass, plays a critical role in enhancing building safety by preventing the spread of fire and smoke through openings. Bulletproof glass, designed for high impact resistance, often incorporates multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate to maintain its integrity under extreme conditions. Wired glass contains embedded wire mesh that helps hold the glass together when exposed to heat, providing fire resistance but typically less impact resistance compared to bulletproof versions.
Understanding Bulletproof Glass
Bulletproof glass for fire-resistant openings is designed with multiple laminated layers of polycarbonate and glass, providing high impact resistance and thermal protection during fires. It offers superior clarity and durability compared to wired glass, which contains embedded metal wire mesh but tends to be less resistant to heat and prone to shattering under extreme temperature changes. Understanding the composition and fire-rated certification of bulletproof glass is crucial for selecting optimal safety and performance in hazardous environments.
What is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of fire-resistant glass that contains a mesh of metal wire embedded within the glass pane, providing additional strength and preventing the glass from shattering during a fire. This wire mesh maintains the integrity of fire-rated doors and windows by resisting heat and preventing the spread of flames and smoke for a specified duration. Unlike bulletproof glass, which is primarily designed to absorb impact and resist ballistic forces, wired glass specifically enhances fire safety and is commonly used in commercial buildings for fire-rated openings.
Fire Resistance Ratings: Bulletproof vs Wired Glass
Bulletproof glass generally offers lower fire resistance ratings compared to wired glass, which is specifically designed to maintain integrity and prevent fire spread during exposure to high temperatures. Wired glass typically meets fire-resistance standards up to 45 minutes to 3 hours, while bulletproof glass usually focuses on ballistic protection and may require additional treatments to enhance fire resistance. Fire-rated wired glass provides superior performance in safeguarding openings within fire-rated assemblies, making it the preferred choice for fire-resistant doors and windows.
Impact and Security Performance Comparison
Bulletproof glass offers superior impact resistance with multiple laminated layers designed to absorb and dissipate energy from ballistic threats, making it highly effective for security-critical fire-resistant openings. Wired glass, embedded with metal mesh to prevent shattering during fires, provides moderate impact resistance but is more prone to breaking under severe physical force, impacting its security performance. For fire-resistant openings requiring robust security and impact durability, bulletproof glass outperforms wired glass by maintaining integrity against both fire exposure and aggressive attacks.
Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency
Bulletproof glass provides superior thermal insulation due to its laminated multiple layers, reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in fire-resistant openings. Wired glass, while offering basic fire resistance, has higher thermal conductivity, which can lead to greater heat loss and lower overall energy performance. Choosing bulletproof glass improves building thermal performance by maintaining consistent indoor temperatures and reducing HVAC energy consumption.
Safety and Breakage Behavior
Bulletproof glass offers superior impact resistance and maintains structural integrity under extreme force, minimizing the risk of breakage during fire emergencies and enhancing occupant safety in fire-resistant openings. Wired glass, embedded with a metal mesh, prevents glass shattering and maintains a barrier against fire and smoke but is more prone to spalling and cracking under impact or thermal stress. The choice between bulletproof and wired glass for fire-resistant openings significantly influences safety outcomes, with bulletproof glass providing both durability and fire protection, while wired glass primarily focuses on fire containment with moderate impact resistance.
Code Compliance and Certification Requirements
Bulletproof glass and wired glass differ significantly in meeting fire-resistant opening code compliance and certification requirements. Wired glass often meets stringent fire-resistance standards such as NFPA 80 and UL 9 due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread, while bulletproof glass requires specific fire-rated certifications like UL 752 combined with UL 10C for fire door assemblies. Ensuring compliance involves verifying that the fire-resistant glazing holds appropriate listing and labeling for fire ratings, smoke control, and impact resistance mandated by local building codes and the International Fire Code (IFC).
Best Applications for Each Glass Type
Bulletproof glass excels in high-security environments such as banks, government buildings, and military facilities where protection from ballistic threats is paramount, while wired glass is best suited for fire-resistant openings in commercial buildings, schools, and hospitals due to its enhanced fire containment and heat resistance. Bulletproof glass offers superior impact resistance but may lack the same fire endurance as wired glass, which contains embedded wire mesh to prevent glass fragmentation during fires. Choosing the appropriate glass type depends on balancing security needs against fire safety requirements, ensuring compliance with building codes and safety standards.
Choosing the Right Glass for Fire-Resistant Openings
When selecting glass for fire-resistant openings, bulletproof glass offers high security with moderate fire resistance, suitable for areas requiring impact protection and limited flame exposure. Wired glass provides superior fire performance by maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat, preventing fire and smoke spread, and is ideal for compliance with stringent fire safety codes. Understanding the specific fire rating requirements, building codes, and safety priorities is essential to choosing between bulletproof and wired glass for effective fire-resistant glazing solutions.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs Wired glass for Fire-resistant opening
 azmater.com
azmater.com