Bulletproof glass offers high impact resistance and security but has lower thermal insulation properties compared to glass fiber, which excels in thermal resistance and energy efficiency due to its fibrous structure. Glass fiber's lightweight and heat-retentive characteristics make it a superior insulation material in construction and industrial applications.
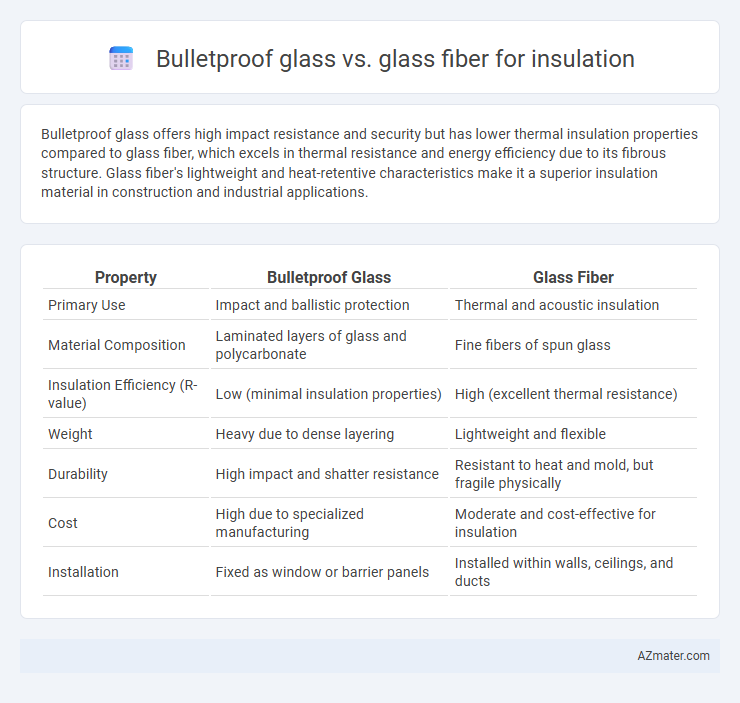
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bulletproof Glass | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Impact and ballistic protection | Thermal and acoustic insulation |
| Material Composition | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate | Fine fibers of spun glass |
| Insulation Efficiency (R-value) | Low (minimal insulation properties) | High (excellent thermal resistance) |
| Weight | Heavy due to dense layering | Lightweight and flexible |
| Durability | High impact and shatter resistance | Resistant to heat and mold, but fragile physically |
| Cost | High due to specialized manufacturing | Moderate and cost-effective for insulation |
| Installation | Fixed as window or barrier panels | Installed within walls, ceilings, and ducts |
Introduction to Bulletproof Glass and Glass Fiber
Bulletproof glass is a laminated material composed of multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate designed to resist high-impact forces, commonly used in security applications. Glass fiber consists of fine strands of glass woven into mats or fabrics, providing thermal insulation and reinforcement in composite materials. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with bulletproof glass focusing on protection and glass fiber prioritizing insulation and structural support.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Bulletproof glass, also known as laminated or bullet-resistant glass, is composed of multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate or PVB (polyvinyl butyral) interlayers, bonded under heat and pressure to absorb and disperse impact energy. Glass fiber insulation consists of fine strands of silica-based glass spun into fibers and formed into mats or batt materials, produced through a melting and fiberizing process followed by binding with a resin or binder. The manufacturing of bulletproof glass emphasizes lamination for strength and clarity, whereas glass fiber insulation focuses on thermal resistance and lightweight, porous structure for effective heat retention.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Bulletproof glass offers moderate thermal insulation due to its layered construction combining glass and polycarbonate, which reduces heat transfer more effectively than standard glass but less than specialized insulating materials. Glass fiber insulation exhibits superior thermal performance with low thermal conductivity, trapping air within its fibrous structure to minimize heat flow and maintain consistent indoor temperatures. Comparing the two, glass fiber provides significantly better thermal insulation properties, making it the preferred choice for energy-efficient building applications despite bulletproof glass's added security benefits.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Bulletproof glass offers superior mechanical strength due to its multi-layered composition of laminated glass and polycarbonate, providing exceptional impact resistance and durability against physical forces. Glass fiber insulation, while effective for thermal and acoustic purposes, lacks the mechanical rigidity and toughness of bulletproof glass, making it more susceptible to damage under stress or impact. The durability of bulletproof glass under extreme conditions far exceeds that of glass fiber, which primarily serves as a lightweight, flexible insulating material rather than a protective barrier.
Applications in Construction and Security
Bulletproof glass provides high-impact resistance and ballistic protection, making it ideal for security-sensitive construction applications such as banks, government buildings, and secure entry points. Glass fiber insulation excels in thermal and acoustic insulation, enhancing energy efficiency and soundproofing in residential and commercial buildings. Combining bulletproof glass with glass fiber insulation supports structures requiring both advanced security measures and superior environmental comfort.
Cost Analysis: Bulletproof Glass vs Glass Fiber
Bulletproof glass typically incurs higher initial costs compared to glass fiber insulation, driven by advanced manufacturing processes and safety features. Glass fiber insulation offers a more budget-friendly option with lower material and installation expenses while providing effective thermal resistance. Long-term savings may favor glass fiber due to its energy efficiency and ease of maintenance.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Bulletproof glass offers superior energy efficiency due to its multi-layered construction that provides enhanced thermal insulation and reduces heat transfer, lowering heating and cooling costs. Glass fiber insulation excels in minimizing environmental impact as it is made from recycled materials and provides effective thermal resistance, decreasing overall energy consumption in buildings. Choosing between the two depends on specific insulation needs, with bulletproof glass offering security alongside energy savings, while glass fiber remains a cost-effective and sustainable thermal barrier option.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Bulletproof glass requires professional installation due to its heavy weight and precision fitting needs, often involving specialized framing and tools to ensure secure and effective protection. Maintenance for bulletproof glass involves regular inspections for cracks or delamination, with cleaning using non-abrasive materials to preserve its clarity and structural integrity. Glass fiber insulation generally offers easier installation, as it can be cut and fitted into various cavity sizes without special tools, but it requires protective gear during handling to avoid irritation, and periodic checks to ensure it has not settled or degraded over time.
Fire Resistance and Safety Standards
Bulletproof glass offers superior fire resistance compared to glass fiber insulation, meeting rigorous safety standards such as ASTM E119 and UL 752 for fire and ballistic protection. Glass fiber insulation, while effective for thermal regulation, typically adheres to ASTM E84 standards but provides limited fire resistance under extreme heat scenarios. Choosing bulletproof glass enhances overall safety by combining impact resistance with certified fire protection, crucial for high-risk environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Insulation
When choosing insulation materials, bulletproof glass offers exceptional durability and impact resistance but is less effective for thermal insulation compared to glass fiber, which excels in thermal resistance and sound absorption due to its fibrous structure. Glass fiber insulation is lightweight, cost-effective, and provides superior energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer in buildings. Consider the specific insulation needs--security versus thermal performance--when selecting between bulletproof glass and glass fiber to optimize energy savings and safety.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs Glass fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com