Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and high optical clarity, making it ideal for advanced display technologies. Low-iron glass enhances light transmission by reducing greenish tints, improving color accuracy and brightness in display panels.
Table of Comparison
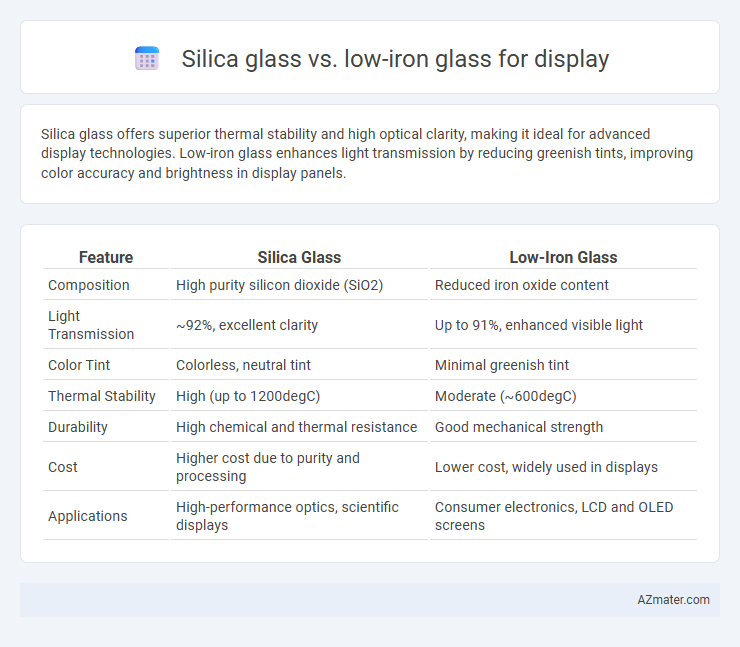
| Feature | Silica Glass | Low-Iron Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Reduced iron oxide content |
| Light Transmission | ~92%, excellent clarity | Up to 91%, enhanced visible light |
| Color Tint | Colorless, neutral tint | Minimal greenish tint |
| Thermal Stability | High (up to 1200degC) | Moderate (~600degC) |
| Durability | High chemical and thermal resistance | Good mechanical strength |
| Cost | Higher cost due to purity and processing | Lower cost, widely used in displays |
| Applications | High-performance optics, scientific displays | Consumer electronics, LCD and OLED screens |
Introduction to Silica Glass and Low-Iron Glass
Silica glass, primarily composed of silicon dioxide, offers superior thermal stability, high purity, and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for advanced display applications requiring precise light transmission and minimal distortion. Low-iron glass contains reduced iron oxide levels, enhancing transparency and reducing greenish tint typically found in standard glass, thus improving color accuracy and brightness in display panels. Both materials are critical in display technology, with silica glass emphasizing durability and stability, while low-iron glass prioritizes enhanced visual performance.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Silica glass is primarily composed of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) and is manufactured through high-temperature melting processes, resulting in exceptional thermal stability and optical clarity. Low-iron glass contains a small percentage of iron oxide impurities, which are reduced during manufacturing to improve transparency and reduce the green tint typically associated with standard glass. The refined composition and advanced manufacturing techniques of low-iron glass make it more suitable for display applications demanding high color fidelity and brightness.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Silica glass exhibits exceptional optical clarity due to its high purity and minimal impurities, resulting in superior light transmission and reduced distortion for display applications. Low-iron glass enhances light transmission by significantly reducing the greenish tint found in standard glass, providing a clearer and brighter visual experience. Both materials optimize display performance, but silica glass generally offers higher optical precision essential for high-end, color-critical devices.
Color and Visual Appearance
Silica glass offers superior color neutrality and minimal spectral distortion, making it ideal for high-precision display applications requiring true-to-life visual accuracy. Low-iron glass enhances clarity by reducing the greenish tint found in standard glass, resulting in brighter and more vibrant color reproduction for screens. Both materials contribute to improved display quality, but silica glass provides unmatched purity in color rendering and visual consistency.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Silica glass offers superior durability and enhanced scratch resistance due to its high purity and robust molecular structure, making it ideal for demanding display applications. Low-iron glass, while providing excellent clarity and reduced green tint, typically exhibits lower hardness and is more prone to surface scratches under heavy use. For displays requiring long-term durability and resistance to abrasion, silica glass remains the preferred material.
Applications in Display Technologies
Silica glass offers exceptional thermal stability and ultra-low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-precision display technologies such as OLED and microLED panels where dimensional stability is critical. Low-iron glass provides enhanced optical clarity and superior light transmission, optimizing brightness and color accuracy in LCD screens and touch displays. Both materials support advanced display applications but are selected based on specific performance requirements like durability, optical quality, and environmental resistance.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Silica glass typically incurs higher production costs due to its purity and specialized manufacturing processes, resulting in premium pricing compared to low-iron glass, which benefits from more widespread and cost-effective production methods. Low-iron glass is more readily available globally, supported by extensive supply chains catering to consumer electronics and display markets, whereas silica glass availability is limited to niche applications requiring superior optical clarity. Cost-efficiency and supply scalability make low-iron glass the preferred choice for mainstream display manufacturing despite silica glass offering higher performance in specific optical conditions.
Environmental Impact
Silica glass offers superior environmental benefits due to its high durability and recyclability, resulting in reduced resource extraction and lower carbon emissions throughout its lifecycle. Low-iron glass, while providing enhanced clarity and light transmission for displays, typically requires more energy-intensive refining processes that contribute to a higher overall environmental footprint. Choosing silica glass for display applications supports sustainability by minimizing energy consumption and promoting eco-friendly recycling practices.
Suitability for High-Resolution Displays
Silica glass offers exceptional optical clarity and minimal light distortion, making it highly suitable for high-resolution displays requiring precise color accuracy and sharpness. Low-iron glass reduces greenish tint significantly compared to standard glass, enhancing brightness and contrast in display panels, which is critical for vibrant high-definition images. Both materials support high-resolution displays, but silica glass typically provides superior transmittance and stability under varied temperatures, optimizing long-term performance.
Choosing the Right Glass for Display Needs
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and high optical clarity, making it ideal for demanding display applications requiring precise color accuracy and durability. Low-iron glass enhances light transmission and reduces greenish tint, ensuring brighter and more vibrant displays suited for high-end screens and touch panels. Selecting the right glass depends on prioritizing factors like transmission efficiency, color fidelity, thermal resistance, and budget constraints for optimal display performance.
Infographic: Silica glass vs Low-iron glass for Display
 azmater.com
azmater.com