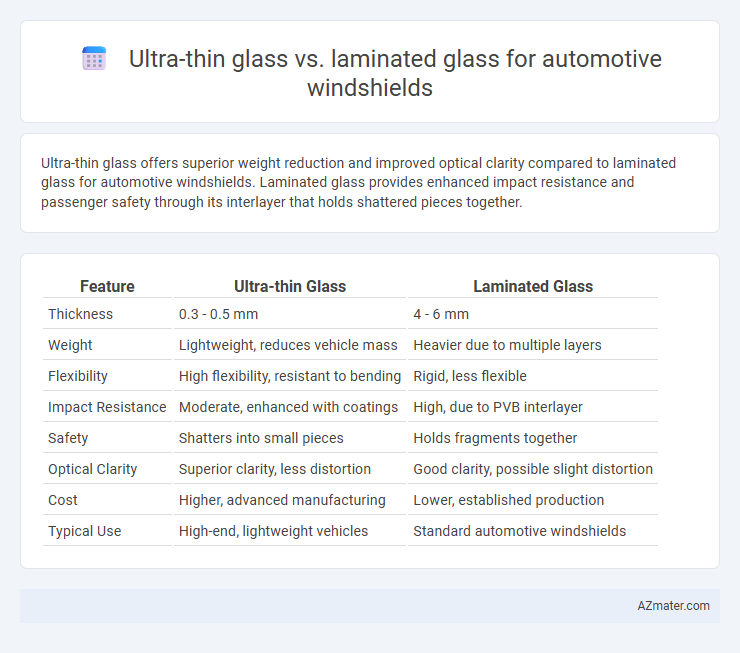
Ultra-thin glass offers superior weight reduction and improved optical clarity compared to laminated glass for automotive windshields. Laminated glass provides enhanced impact resistance and passenger safety through its interlayer that holds shattered pieces together.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-thin Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.3 - 0.5 mm | 4 - 6 mm |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces vehicle mass | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, resistant to bending | Rigid, less flexible |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, enhanced with coatings | High, due to PVB interlayer |
| Safety | Shatters into small pieces | Holds fragments together |
| Optical Clarity | Superior clarity, less distortion | Good clarity, possible slight distortion |
| Cost | Higher, advanced manufacturing | Lower, established production |
| Typical Use | High-end, lightweight vehicles | Standard automotive windshields |
Introduction: Ultra-thin Glass vs Laminated Glass
Ultra-thin glass offers significantly reduced weight and improved optical clarity compared to traditional laminated glass used in automotive windshields, enhancing fuel efficiency and driver visibility. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides superior impact resistance and safety by preventing shattering upon collision. Automakers are increasingly considering ultra-thin glass for weight reduction while maintaining the laminated structure's essential protective properties.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Ultra-thin glass for automotive windshields is composed primarily of specialized aluminosilicate glass with thicknesses often below 0.5 mm, produced through advanced float or fusion forming processes that enable high strength and flexibility. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) interlayers, manufactured through heat and pressure to enhance impact resistance and safety. The ultra-thin glass manufacturing emphasizes reducing weight and improving optical clarity, while laminated glass focuses on layered safety and structural integrity in automotive applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Ultra-thin glass offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to laminated glass, enhancing vehicle safety without adding significant mass. Laminated glass provides exceptional durability through its layered structure, which resists shattering and maintains integrity upon impact. In automotive windshield applications, ultra-thin glass excels in flexibility and impact resistance, while laminated glass offers proven long-term durability and crack containment.
Safety Performance and Impact Resistance
Ultra-thin glass for automotive windshields offers enhanced impact resistance due to its flexibility and ability to absorb energy, reducing the risk of shattering upon collision. In contrast, laminated glass incorporates a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that holds glass fragments together, significantly improving safety performance by preventing glass shards from causing injury. While laminated glass excels in crack resistance and maintaining windshield integrity during impacts, ultra-thin glass provides a lightweight alternative with promising advancements in durability and impact absorption for automotive safety.
Weight Reduction and Fuel Efficiency
Ultra-thin glass in automotive windshields significantly reduces weight compared to traditional laminated glass, contributing to overall vehicle mass reduction. This lighter glass enhances fuel efficiency by decreasing the energy required for acceleration and improving handling dynamics. Automakers increasingly adopt ultra-thin glass to meet stringent emission standards while maintaining safety and durability.
Optical Clarity and Driver Visibility
Ultra-thin glass for automotive windshields offers superior optical clarity due to its reduced thickness, minimizing light distortion and enhancing driver visibility in various lighting conditions. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded with a PVB interlayer, provides improved safety but can introduce slight optical distortions caused by the interlayer, potentially affecting visual acuity. Advanced ultra-thin glass technologies outperform traditional laminated glass by delivering clearer, sharper views that contribute to safer driving experiences.
Acoustic Insulation and Noise Reduction
Ultra-thin glass for automotive windshields offers superior acoustic insulation by effectively dampening high-frequency noise due to its reduced thickness and enhanced material properties. Laminated glass excels in noise reduction by incorporating a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that absorbs and blocks a wide range of sound frequencies, particularly low-frequency road and engine noise. Combining ultra-thin glass with laminated technology in windshields results in optimal noise reduction, improving cabin comfort and minimizing acoustic disturbances.
Cost Implications and Availability
Ultra-thin glass offers a cost advantage due to reduced raw material usage and lower weight, which can improve fuel efficiency in automotive applications, but its production requires advanced manufacturing techniques that may limit widespread availability. Laminated glass, widely available and standard in automotive windshields, incurs higher costs due to multi-layer construction involving PVB interlayers for enhanced safety and durability. Cost implications favor ultra-thin glass for long-term economic benefits in lightweight vehicle design, while laminated glass remains the prevalent choice given established supply chains and regulatory approvals.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Ultra-thin glass for automotive windshields reduces overall vehicle weight, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and lower CO2 emissions during the vehicle's lifecycle. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers including polyvinyl butyral (PVB), poses challenges for recycling due to the difficulty in separating materials, leading to higher environmental impact in waste management. The advanced manufacturing process of ultra-thin glass offers enhanced sustainability by enabling better recyclability and reducing raw material consumption compared to traditional laminated glass.
Future Trends in Automotive Windshield Technology
Ultra-thin glass offers significant weight reduction and enhanced flexibility compared to laminated glass, enabling improved fuel efficiency and design innovation in automotive windshields. Advancements in coating technologies integrated with ultra-thin glass improve UV protection and glare reduction, addressing increasing safety and comfort demands. Future trends emphasize embedding smart sensors and heads-up display capabilities, positioning ultra-thin glass as a key material for next-generation connected and autonomous vehicles.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Laminated glass for Automotive windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com