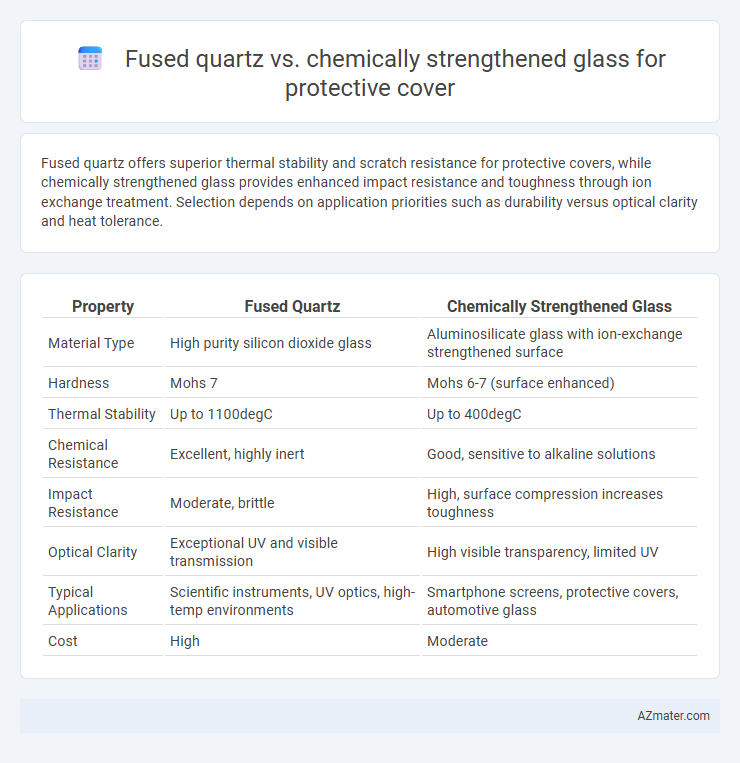
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and scratch resistance for protective covers, while chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced impact resistance and toughness through ion exchange treatment. Selection depends on application priorities such as durability versus optical clarity and heat tolerance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | Chemically Strengthened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High purity silicon dioxide glass | Aluminosilicate glass with ion-exchange strengthened surface |
| Hardness | Mohs 7 | Mohs 6-7 (surface enhanced) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1100degC | Up to 400degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, highly inert | Good, sensitive to alkaline solutions |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, brittle | High, surface compression increases toughness |
| Optical Clarity | Exceptional UV and visible transmission | High visible transparency, limited UV |
| Typical Applications | Scientific instruments, UV optics, high-temp environments | Smartphone screens, protective covers, automotive glass |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
Introduction to Fused Quartz and Chemically Strengthened Glass
Fused quartz, made from pure silica, offers exceptional thermal stability and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for protective covers requiring durability under extreme conditions. Chemically strengthened glass undergoes an ion-exchange process that significantly enhances its surface compressive stress, improving strength and scratch resistance. Both materials provide robust protection but differ in composition, processing, and performance characteristics for applications such as electronic displays or optical devices.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Fused quartz is composed of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) formed by melting high-purity quartz sand at extremely high temperatures, resulting in a non-crystalline, amorphous glass with superior thermal stability and chemical resistance. Chemically strengthened glass is made from alkali aluminosilicate glass that undergoes an ion-exchange process, typically replacing smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions on the surface to create compressive stress and enhance strength. The manufacturing of fused quartz involves flame fusion or electric fusion melting, whereas chemically strengthened glass relies on precise ion-exchange baths to improve durability and resistance to scratches and impacts.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Fused quartz exhibits higher mechanical strength due to its exceptional hardness and resistance to deformation, making it ideal for high-stress environments. Chemically strengthened glass gains increased surface compression through ion exchange processes, improving its tensile strength and resistance to impact. While fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and scratch resistance, chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced toughness and flexibility for protective covers under mechanical stress.
Optical Clarity and Transmittance
Fused quartz offers superior optical clarity and transmittance, with over 90% light transmission across ultraviolet to infrared wavelengths, making it ideal for high-precision optical applications. Chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced surface strength while maintaining good optical clarity, typically transmitting around 90%, but may exhibit slight distortions or lower UV transmission compared to fused quartz. The choice between fused quartz and chemically strengthened glass depends on the balance between required optical performance and mechanical durability for protective covers.
Thermal Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional thermal resistance with a melting point around 1,710degC and minimal thermal expansion, making it highly suitable for protective covers in extreme temperature environments. Chemically strengthened glass, while offering enhanced surface hardness and scratch resistance, generally tolerates temperatures up to approximately 250degC to 300degC before structural degradation occurs. The superior temperature tolerance and low thermal expansion of fused quartz make it the preferred material for applications requiring durable thermal performance and stability under rapid temperature fluctuations.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Fused quartz offers exceptional scratch resistance due to its high hardness and chemical inertness, making it ideal for applications requiring durable, clear protective covers. Chemically strengthened glass, achieved through ion-exchange processes, significantly improves impact resistance by creating surface compressive stress, enhancing durability against drops and shocks. While fused quartz excels in scratch resistance, chemically strengthened glass provides a superior balance of scratch and impact resistance for protective cover applications.
Chemical Stability and Environmental Durability
Fused quartz offers exceptional chemical stability due to its high purity and resistance to most acids and alkalis, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments. Chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced environmental durability through its compressive surface layer, which improves resistance to surface damage and extends lifespan under mechanical stress. Both materials excel in protective cover applications, with fused quartz being superior in chemical inertness and chemically strengthened glass offering better impact and scratch resistance in variable environmental conditions.
Cost and Availability
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and high purity but comes at a significantly higher cost and limited availability compared to chemically strengthened glass. Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, provides enhanced strength and scratch resistance at a lower price point and is widely available for various protective cover applications. The choice hinges on budget constraints and the specific performance requirements of the protective cover.
Common Applications and Industry Use Cases
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for semiconductor manufacturing and high-temperature optical devices. Chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced surface durability and scratch resistance, commonly used in smartphone screens, automotive glass, and architectural applications. Both materials are favored in industries requiring precise protection, with fused quartz preferred for extreme heat environments and chemically strengthened glass for impact and abrasion protection.
Which Material is Better for Protective Covers?
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability, high purity, and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for protective covers requiring resistance to extreme temperatures and minimal optical distortion. Chemically strengthened glass provides enhanced surface hardness and improved impact resistance due to ion exchange processes, delivering better scratch and break resistance for everyday use. Choosing the better material depends on the application, with fused quartz excelling in high-heat, precision environments and chemically strengthened glass being preferable for robust, affordable protection in consumer electronics.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Chemically strengthened glass for Protective cover
 azmater.com
azmater.com