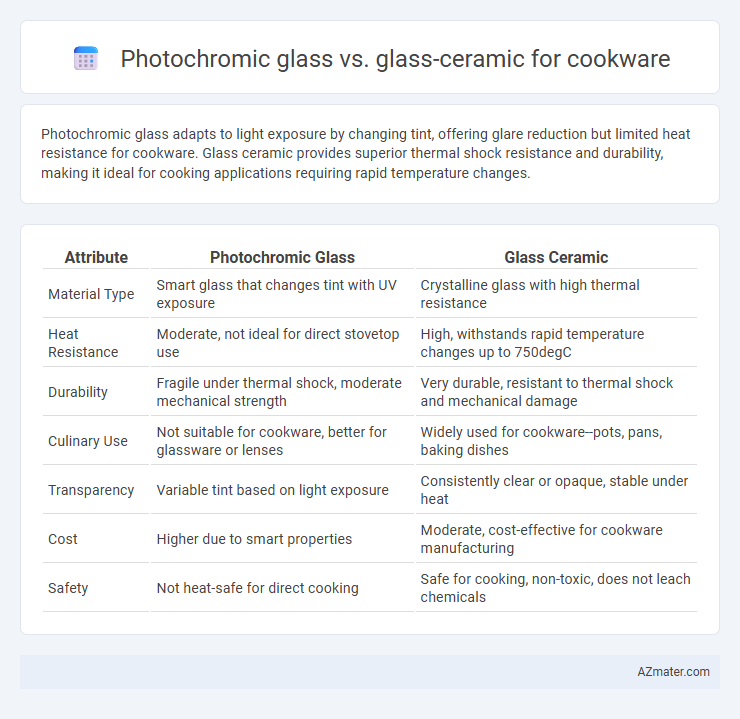
Photochromic glass adapts to light exposure by changing tint, offering glare reduction but limited heat resistance for cookware. Glass ceramic provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for cooking applications requiring rapid temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Photochromic Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Smart glass that changes tint with UV exposure | Crystalline glass with high thermal resistance |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, not ideal for direct stovetop use | High, withstands rapid temperature changes up to 750degC |
| Durability | Fragile under thermal shock, moderate mechanical strength | Very durable, resistant to thermal shock and mechanical damage |
| Culinary Use | Not suitable for cookware, better for glassware or lenses | Widely used for cookware--pots, pans, baking dishes |
| Transparency | Variable tint based on light exposure | Consistently clear or opaque, stable under heat |
| Cost | Higher due to smart properties | Moderate, cost-effective for cookware manufacturing |
| Safety | Not heat-safe for direct cooking | Safe for cooking, non-toxic, does not leach chemicals |
Introduction to Modern Cookware Materials
Photochromic glass and glass ceramic represent two advanced materials used in modern cookware, each offering unique benefits for heat resistance and durability. Photochromic glass adapts to light exposure by changing its tint, providing dynamic visual appeal but is less common in cookware due to limited heat tolerance. Glass ceramic, with exceptional thermal shock resistance and the ability to withstand rapid temperature changes up to 1,250degC, is widely favored for stovetop and oven cookware applications.
What is Photochromic Glass?
Photochromic glass is a type of glass that changes its tint in response to ultraviolet (UV) light, providing adaptive shading by darkening when exposed to sunlight and returning to clear indoors. This glass contains photochromic dyes or molecules embedded within its structure, enabling dynamic light modulation that enhances energy efficiency and user comfort. In contrast to glass ceramic cookware, which is valued for thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, photochromic glass primarily focuses on optical properties rather than heat endurance required for cooking surfaces.
Understanding Glass Ceramic Cookware
Glass ceramic cookware offers superior thermal shock resistance and even heat distribution compared to photochromic glass, making it ideal for cooking applications. Its microcrystalline structure allows rapid temperature changes without cracking, ensuring durability and consistent performance in stovetop and oven use. Unlike photochromic glass, which changes properties based on light exposure, glass ceramic focuses on functional heat management tailored for cookware efficiency.
Heat Resistance: Photochromic Glass vs Glass Ceramic
Glass ceramic offers superior heat resistance compared to photochromic glass, withstanding rapid temperature changes up to 700degC without cracking or deforming. Photochromic glass, primarily designed for light-sensitive applications, typically endures lower thermal stress and is more prone to thermal shock in cookware use. Heat tolerance in glass ceramics ensures durability and safety in high-temperature cooking environments, making it the preferred choice for cookware.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Photochromic glass offers moderate durability but is primarily valued for its ability to change tint based on light exposure, making it less ideal for high-impact cookware use. Glass ceramic cookware, composed of crystalline and glass phases, provides superior thermal resistance and exceptional durability, maintaining integrity under rapid temperature changes and frequent use. Longevity in glass ceramic cookware surpasses photochromic glass due to its enhanced resistance to cracking, chipping, and thermal shock.
Thermal Shock and Safety in Cooking
Photochromic glass offers moderate thermal shock resistance but may crack under sudden temperature changes, limiting its safety in high-heat cooking environments. Glass ceramic cookware, engineered with a crystalline structure, provides superior thermal shock resistance, allowing rapid temperature fluctuations without cracking, ensuring safer cooking performance. The enhanced durability of glass ceramic makes it a more reliable choice for intense cooking applications compared to photochromic glass.
Cooking Performance and Efficiency
Photochromic glass adjusts its tint based on light exposure but offers limited heat resistance and uneven thermal distribution, making it less ideal for cookware focused on consistent cooking performance. Glass ceramic cookware excels in heat retention and uniform heat distribution, enabling precise temperature control and efficient energy use during cooking. Its thermal shock resistance and durability enhance overall cooking efficiency compared to photochromic glass.
Design Versatility and Aesthetic Appeal
Photochromic glass offers dynamic design versatility by changing color in response to light, enhancing aesthetic appeal with its modern, interactive look ideal for innovative cookware designs. Glass ceramic provides exceptional design flexibility due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and maintain clarity, supporting sleek, elegant cookware styles that combine durability with visual appeal. Both materials contribute uniquely to cookware aesthetics, with photochromic glass emphasizing adaptability and visual interaction, while glass ceramic prioritizes timeless elegance and practical functionality.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Value
Photochromic glass cookware tends to be more expensive due to advanced light-adaptive properties enhancing user convenience and energy efficiency. Glass ceramic cookware offers a more affordable option with excellent heat retention and durability, providing reliable value for everyday cooking needs. When balancing cost and performance, glass ceramic delivers greater affordability, while photochromic glass appeals to premium users seeking innovative features.
Choosing the Best Cookware for Your Kitchen
Photochromic glass offers adaptive light filtering that helps reduce glare when cooking, enhancing visual comfort in bright kitchens. Glass ceramic cookware provides exceptional thermal stability and rapid heat distribution, making it ideal for precise cooking techniques and energy efficiency. Choosing between these materials depends on whether you prioritize visual comfort with photochromic properties or superior cooking performance with glass ceramics.
Infographic: Photochromic glass vs Glass ceramic for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com