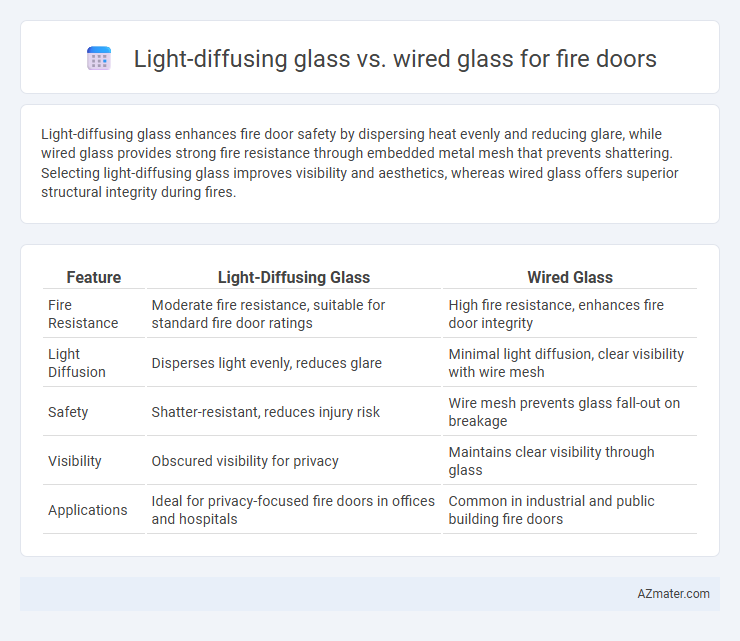
Light-diffusing glass enhances fire door safety by dispersing heat evenly and reducing glare, while wired glass provides strong fire resistance through embedded metal mesh that prevents shattering. Selecting light-diffusing glass improves visibility and aesthetics, whereas wired glass offers superior structural integrity during fires.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Light-Diffusing Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Moderate fire resistance, suitable for standard fire door ratings | High fire resistance, enhances fire door integrity |
| Light Diffusion | Disperses light evenly, reduces glare | Minimal light diffusion, clear visibility with wire mesh |
| Safety | Shatter-resistant, reduces injury risk | Wire mesh prevents glass fall-out on breakage |
| Visibility | Obscured visibility for privacy | Maintains clear visibility through glass |
| Applications | Ideal for privacy-focused fire doors in offices and hospitals | Common in industrial and public building fire doors |
Introduction to Fire Door Glazing Options
Fire door glazing options include light-diffusing glass and wired glass, each offering unique benefits for fire safety and visibility. Light-diffusing glass enhances natural light while maintaining privacy and meeting fire resistance standards, making it ideal for environments requiring both safety and ambiance. Wired glass provides robust fire protection with embedded wire mesh to prevent shattering, commonly used in industrial and high-heat applications where maximum fire containment is critical.
What is Light-Diffusing Glass?
Light-diffusing glass is engineered to scatter incoming light, creating a soft, even illumination while maintaining privacy and safety in fire door applications. Unlike wired glass, which contains embedded metal wires to hold glass fragments in place, light-diffusing glass offers enhanced visibility without compromising fire resistance or structural integrity. This glass type improves natural light distribution in corridors and rooms, making it a preferred choice in modern fire-rated door designs.
What is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of safety glass embedded with a metal wire mesh that provides additional fire resistance and prevents the glass from shattering during exposure to high temperatures. Commonly used in fire doors, wired glass maintains structural integrity by holding fragments together, which helps delay the spread of flames and smoke. Its combination of durability and fire protection makes it a popular choice in commercial and industrial buildings requiring compliance with fire safety standards.
Fire Resistance Capabilities: Light-Diffusing vs Wired Glass
Light-diffusing glass offers enhanced fire resistance capabilities by scattering heat and reducing thermal stress, which helps maintain structural integrity longer during fires. Wired glass, reinforced with embedded wire mesh, provides strong mechanical stability and prevents glass shattering but can fail under prolonged fire exposure due to heat conduction through the metal wires. Fire doors equipped with light-diffusing glass typically achieve higher fire ratings and better visibility compared to wired glass, making them preferable for maintaining safety and compliance in fire protection systems.
Safety Considerations and Impact Resistance
Light-diffusing glass for fire doors enhances occupant safety by evenly dispersing light and maintaining clear visibility while meeting stringent fire-resistance ratings, typically up to 60 minutes or more. Wired glass provides excellent impact resistance and fire protection with embedded wire mesh that prevents breakage during exposure to heat, although it may compromise visibility due to the mesh pattern. Selecting between light-diffusing and wired glass depends on balancing fire safety standards, impact resistance requirements, and visual clarity for effective emergency response and occupant protection.
Light Transmission and Privacy Features
Light-diffusing glass in fire doors offers enhanced light transmission by scattering light evenly, which creates a bright environment while obscuring clear views to maintain privacy. Wired glass provides excellent fire resistance and security but typically transmits less light due to its embedded wire mesh, resulting in reduced visibility and increased opacity. Choosing between these materials depends on balancing the need for natural illumination against the desired level of visual privacy in fire-rated applications.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Light-diffusing glass enhances fire doors by scattering light to create a soft, uniform glow, offering superior aesthetics and increased privacy without compromising fire resistance. Wired glass features embedded metal mesh that ensures structural integrity under heat but offers limited design flexibility and a more industrial appearance. Choosing light-diffusing glass allows architects and designers to integrate fire doors seamlessly into modern, visually appealing spaces while meeting safety standards.
Building Codes and Regulatory Compliance
Light-diffusing glass enhances visibility while meeting stringent fire rating requirements, making it compliant with NFPA 80 and IBC standards for fire door assemblies. Wired glass, although traditionally accepted for fire doors, now faces limitations under updated codes such as the 2018 IBC, which restricts its use due to safety concerns related to shattering and laceration risks. Building codes increasingly favor advanced glass materials that provide fire resistance, impact protection, and transparency, ensuring both regulatory compliance and occupant safety in fire-rated doors.
Cost Comparison: Installation and Maintenance
Light-diffusing glass for fire doors generally incurs higher installation costs due to specialized handling and fitting requirements that ensure optimal light dispersion while maintaining fire resistance. Wired glass tends to be more cost-effective upfront, benefiting from widespread availability and simpler installation processes. Maintenance expenses for light-diffusing glass can increase over time because of potential surface treatments needing replacement, whereas wired glass maintenance primarily involves periodic inspection for cracks or damage, making it cheaper over the product lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Glass for Fire Doors
Selecting the right glass for fire doors requires balancing safety, visibility, and design. Light-diffusing glass provides enhanced privacy and uniform light transmission while meeting fire-resistance standards, making it suitable for spaces requiring controlled visibility. Wired glass offers robust heat and impact resistance but can compromise clarity and aesthetics, often chosen for industrial or high-risk settings needing maximum fire protection.
Infographic: Light-diffusing glass vs Wired glass for Fire door
 azmater.com
azmater.com