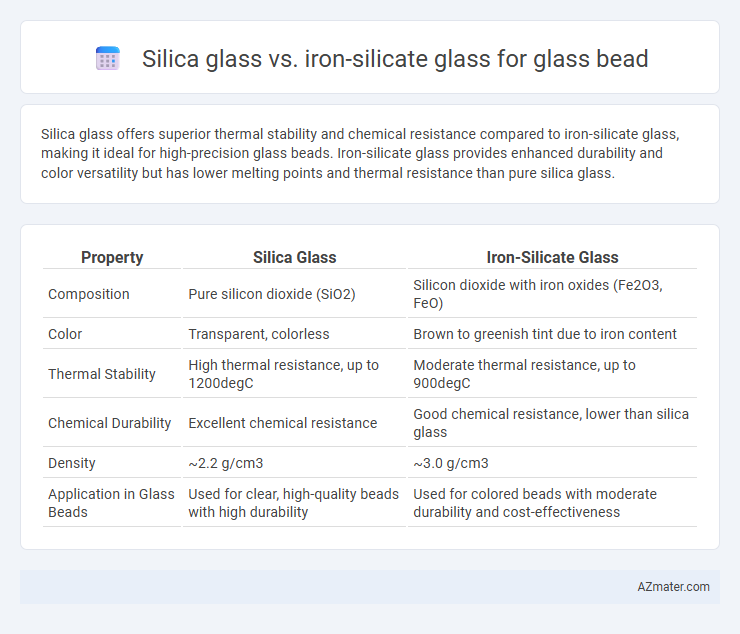
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to iron-silicate glass, making it ideal for high-precision glass beads. Iron-silicate glass provides enhanced durability and color versatility but has lower melting points and thermal resistance than pure silica glass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | Iron-Silicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Silicon dioxide with iron oxides (Fe2O3, FeO) |
| Color | Transparent, colorless | Brown to greenish tint due to iron content |
| Thermal Stability | High thermal resistance, up to 1200degC | Moderate thermal resistance, up to 900degC |
| Chemical Durability | Excellent chemical resistance | Good chemical resistance, lower than silica glass |
| Density | ~2.2 g/cm3 | ~3.0 g/cm3 |
| Application in Glass Beads | Used for clear, high-quality beads with high durability | Used for colored beads with moderate durability and cost-effectiveness |
Overview of Glass Beads
Glass beads made from silica glass offer high chemical resistance and excellent optical clarity, making them ideal for precision applications and decorative purposes. Iron-silicate glass beads provide enhanced durability and improved thermal stability due to the presence of iron oxide, suitable for abrasive and industrial uses. Both types demonstrate unique advantages in hardness and refractive index, influencing their selection based on environmental and functional requirements.
Composition of Silica Glass vs Iron-Silicate Glass
Silica glass primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with a highly pure, amorphous structure, ensuring excellent transparency and chemical stability for glass beads. Iron-silicate glass incorporates iron oxides (Fe2O3 and FeO) into the silica matrix, altering its optical and thermal properties while providing increased durability and a distinctive coloration. The varying ratios of silica and iron oxides in these glasses result in significant differences in density, refractive index, and resistance to environmental factors critical for specialized bead applications.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Silica glass manufacturing involves melting high-purity silica sand at temperatures exceeding 1700degC, resulting in a highly durable and chemically inert glass ideal for precision glass beads. Iron-silicate glass is produced by incorporating iron oxide into the silica matrix, lowering the melting point to around 1400-1500degC and imparting distinct magnetic and optical properties; this process requires careful control of redox conditions to maintain iron valence states. Differences in thermal treatment and annealing cycles also affect bead clarity and mechanical strength, making silica glass preferable for high-purity applications and iron-silicate glass suitable for functional beads with enhanced physical characteristics.
Physical Properties Comparison
Silica glass offers superior hardness and chemical stability compared to iron-silicate glass, making it more resistant to thermal shock and wear in glass bead applications. Iron-silicate glass exhibits higher density and enhanced magnetic properties due to iron content, which can affect bead weight and functionality in specialized uses. Thermal expansion rates are lower in silica glass, providing better dimensional stability during temperature fluctuations.
Optical Qualities and Transparency
Silica glass exhibits superior optical qualities with high transparency, low dispersion, and excellent UV light transmission, making it ideal for precision optical glass beads. Iron-silicate glass contains iron ions that increase absorption, reducing overall transparency and causing darker coloration, which limits its use in applications requiring clarity. The choice between silica and iron-silicate glass for glass beads depends on the specific optical requirements, with silica glass preferred for maximum light transmission and minimal optical distortion.
Chemical Durability and Resistance
Silica glass exhibits superior chemical durability due to its pure silicon dioxide composition, providing excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and environmental corrosion, making it ideal for long-term use in harsh conditions. Iron-silicate glass, containing iron oxides, generally has lower chemical resistance and may be more susceptible to corrosion and degradation under acidic or alkaline environments. For glass beads requiring enhanced longevity and chemical stability, silica glass outperforms iron-silicate glass in resisting chemical attacks and maintaining structural integrity.
Color and Appearance Variations
Silica glass offers high clarity and a nearly colorless appearance, making it ideal for producing glass beads with bright, vibrant hues when colored. Iron-silicate glass inherently contains iron oxide, resulting in a natural greenish or brownish tint that can influence bead color, often producing earthier and more muted tones. Variations in iron concentration within iron-silicate glass create a range of subtle color gradients, whereas silica glass provides a more uniform and transparent base for consistent coloration.
Usability in Industrial Applications
Silica glass offers superior chemical durability and high thermal resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring stability under extreme conditions such as semiconductor manufacturing and high-temperature optics. Iron-silicate glass provides enhanced mechanical strength and impact resistance, which benefits industries needing durable glass beads for abrasive blasting and grinding media. Choosing between these depends on the specific requirements for thermal stability versus mechanical toughness in the intended industrial use.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Silica glass used in glass beads is composed primarily of silicon dioxide, offering high chemical durability and resistance to leaching, which minimizes environmental contamination and reduces health risks during handling. Iron-silicate glass contains iron oxides that can introduce trace metal leaching, potentially impacting soil and water quality and raising concerns for long-term environmental exposure. Both materials require careful consideration of manufacturing emissions and disposal methods to ensure minimal ecological footprint and occupational safety.
Cost and Market Availability
Silica glass beads generally have higher raw material costs but offer superior purity and thermal stability, making them preferred in high-performance applications. Iron-silicate glass beads are more cost-effective due to lower production expenses and abundant iron content, resulting in wider market availability for decorative and industrial uses. The choice depends on balancing budget constraints with specific performance requirements.
Infographic: Silica glass vs Iron-silicate glass for Glass bead
 azmater.com
azmater.com