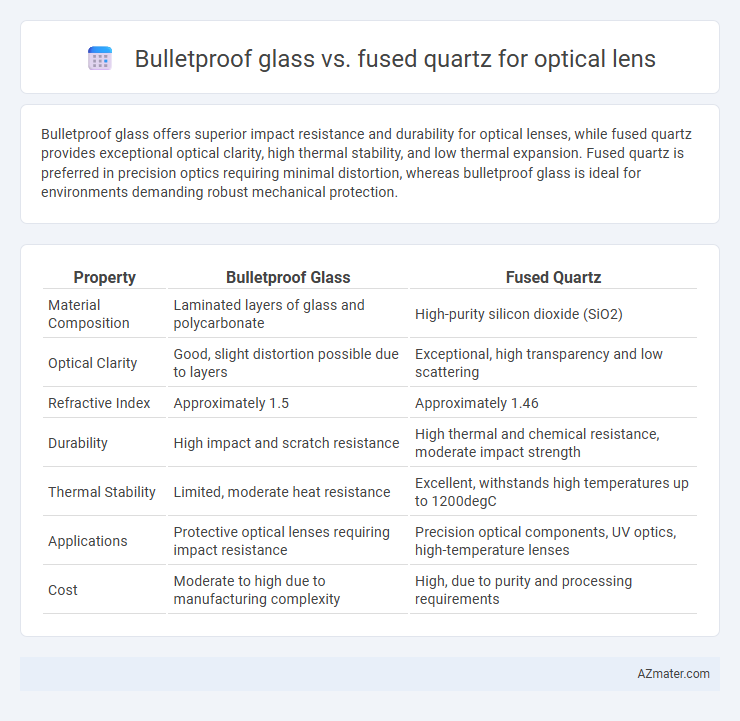
Bulletproof glass offers superior impact resistance and durability for optical lenses, while fused quartz provides exceptional optical clarity, high thermal stability, and low thermal expansion. Fused quartz is preferred in precision optics requiring minimal distortion, whereas bulletproof glass is ideal for environments demanding robust mechanical protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bulletproof Glass | Fused Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate | High-purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) |
| Optical Clarity | Good, slight distortion possible due to layers | Exceptional, high transparency and low scattering |
| Refractive Index | Approximately 1.5 | Approximately 1.46 |
| Durability | High impact and scratch resistance | High thermal and chemical resistance, moderate impact strength |
| Thermal Stability | Limited, moderate heat resistance | Excellent, withstands high temperatures up to 1200degC |
| Applications | Protective optical lenses requiring impact resistance | Precision optical components, UV optics, high-temperature lenses |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to manufacturing complexity | High, due to purity and processing requirements |
Introduction to Optical Lens Materials
Bulletproof glass and fused quartz serve distinct roles in optical lens applications due to their differing physical and optical properties. Bulletproof glass offers high impact resistance and durability, making it ideal for protective optical systems, while fused quartz provides superior transparency, low thermal expansion, and excellent UV transmission, critical for precision lenses in harsh environments. Understanding these material characteristics is essential for selecting the appropriate optical lens material for applications ranging from security to scientific instrumentation.
Overview of Bulletproof Glass Properties
Bulletproof glass, also known as laminated glass, consists of multiple layers of glass and polymer interlayers that provide high impact resistance and shatterproof properties, making it ideal for protective optical lenses in hostile environments. It offers excellent clarity, good scratch resistance, and enhanced durability, with a thickness typically ranging from 0.5 to 2 inches depending on the level of protection required. While fused quartz excels in thermal and UV transmission, bulletproof glass remains preferred for applications demanding both optical clarity and strong mechanical protection.
Fused Quartz: Composition and Characteristics
Fused quartz is composed primarily of high-purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) with a non-crystalline, amorphous structure, offering exceptional thermal stability and optical clarity. Its low thermal expansion coefficient and high resistance to thermal shock make it ideal for precision optical lenses requiring durability under varying temperature conditions. Unlike bulletproof glass, fused quartz provides superior ultraviolet transmission and minimal internal stress, enhancing performance in high-precision optical applications.
Optical Clarity: Bulletproof Glass vs Fused Quartz
Fused quartz offers superior optical clarity compared to bulletproof glass, exhibiting higher light transmission and lower internal scattering, essential for precision optical lenses. Bulletproof glass, typically composed of laminated layers including polycarbonate and glass, often introduces slight distortions and reduced transparency due to its multi-layer structure. For applications demanding minimal aberrations and maximum clarity, fused quartz remains the preferred material despite bulletproof glass's enhanced impact resistance.
Light Transmission and Refractive Index Comparison
Bulletproof glass exhibits high durability with a typical light transmission of around 85-90% and a refractive index ranging from 1.5 to 1.6, making it suitable for impact-resistant optical lenses. Fused quartz offers superior optical clarity with light transmission exceeding 92% across a wide spectral range and a lower refractive index of approximately 1.46, enabling minimal light distortion and higher precision in lens applications. The choice between bulletproof glass and fused quartz hinges on balancing impact resistance with optical performance requirements such as clarity and refractive control.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Bulletproof glass offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to fused quartz, making it ideal for high-threat environments where shatterproof lenses are critical. Fused quartz, while highly resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, tends to be more brittle and less effective against mechanical impacts. The combination of high hardness and laminated layers in bulletproof glass enhances its ability to absorb and disperse energy, ensuring greater longevity under harsh conditions.
Thermal Stability and Environmental Performance
Bulletproof glass offers high thermal stability with resistance to temperature fluctuations and mechanical impact, making it suitable for rugged optical lenses in harsh environments. Fused quartz excels in thermal stability due to its low thermal expansion coefficient and excellent resistance to high temperatures, ensuring minimal distortion in precision optical applications. Environmentally, fused quartz is chemically inert and highly durable under UV exposure, while bulletproof glass can degrade over time with prolonged environmental stress.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Bulletproof glass typically costs less and is easier to manufacture in large, uniform sheets compared to fused quartz, which involves more complex and expensive processes such as high-temperature melting and precise annealing. Fused quartz offers superior optical clarity, thermal stability, and chemical resistance, but these benefits come with higher production costs and longer fabrication times. Cost efficiency is a major factor for applications prioritizing durability over optical perfection, while fused quartz is preferred in high-precision optical lens manufacturing despite its higher price.
Application Suitability in Optical Devices
Bulletproof glass offers exceptional impact resistance, making it suitable for optical lenses in environments requiring high durability such as military, automotive, and security applications. Fused quartz provides superior optical clarity, low thermal expansion, and excellent UV transparency, ideal for precision instruments like microscopes, telescopes, and laser systems. The choice between bulletproof glass and fused quartz depends on balancing mechanical protection with optical performance requirements in specific optical devices.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Lens Material
Bulletproof glass provides superior impact resistance and durability, making it ideal for lenses exposed to harsh environments, while fused quartz excels in optical clarity, UV transparency, and thermal stability, crucial for high-precision applications. Selecting the optimal lens material depends on balancing mechanical protection needs with required optical performance, with fused quartz favored for advanced optical systems and bulletproof glass preferred where safety and robustness are paramount. Consider specific use cases such as aerospace or security to determine whether optical quality or physical resilience takes precedence.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs Fused quartz for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com