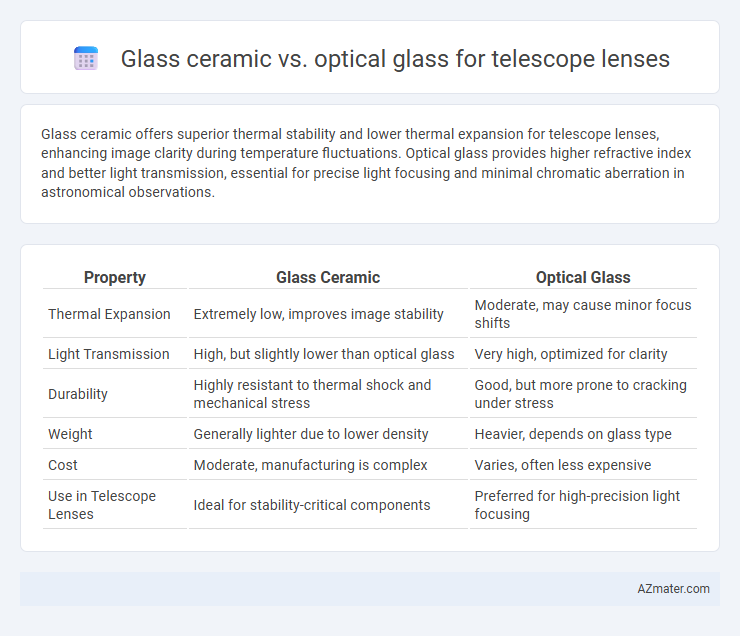
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal stability and lower thermal expansion for telescope lenses, enhancing image clarity during temperature fluctuations. Optical glass provides higher refractive index and better light transmission, essential for precise light focusing and minimal chromatic aberration in astronomical observations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Ceramic | Optical Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Expansion | Extremely low, improves image stability | Moderate, may cause minor focus shifts |
| Light Transmission | High, but slightly lower than optical glass | Very high, optimized for clarity |
| Durability | Highly resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress | Good, but more prone to cracking under stress |
| Weight | Generally lighter due to lower density | Heavier, depends on glass type |
| Cost | Moderate, manufacturing is complex | Varies, often less expensive |
| Use in Telescope Lenses | Ideal for stability-critical components | Preferred for high-precision light focusing |
Overview of Telescope Lens Materials
Glass ceramic and optical glass are two primary materials used in telescope lenses, each offering distinct advantages based on their composition and optical properties. Glass ceramics exhibit low thermal expansion and high mechanical stability, making them ideal for maintaining lens shape under temperature fluctuations; optical glass, on the other hand, provides superior clarity and a wider range of refractive indices essential for precise light focusing. Selection between glass ceramic and optical glass depends on factors such as thermal durability, chromatic aberration correction, and specific telescope design requirements.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a composite material combining glass and crystalline phases, offering enhanced thermal stability and minimal expansion compared to conventional optical glass. Its low thermal expansion makes it ideal for telescope lenses, reducing distortions caused by temperature fluctuations. This property ensures sharper, more accurate astronomical observations over time.
What is Optical Glass?
Optical glass is a high-quality, precisely manufactured material designed specifically for lenses and optical components in telescopes, offering superior clarity, controlled refractive indices, and minimal light dispersion. Unlike glass ceramics, which exhibit a crystalline structure and are primarily valued for durability and thermal stability, optical glass provides enhanced light transmission and image resolution crucial for astronomical observations. Its tailored optical properties enable precise focusing and minimal chromatic aberration, making it the preferred choice for telescope lenses.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Glass ceramics used in telescope lenses exhibit superior thermal stability and lower thermal expansion coefficients compared to optical glass, minimizing image distortion during temperature fluctuations. Optical glass typically offers higher optical homogeneity and refractive index precision, enhancing image clarity and color correction capabilities. Mechanical strength varies, with glass ceramics providing enhanced durability and resistance to mechanical stress, while optical glass remains favored for finely tuned optical performance.
Optical Performance Differences
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal stability and reduced chromatic aberration compared to conventional optical glass, enhancing image clarity in telescopes. Optical glass, while versatile and widely used, may introduce slight dispersion and thermal expansion affecting focus precision. The choice between glass ceramic and optical glass directly impacts resolution and color fidelity in astronomical observations.
Thermal Stability and Expansion
Glass ceramic exhibits superior thermal stability and minimal thermal expansion compared to optical glass, making it ideal for telescope lenses exposed to temperature fluctuations. Its low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), often near zero (e.g., Zerodur ~0 +- 0.02 x10^-6 /K), prevents shape distortion and maintains optical precision. Optical glass, such as BK7 or fused silica, has higher thermal expansion rates, which can lead to focal shifts and image degradation under varying thermal conditions.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Glass ceramic offers lower thermal expansion and higher durability compared to optical glass, reducing deformation and improving image stability in telescope lenses. The manufacturing process for glass ceramic involves complex crystallization steps, increasing production costs but resulting in better long-term performance. Optical glass is generally cheaper and easier to produce but may require additional coatings and treatments to achieve comparable thermal and mechanical stability, impacting overall cost efficiency.
Durability and Longevity
Glass ceramic lenses for telescopes offer superior durability and resistance to thermal shock compared to optical glass, enabling stable performance in varying environmental conditions. Optical glass, while providing excellent optical clarity and light transmission, tends to be more prone to chipping and requires careful handling to maintain longevity. The low coefficient of thermal expansion in glass ceramic ensures minimal deformation over time, enhancing the lens's lifespan and consistent image quality.
Applications in Modern Telescopes
Glass ceramic materials in modern telescope lenses offer superior thermal stability and reduced chromatic aberration, making them ideal for high-precision astronomical imaging and spectroscopy. Optical glass, renowned for its diverse refractive indices and low dispersion properties, remains the standard choice for traditional refractors and wide-field telescopes where cost-efficiency and versatility are critical. Advanced research telescopes increasingly integrate glass ceramic elements to enhance resolution and image clarity, particularly in adaptive optics and space-based observatories.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Telescope
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal stability and resistance to expansion, making it ideal for maintaining precise focus in varying temperatures. Optical glass provides high optical clarity and low dispersion, essential for sharp, clear images in telescopes. Choosing the right material depends on balancing thermal performance and optical quality to optimize the telescope's imaging capabilities.
Infographic: Glass ceramic vs Optical glass for Telescope lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com