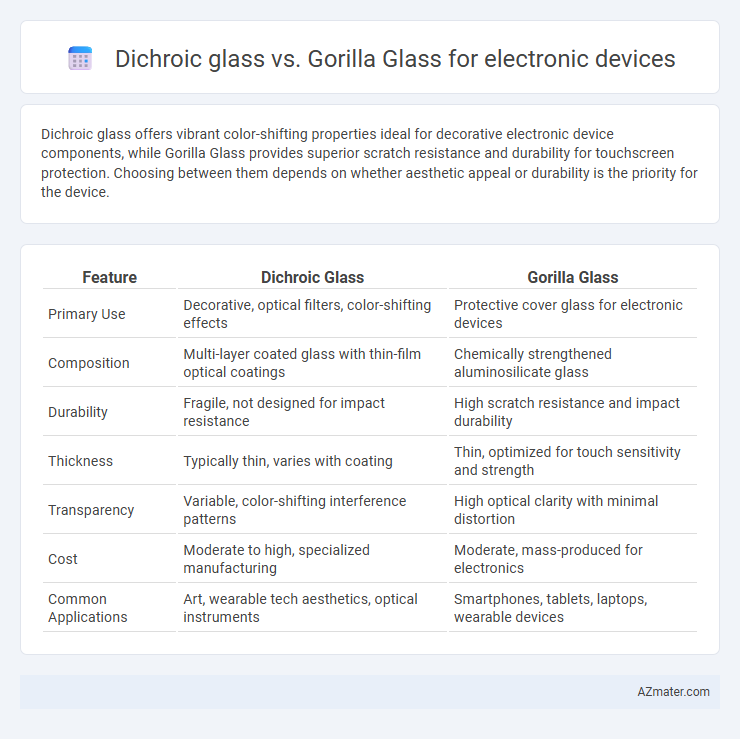
Dichroic glass offers vibrant color-shifting properties ideal for decorative electronic device components, while Gorilla Glass provides superior scratch resistance and durability for touchscreen protection. Choosing between them depends on whether aesthetic appeal or durability is the priority for the device.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dichroic Glass | Gorilla Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Decorative, optical filters, color-shifting effects | Protective cover glass for electronic devices |
| Composition | Multi-layer coated glass with thin-film optical coatings | Chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass |
| Durability | Fragile, not designed for impact resistance | High scratch resistance and impact durability |
| Thickness | Typically thin, varies with coating | Thin, optimized for touch sensitivity and strength |
| Transparency | Variable, color-shifting interference patterns | High optical clarity with minimal distortion |
| Cost | Moderate to high, specialized manufacturing | Moderate, mass-produced for electronics |
| Common Applications | Art, wearable tech aesthetics, optical instruments | Smartphones, tablets, laptops, wearable devices |
Introduction to Dichroic Glass and Gorilla Glass
Dichroic glass is a specialized material known for its multi-layer optical coatings that selectively reflect and transmit specific wavelengths of light, creating vibrant color effects ideal for artistic electronic displays. Gorilla Glass, developed by Corning, is a chemically strengthened, aluminosilicate glass designed to provide high durability and scratch resistance in electronic device screens. While Dichroic glass enhances visual aesthetics through its unique light-reflective properties, Gorilla Glass prioritizes functional toughness and impact protection for daily use.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Dichroic glass is composed of multiple ultra-thin layers of metal oxides deposited on glass, created through a complex vacuum deposition process to achieve its unique reflective and transmissive optical properties. Gorilla Glass, engineered by Corning, is an alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass chemically strengthened through an ion-exchange process, enhancing its scratch resistance and durability for electronic device screens. The manufacturing of dichroic glass focuses on precision layering for color effects, whereas Gorilla Glass prioritizes mechanical strength and scratch resistance through ion exchange and thermal tempering.
Optical Properties and Aesthetics
Dichroic glass offers unique optical properties with its ability to reflect and transmit multiple colors depending on the angle of light, creating vibrant, shifting hues that enhance the aesthetics of electronic devices. Gorilla Glass provides superior clarity and durability with excellent scratch and impact resistance, maintaining a sleek and polished appearance over time. While dichroic glass emphasizes visual appeal through dynamic color effects, Gorilla Glass prioritizes functional optical transparency and toughness for everyday use.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Gorilla Glass, engineered with aluminosilicate sheets and chemically strengthened through ion exchange, offers superior impact resistance and scratch durability, making it highly effective for electronic device screens. Dichroic glass, while prized for its unique optical properties and vibrant color shifts, generally lacks the mechanical strength and scratch resistance of Gorilla Glass, limiting its use in high-impact environments. In terms of longevity and robustness for electronic devices, Gorilla Glass outperforms Dichroic glass due to its advanced structural composition and enhanced durability.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Dichroic glass offers unique optical properties but generally lacks the robust scratch and impact resistance required for electronic device screens compared to Gorilla Glass. Gorilla Glass, developed by Corning, is chemically strengthened through ion-exchange processes, providing superior durability and resilience against everyday wear and accidental drops. Its high scratch resistance and impact tolerance make it the industry standard for smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Dichroic glass typically features a lightweight, thin composition ideal for decorative applications but lacks the structural robustness required for electronic devices. Gorilla Glass, engineered from aluminosilicate, offers a superior balance of reduced thickness and enhanced durability, making it the preferred choice for lightweight, slim-profile electronic displays. Weight and thickness considerations favor Gorilla Glass due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, enabling thinner screens without compromising device protection.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Dichroic glass, known for its vibrant color-shifting properties, commands higher production costs and faces limited market availability compared to Gorilla Glass, which is widely used due to its durability and cost-effectiveness. Gorilla Glass benefits from mass production and extensive supplier networks, driving down costs and making it the preferred choice for most electronic devices. Cost analysis reveals Gorilla Glass offers a better price-to-performance ratio, supporting its dominance in the smartphone and tablet markets.
Applications in Electronic Devices
Dichroic glass offers unique optical properties making it ideal for decorative displays and augmented reality interfaces in electronic devices, where color-shifting effects enhance user experience. Gorilla Glass provides superior scratch resistance and durability, making it the preferred choice for touchscreens and protective covers in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The selection between dichroic and Gorilla glass depends largely on whether visual aesthetics or mechanical protection is prioritized in the device design.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Dichroic glass, known for its multi-layered coatings that reflect specific wavelengths, offers potential in sustainable design due to its durability and recyclability, reducing electronic waste. Gorilla Glass, a chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass, is widely used for its scratch resistance and long lifespan, lowering device replacement frequency and minimizing environmental impact. Both materials contribute to sustainability by enhancing device longevity, but dichroic glass's recyclable coatings provide an edge in eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Device
Dichroic glass offers vibrant color effects and artistic appeal but lacks the durability and scratch resistance critical for daily electronic device use. Gorilla Glass, engineered with alkali-aluminosilicate sheets, provides robust protection against impacts and scratches, making it the preferred choice for smartphones, tablets, and wearables. Selecting the right glass involves prioritizing toughness and clarity; Gorilla Glass ensures both, while dichroic glass suits decorative or niche applications rather than mainstream device screens.
Infographic: Dichroic glass vs Gorilla glass for Electronic device
 azmater.com
azmater.com