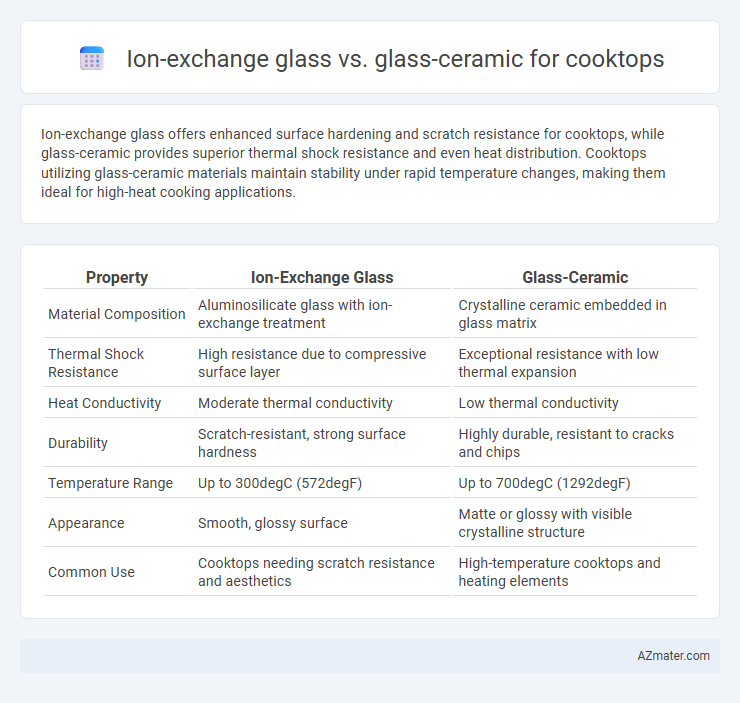
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced surface hardening and scratch resistance for cooktops, while glass-ceramic provides superior thermal shock resistance and even heat distribution. Cooktops utilizing glass-ceramic materials maintain stability under rapid temperature changes, making them ideal for high-heat cooking applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ion-Exchange Glass | Glass-Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Aluminosilicate glass with ion-exchange treatment | Crystalline ceramic embedded in glass matrix |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High resistance due to compressive surface layer | Exceptional resistance with low thermal expansion |
| Heat Conductivity | Moderate thermal conductivity | Low thermal conductivity |
| Durability | Scratch-resistant, strong surface hardness | Highly durable, resistant to cracks and chips |
| Temperature Range | Up to 300degC (572degF) | Up to 700degC (1292degF) |
| Appearance | Smooth, glossy surface | Matte or glossy with visible crystalline structure |
| Common Use | Cooktops needing scratch resistance and aesthetics | High-temperature cooktops and heating elements |
Introduction to Cooktop Materials
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance due to its chemical strengthening process, making it a premium choice for cooktops that require high thermal shock resistance. Glass-ceramic cooktops, such as those made from vitroceramic materials, provide superior heat distribution and can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, ideal for induction and electric cooking surfaces. Both materials deliver sleek aesthetics and easy maintenance, with the choice depending on specific performance needs like thermal stability or surface hardness.
Overview of Ion-Exchange Glass
Ion-exchange glass is a durable material commonly used in cooktops due to its enhanced strength and resistance to thermal shock, achieved through a chemical process that replaces smaller ions in the glass with larger ones. This process results in a tougher surface that withstands scratches and high temperatures better than standard glass. Compared to glass-ceramic, ion-exchange glass offers improved impact resistance but generally exhibits lower heat resistance and thermal stability.
Key Properties of Glass-Ceramic
Glass-ceramic cooktops feature high thermal resistance, enabling rapid heating and cooling without thermal shock, unlike ion-exchange glass which primarily enhances surface strength. Their low thermal expansion coefficient ensures structural stability under temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for cooking applications. Additionally, glass-ceramics offer superior scratch resistance and durability, providing a long-lasting, easy-to-clean surface essential for kitchen environments.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Ion-exchange glass offers exceptional thermal resistance by undergoing a chemical strengthening process that compresses its surface, enabling it to withstand rapid temperature changes up to 600degF without cracking. Glass-ceramic cooktops, however, provide superior thermal shock resistance and can endure even higher temperatures, often exceeding 1000degF, due to their unique crystalline structure formed through controlled crystallization. While ion-exchange glass provides durability and moderate heat tolerance, glass-ceramic remains the preferred choice for cooktops requiring extreme temperature stability and resistance to thermal stress.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ion-exchange glass exhibits superior mechanical strength due to a surface compression layer created by replacing smaller ions with larger ones, enhancing resistance to scratches and impact. Glass-ceramic cooktops offer exceptional durability with their crystalline microstructure that withstands thermal shock and high temperatures better than ion-exchange glass. While ion-exchange glass provides excellent everyday durability, glass-ceramic is preferred for heavy-duty cooking environments due to its increased thermal resistance and long-term stability.
Heat Distribution and Cooking Performance
Ion-exchange glass offers excellent heat distribution due to its uniform surface and enhanced strength, reducing hotspots and ensuring consistent cooking performance. Glass-ceramic cooktops provide superior thermal shock resistance and can withstand rapid temperature changes, which benefits high-heat cooking and durability. Both materials excel in smooth surface maintenance, but glass-ceramic typically delivers faster heat response times, improving overall cooking efficiency.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Ion-exchange glass offers superior scratch resistance due to a surface-strengthening process that replaces smaller ions with larger ones, creating a compressive stress layer that protects against abrasions. Glass-ceramic cooktops excel in impact resistance because of their crystalline structure, which enhances thermal shock tolerance and reduces the likelihood of cracks or fractures from sudden temperature changes or heavy impacts. Both materials provide durability, but ion-exchange glass prioritizes surface hardness while glass-ceramic emphasizes toughness under mechanical and thermal stress.
Aesthetic Differences and Design Options
Ion-exchange glass offers a sleek, glossy surface with a uniform black or colored finish that enhances modern kitchen aesthetics, while glass-ceramic cooktops provide a matte or textured appearance with visible outlines for heating zones, contributing to a more technical and utilitarian look. Design options for ion-exchange glass are often limited to smooth, flat surfaces that blend seamlessly into countertops, whereas glass-ceramic cooktops allow for integrated control panels and customizable zones, offering greater versatility in kitchen layouts. The reflective quality of ion-exchange glass lends a high-end, minimalist appeal, contrasting with the practical, engineered design emphasis found in glass-ceramic cooktops.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Ion-exchange glass cooktops feature a durable, chemically strengthened surface that resists scratches and stains, making cleaning easier with just a soft cloth and mild detergent. Glass-ceramic cooktops, while heat resistant and visually appealing, require careful cleaning to avoid abrasive damage and discoloration, often needing specialized cooktop cleaners for residue removal. Regular maintenance of ion-exchange glass involves less intensive care compared to glass-ceramic, which is more prone to surface etching and requires gentle, non-abrasive cleaning methods to maintain its clarity and smooth finish.
Cost and Market Availability
Ion-exchange glass cooktops typically have a higher upfront cost due to advanced surface strengthening processes that enhance durability and scratch resistance. Glass-ceramic cooktops offer wider market availability and generally lower prices, benefiting from established manufacturing techniques and broader consumer adoption. Cost efficiency and accessibility make glass-ceramic models more prevalent, while ion-exchange glass surfaces cater to premium segments requiring superior toughness.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Glass-ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com