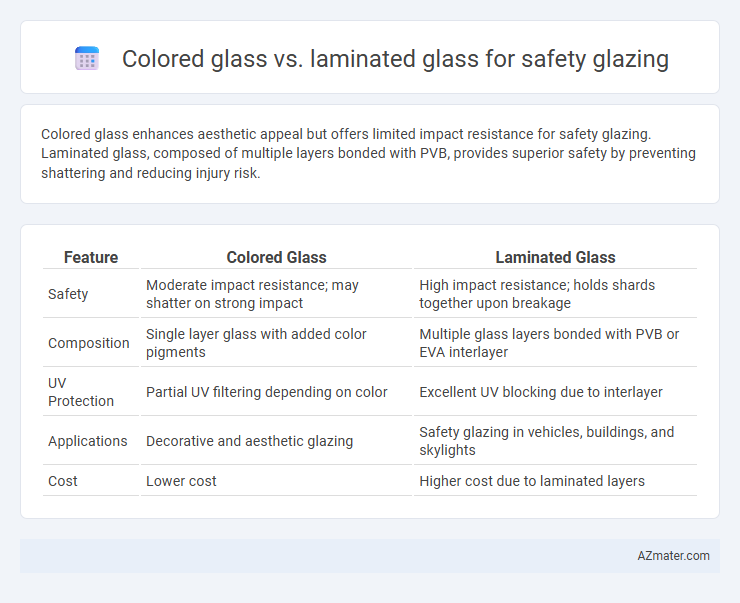
Colored glass enhances aesthetic appeal but offers limited impact resistance for safety glazing. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers bonded with PVB, provides superior safety by preventing shattering and reducing injury risk.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Colored Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Moderate impact resistance; may shatter on strong impact | High impact resistance; holds shards together upon breakage |
| Composition | Single layer glass with added color pigments | Multiple glass layers bonded with PVB or EVA interlayer |
| UV Protection | Partial UV filtering depending on color | Excellent UV blocking due to interlayer |
| Applications | Decorative and aesthetic glazing | Safety glazing in vehicles, buildings, and skylights |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to laminated layers |
Introduction to Safety Glazing Options
Colored glass enhances safety glazing by providing both aesthetic appeal and UV protection, often used in architectural applications to reduce glare and improve privacy while maintaining structural integrity. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers with an interlayer, offering superior impact resistance and preventing shattering upon breakage, making it ideal for safety-critical environments. Both options meet essential safety standards, yet laminated glass is preferred where maximum protection against injury and forced entry is required.
What is Colored Glass?
Colored glass is glass infused with metal oxides or other additives during production to achieve various tints and hues, enhancing aesthetic appeal and reducing glare and solar heat gain. This type of glass provides moderate safety glazing by obscuring visibility and offering some protection against impact, but it does not have the high resistance or shatter-retention properties of laminated glass. Compared to laminated glass, which consists of multiple layers bonded with an interlayer for enhanced safety and structural integrity, colored glass prioritizes design and energy efficiency rather than maximum safety performance.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety and security by holding shards in place upon impact. Colored glass is primarily used for aesthetic purposes and solar control but lacks the impact resistance and shatter-retention properties inherent to laminated glass. Laminated glass is preferred in safety glazing applications due to its ability to prevent injury from glass breakage and enhance structural integrity.
Key Differences: Colored Glass vs Laminated Glass
Colored glass primarily offers aesthetic appeal and UV protection by incorporating pigments directly into the glass, while laminated glass focuses on safety by sandwiching a plastic interlayer between glass layers to hold shards together upon breakage. Laminated glass provides superior impact resistance and prevents glass from shattering, making it ideal for safety glazing in vehicles and buildings. Unlike colored glass, laminated glass enhances structural integrity and sound insulation, crucial for security and accident prevention.
Safety Features of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass offers superior safety features by holding shattered pieces together with a durable interlayer, reducing the risk of injury from sharp glass fragments during impact. Unlike colored glass, which mainly provides aesthetic and UV filtering benefits, laminated glass maintains structural integrity even when broken, preventing accidental falls or breaches. Its enhanced impact resistance and ability to absorb energy make laminated glass an ideal choice for safety glazing in vehicles, buildings, and protective installations.
Impact Resistance: Colored vs Laminated Glass
Colored glass offers limited impact resistance due to its solid, single-layer structure, making it prone to shattering under strong force. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing superior impact resistance by holding fragments together upon breakage. This makes laminated glass a safer choice for applications requiring enhanced protection against impacts and break-ins.
UV Protection and Performance
Colored glass provides moderate UV protection by absorbing certain wavelengths, reducing glare and heat transmission, whereas laminated glass offers superior UV blocking through its interlayer, effectively filtering up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays. Laminated glass enhances safety by holding shards together upon impact, outperforming colored glass in preventing injury during breakage. Both options improve energy efficiency, but laminated glass is preferred in applications demanding stringent UV protection and high-performance safety glazing.
Aesthetic Considerations for Glazing
Colored glass offers a vibrant aesthetic appeal by incorporating natural or tinted hues directly into the glass, enhancing design flexibility and visual interest in architectural projects. Laminated glass, while primarily focused on safety and impact resistance, allows for the inclusion of interlayers with decorative films or fabrics, enabling customized patterns and textures without sacrificing strength. Both options harmonize safety with visual style, but colored glass delivers a more uniform coloration, whereas laminated glass provides versatile design opportunities through layered aesthetics.
Cost Comparison and Installation
Colored glass generally has a lower initial cost compared to laminated glass due to simpler manufacturing processes, while laminated glass involves higher expenses from its multi-layered construction with interlayers for enhanced safety. Installation of colored glass is typically more straightforward and quicker, reducing labor costs, whereas laminated glass requires careful handling and precise fitting to maintain its integrity and safety performance. Despite higher upfront and installation costs, laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and security, which may result in long-term savings by preventing damage and increasing durability.
Choosing the Best Safety Glazing for Your Needs
Colored glass offers aesthetic appeal and UV protection but may compromise visibility and strength compared to laminated glass, which provides superior impact resistance and holds shards together upon breakage, enhancing safety. Laminated glass is ideal for safety glazing in areas prone to impact or where glass integrity is critical, such as in automotive windshields or building facades. Choosing between colored and laminated glass depends on balancing design preferences with safety requirements and regulatory standards for impact resistance.
Infographic: Colored glass vs Laminated glass for Safety glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com