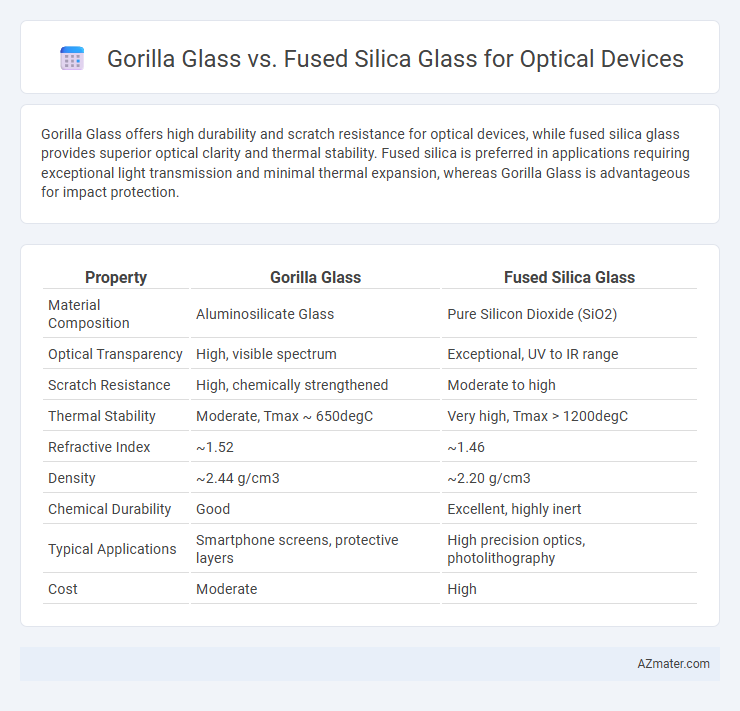
Gorilla Glass offers high durability and scratch resistance for optical devices, while fused silica glass provides superior optical clarity and thermal stability. Fused silica is preferred in applications requiring exceptional light transmission and minimal thermal expansion, whereas Gorilla Glass is advantageous for impact protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gorilla Glass | Fused Silica Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Aluminosilicate Glass | Pure Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) |
| Optical Transparency | High, visible spectrum | Exceptional, UV to IR range |
| Scratch Resistance | High, chemically strengthened | Moderate to high |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, Tmax ~ 650degC | Very high, Tmax > 1200degC |
| Refractive Index | ~1.52 | ~1.46 |
| Density | ~2.44 g/cm3 | ~2.20 g/cm3 |
| Chemical Durability | Good | Excellent, highly inert |
| Typical Applications | Smartphone screens, protective layers | High precision optics, photolithography |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Optical Device Glass Materials
Gorilla Glass and fused silica glass serve distinct roles in optical device applications due to their unique physical and chemical properties. Gorilla Glass, chemically strengthened through ion exchange, offers exceptional scratch resistance and durability, making it ideal for touchscreen surfaces and protective covers. Fused silica glass, composed of high-purity silicon dioxide, provides superior optical clarity, low thermal expansion, and excellent UV transparency, crucial for precision lenses, laser systems, and high-performance optical components.
Overview of Gorilla Glass
Gorilla Glass is a chemically strengthened alkali-aluminosilicate glass known for its high scratch resistance and durability, making it ideal for optical devices exposed to frequent handling and environmental stress. It offers superior toughness and impact resistance compared to traditional fused silica glass, which primarily provides excellent optical clarity and thermal stability but lower mechanical strength. The enhanced surface strength of Gorilla Glass enables thinner, lighter optical components without compromising durability, benefiting portable and rugged optical devices.
Overview of Fused Silica Glass
Fused silica glass is a high-purity, non-crystalline form of silicon dioxide known for its exceptional optical clarity, low thermal expansion, and superior resistance to UV radiation and thermal shock. It offers excellent transparency across a wide range of wavelengths, making it ideal for precision optical devices requiring minimal distortion and high durability. Compared to Gorilla Glass, fused silica excels in maintaining optical performance under extreme environmental conditions due to its stable chemical structure and enhanced thermal stability.
Optical Clarity and Transmission Comparison
Gorilla Glass offers high optical clarity with excellent scratch resistance, making it suitable for durable optical devices, while fused silica glass provides superior optical transmission across a broader wavelength range, especially in UV and infrared spectrums. Fused silica's low thermal expansion and high purity contribute to minimal light distortion and superior transparency compared to Gorilla Glass. For applications demanding highest optical clarity and transmission, fused silica glass remains the preferred choice, though Gorilla Glass balances durability and optical performance effectively.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Gorilla Glass offers superior mechanical strength with enhanced hardness and scratch resistance compared to fused silica glass, making it ideal for high-impact optical devices. While fused silica glass excels in thermal stability and optical clarity, its mechanical durability is lower, making it more prone to cracking under stress. The chemically strengthened composition of Gorilla Glass provides better resistance to mechanical wear and fracture, ensuring longer device lifespan in demanding environments.
Scratch and Abrasion Resistance
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance due to its chemically strengthened surface, making it highly durable for optical devices exposed to daily wear. Fused silica glass exhibits excellent abrasion resistance and maintains optical clarity under harsh environments, ideal for precision instruments requiring minimal surface distortion. Both materials provide robust protection, but Gorilla Glass excels in impact and scratch durability, while fused silica glass ensures enhanced abrasion resistance with stable optical performance.
Thermal and Chemical Stability
Gorilla Glass offers high chemical stability due to its alkali-aluminosilicate composition, making it resistant to scratches and surface degradation in optical devices. Fused silica glass exhibits superior thermal stability with a low coefficient of thermal expansion and excellent resistance to high temperatures, ensuring minimal distortion under extreme thermal conditions. For optical applications requiring both chemical durability and thermal resistance, fused silica glass outperforms Gorilla Glass in maintaining optical clarity and structural integrity.
Refractive Index and Light Manipulation
Gorilla Glass typically has a refractive index around 1.5, providing moderate light transmission with strong durability and scratch resistance suitable for optical device covers. Fused silica glass offers a lower refractive index near 1.46, enabling superior light manipulation with minimal chromatic aberration and high transmission in UV to IR wavelengths. The choice between Gorilla Glass and fused silica glass depends on the balance between optical clarity and mechanical robustness required for specialized optical applications.
Cost and Availability in Optical Applications
Gorilla Glass offers cost-effective manufacturing and widespread availability, making it a popular choice for optical device applications requiring durable, scratch-resistant surfaces. Fused silica glass, while more expensive and less readily available, provides superior optical clarity and thermal stability essential for high-precision optics and UV applications. The cost disparity arises from fused silica's complex fabrication process, limiting its use to specialized optical devices where performance justifies higher expense.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for Optical Devices
Gorilla Glass offers superior impact resistance and scratch durability, making it ideal for portable optical devices requiring robust protection. Fused silica glass provides exceptional optical clarity and thermal stability, essential for high-precision optical instruments and high-temperature environments. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing durability needs with optical performance requirements specific to the device's application.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs Fused silica glass for Optical device
 azmater.com
azmater.com