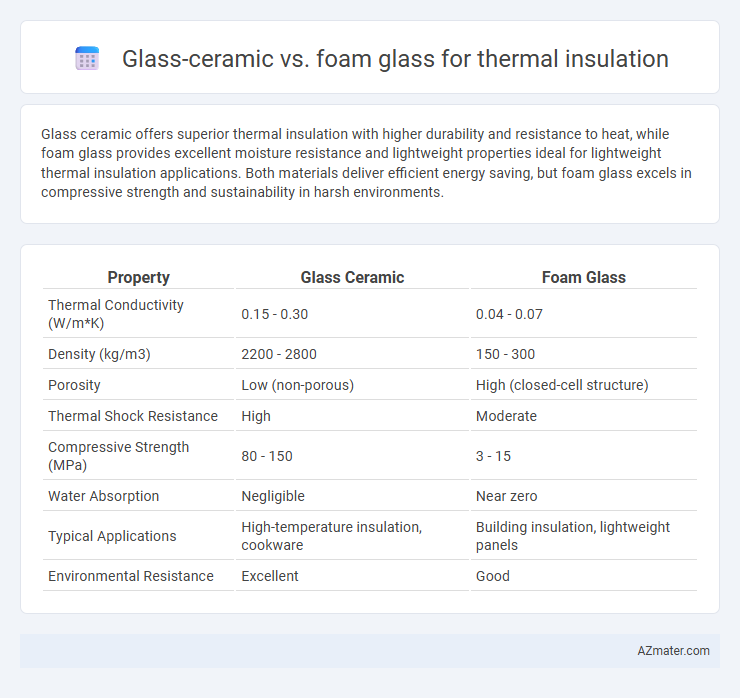
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal insulation with higher durability and resistance to heat, while foam glass provides excellent moisture resistance and lightweight properties ideal for lightweight thermal insulation applications. Both materials deliver efficient energy saving, but foam glass excels in compressive strength and sustainability in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Ceramic | Foam Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.15 - 0.30 | 0.04 - 0.07 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 2200 - 2800 | 150 - 300 |
| Porosity | Low (non-porous) | High (closed-cell structure) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 80 - 150 | 3 - 15 |
| Water Absorption | Negligible | Near zero |
| Typical Applications | High-temperature insulation, cookware | Building insulation, lightweight panels |
| Environmental Resistance | Excellent | Good |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Materials
Thermal insulation materials like glass ceramic and foam glass play a crucial role in reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in buildings and industrial applications. Glass ceramics offer high thermal stability, low thermal conductivity, and excellent mechanical strength due to their crystalline-amorphous structure, making them ideal for high-temperature environments. Foam glass, composed of recycled glass with a cellular structure, provides lightweight, moisture-resistant, and fireproof insulation with superior compressive strength and durability for various thermal insulation needs.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a type of material formed through controlled crystallization of certain glasses, resulting in a composite with both glassy and crystalline phases that enhance thermal stability and mechanical strength. It offers superior resistance to thermal shock and low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. Compared to foam glass, glass ceramic provides improved durability and heat resistance but may have higher density and manufacturing costs.
What is Foam Glass?
Foam glass is a highly durable, lightweight thermal insulation material made from recycled glass that is crushed, mixed with a foaming agent, and then heated to create a closed-cell structure filled with gas bubbles. It offers excellent thermal resistance, moisture impermeability, and fire resistance, making it ideal for various industrial and construction applications. Compared to glass ceramic, foam glass provides superior compressive strength and insulation performance in moisture-prone environments.
Thermal Insulation Properties: Glass Ceramic vs Foam Glass
Glass ceramic exhibits superior thermal insulation properties with low thermal conductivity typically ranging from 0.05 to 0.15 W/m*K, making it highly efficient for high-temperature applications. Foam glass, with thermal conductivity around 0.04 to 0.06 W/m*K, offers excellent insulation due to its closed-cell structure and lightweight nature, providing added benefits in moisture resistance and compressive strength. The choice between glass ceramic and foam glass largely depends on the specific thermal resistance requirements, mechanical durability, and environmental conditions of the insulation application.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Glass ceramic exhibits superior strength and durability compared to foam glass due to its dense, crystalline microstructure, which provides high mechanical resistance and thermal stability. Foam glass, while lightweight and possessing excellent thermal insulation properties, is more brittle and prone to cracking under mechanical stress. The robust composition of glass ceramic ensures longer lifespan and better resistance to thermal cycling, making it preferable for applications requiring sustained structural integrity.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Glass ceramic offers superior fire resistance with a high melting point above 1400degC, making it highly effective in withstanding extreme temperatures without deforming or releasing toxic fumes. Foam glass provides excellent thermal insulation combined with non-combustibility and minimal smoke emission, ensuring fire safety in building applications. Both materials are non-toxic and resistant to combustion, but glass ceramic's structural integrity under fire conditions surpasses foam glass, enhancing long-term safety in high-risk environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass ceramic offers high thermal insulation with excellent durability and recyclability, reducing waste over time. Foam glass is composed of recycled glass, providing superior insulation while being non-toxic, moisture-resistant, and highly sustainable due to its closed-cell structure and long lifespan. Both materials contribute to eco-friendly building practices, but foam glass often excels in minimizing environmental impact through lower embodied energy and enhanced recyclability.
Installation and Application Methods
Glass ceramic insulation offers superior thermal stability and is commonly installed in rigid board or tile form, suitable for high-temperature industrial applications requiring precise shaping and fast installation using adhesives or mechanical fasteners. Foam glass insulation, characterized by its lightweight and closed-cell structure, is typically applied as blocks or panels ideal for pipe insulation, roofing, and perimeter insulation, installed with cementitious mortars or adhesives due to its compressive strength and moisture resistance. Both materials require surface preparation and careful handling to maintain insulating performance, with foam glass favored in moisture-prone environments and glass ceramic preferred for extreme heat or fire resistance.
Cost Analysis: Glass Ceramic vs Foam Glass
Glass ceramic insulation typically incurs higher upfront costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior thermal stability. Foam glass offers a more cost-effective solution, with lower material and installation expenses, making it ideal for large-scale projects requiring budget efficiency. Despite the initial price difference, glass ceramic's enhanced durability and insulation performance can result in long-term energy savings and reduced maintenance costs.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Glass ceramic offers superior thermal stability and higher temperature resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durable insulation under extreme heat. Foam glass provides excellent moisture resistance and compressive strength, suitable for environments exposed to water or mechanical stress. Selecting the right material depends on project-specific factors like temperature range, structural demands, and exposure to moisture.
Infographic: Glass ceramic vs Foam glass for Thermal insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com