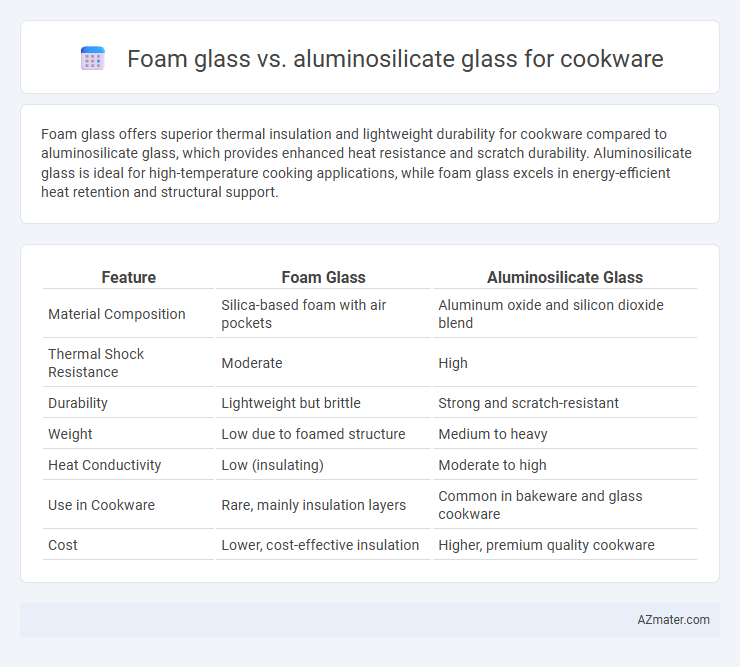
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight durability for cookware compared to aluminosilicate glass, which provides enhanced heat resistance and scratch durability. Aluminosilicate glass is ideal for high-temperature cooking applications, while foam glass excels in energy-efficient heat retention and structural support.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Foam Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silica-based foam with air pockets | Aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide blend |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Durability | Lightweight but brittle | Strong and scratch-resistant |
| Weight | Low due to foamed structure | Medium to heavy |
| Heat Conductivity | Low (insulating) | Moderate to high |
| Use in Cookware | Rare, mainly insulation layers | Common in bakeware and glass cookware |
| Cost | Lower, cost-effective insulation | Higher, premium quality cookware |
Introduction to Cookware Materials
Foam glass offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight durability, making it suitable for cookware requiring heat retention and resistance to thermal shock. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its high strength, chemical stability, and resistance to thermal expansion, is commonly used in cookware to withstand rapid temperature changes and prevent breakage. Both materials serve distinct purposes in cookware, with foam glass excelling in insulation and aluminosilicate glass providing robust, heat-resistant surfaces.
What is Foam Glass?
Foam glass is a lightweight, porous material created by heating crushed glass with foaming agents, forming a durable, insulating structure ideal for cookware bases and insulation layers. Its closed-cell composition provides excellent thermal insulation and resistance to heat shock, distinguishing it from dense, non-porous aluminosilicate glass commonly used for cookware surfaces. Foam glass enhances heat retention and energy efficiency, making it a valuable component in advanced cookware designs.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a high-strength, heat-resistant material composed primarily of alumina (Al2O3) and silica (SiO2), widely used in cookware for its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. Compared to foam glass, aluminosilicate glass offers superior durability, scratch resistance, and transparency, making it ideal for oven-safe and microwave-safe cookware. Its chemical composition allows it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, ensuring longevity and safety during cooking processes.
Heat Resistance Comparison
Foam glass offers excellent heat resistance up to approximately 700degC, making it highly durable for high-temperature cookware applications. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in cookware, withstands thermal shock and heat up to around 500degC but typically performs better under rapid temperature changes. The superior heat tolerance of foam glass allows it to maintain structural integrity at higher temperatures, while aluminosilicate glass excels in resistance to thermal shock during everyday cooking.
Thermal Shock Performance
Foam glass exhibits superior thermal shock resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass, making it highly suitable for cookware exposed to rapid temperature changes. Its cellular structure allows efficient heat dissipation, reducing the risk of cracking under extreme thermal gradients. Aluminosilicate glass, while durable and resistant to chemical corrosion, generally has lower thermal shock performance due to its denser, less porous composition.
Durability and Lifespan
Foam glass offers exceptional durability due to its cellular structure, providing high resistance to thermal shock and mechanical impact, making it less prone to cracking or breaking over time. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its enhanced chemical and thermal stability, delivers superior resistance to high temperatures and sudden temperature changes, extending cookware lifespan significantly compared to standard glass. Both materials provide long-lasting performance, but aluminosilicate glass typically offers greater longevity under extreme cooking conditions.
Chemical Resistance and Safety
Foam glass exhibits superior chemical resistance due to its inert silica composition, making it highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and other corrosive substances commonly encountered in cookware use. Aluminosilicate glass, while durable and resistant to thermal shock, can be more susceptible to chemical degradation from prolonged exposure to strong bases or acids. Safety profiles favor foam glass for applications requiring long-term chemical stability, whereas aluminosilicate glass offers robust heat resistance but necessitates cautious use with aggressive chemicals.
Weight and Handling Differences
Foam glass cookware is significantly lighter than aluminosilicate glass, making it easier to handle and reducing fatigue during use. The lightweight nature of foam glass also offers improved maneuverability in the kitchen without compromising durability. In contrast, aluminosilicate glass is denser and heavier, providing better heat retention but requiring more effort to lift and transport.
Cost and Availability
Foam glass cookware is generally more expensive due to its specialized manufacturing process and limited availability, making it less common in mainstream markets. Aluminosilicate glass offers a cost-effective alternative with widespread availability, commonly found in various cookware brands due to its durability and heat resistance. Consumers seeking affordable and easily accessible cookware typically prefer aluminosilicate glass over foam glass options.
Which Glass is Better for Cookware?
Foam glass offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it less suitable for direct cookware applications due to its porous structure and potential fragility under thermal shock. Aluminosilicate glass is superior for cookware because of its high thermal resistance, durability, and resistance to chemical corrosion, ensuring safe cooking at varying temperatures. The dense, non-porous nature of aluminosilicate glass enhances safety and longevity, confirming it as the preferred choice for cookware manufacturing.
Infographic: Foam glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com