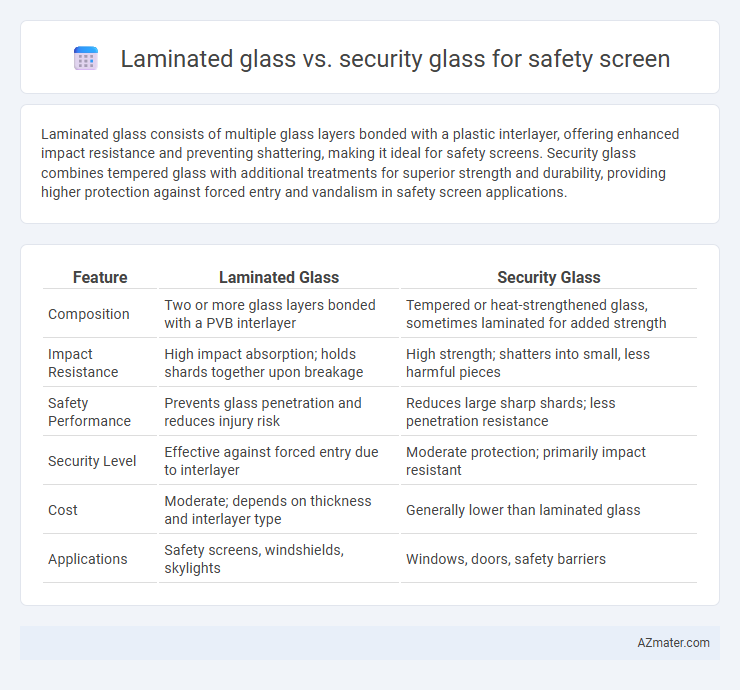
Laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, offering enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering, making it ideal for safety screens. Security glass combines tempered glass with additional treatments for superior strength and durability, providing higher protection against forced entry and vandalism in safety screen applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Security Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with a PVB interlayer | Tempered or heat-strengthened glass, sometimes laminated for added strength |
| Impact Resistance | High impact absorption; holds shards together upon breakage | High strength; shatters into small, less harmful pieces |
| Safety Performance | Prevents glass penetration and reduces injury risk | Reduces large sharp shards; less penetration resistance |
| Security Level | Effective against forced entry due to interlayer | Moderate protection; primarily impact resistant |
| Cost | Moderate; depends on thickness and interlayer type | Generally lower than laminated glass |
| Applications | Safety screens, windshields, skylights | Windows, doors, safety barriers |
Introduction to Safety Screens: Laminated vs Security Glass
Safety screens using laminated glass provide enhanced impact resistance by bonding multiple layers of glass with a durable interlayer, preventing shattering and offering superior protection against break-ins and accidents. Security glass, often incorporating tempered glass with reinforced elements, delivers high strength and shatterproof performance designed to withstand forced entry and extreme impacts. Both laminated and security glass prioritize safety, but laminated glass excels in retaining glass fragments while security glass focuses on overall toughness and resistance to penetration.
Understanding Laminated Glass: Composition and Features
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances safety by holding shards in place upon impact. This composition provides excellent resistance to penetration, reducing the risk of injury from broken glass, making it ideal for safety screens in high-traffic or vulnerable areas. Its sound insulation properties and UV protection add functional benefits, distinguishing laminated glass from standard security glass options.
What is Security Glass? Types and Characteristics
Security glass is a reinforced glass designed to resist impact, breakage, and forced entry, commonly used in safety screens for enhanced protection. It typically includes laminated glass, tempered glass, or a combination, with laminated glass featuring layers of glass bonded by a resilient interlayer that holds shards together upon impact. Characteristics of security glass include high resistance to shattering, improved durability, and compliance with safety standards like ASTM or EN 356, making it ideal for preventing injury and deterring intruders.
Key Differences Between Laminated and Security Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced durability and preventing shattering upon impact, making it ideal for safety screens. Security glass, often made from tempered or toughened glass, is heat-treated to increase strength and resistance to breakage but may still shatter into small, less dangerous pieces when broken. Key differences lie in laminated glass's ability to hold fragments together, offering better protection from intrusion and injury, whereas security glass focuses on strength and impact resistance but lacks the same level of fragment retention.
Impact Resistance: Which Glass Offers Better Protection?
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing excellent impact resistance by holding shards together upon breakage, reducing the risk of injury. Security glass, often tempered or chemically strengthened, offers higher strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces, minimizing severe cuts but may not stay intact like laminated glass. For safety screens, laminated glass offers superior protection by combining impact resistance with structural integrity, preventing penetration and maintaining visual clarity after impacts.
Intrusion Prevention: Effectiveness of Each Glass Type
Laminated glass consists of multiple layers bonded with an interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, significantly reducing the likelihood of penetration during forced entry attempts. Security glass, often made with tempered or specially treated materials, offers enhanced resistance to impact and shattering but may vary in effectiveness depending on thickness and construction. For intrusion prevention in safety screens, laminated glass generally provides superior protection by maintaining integrity while delaying or deterring break-in efforts.
Soundproofing and UV Protection: Added Benefits Compared
Laminated glass offers superior soundproofing due to its interlayer that effectively dampens noise, making it ideal for safety screens in noise-sensitive environments. Both laminated and security glass provide UV protection; however, laminated glass typically includes a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that blocks up to 99% of harmful UV rays. Security glass focuses more on impact resistance and shatterproof qualities, whereas laminated glass combines safety with enhanced acoustic insulation and UV shielding benefits.
Cost Analysis: Laminated Glass vs Security Glass
Laminated glass generally offers a lower initial cost compared to security glass, making it a more budget-friendly option for safety screens without compromising basic protection. Security glass, often made from tempered or reinforced materials, incurs higher manufacturing and installation costs but provides superior impact resistance and durability, which can reduce long-term replacement expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, laminated glass may require more frequent replacement after damage, whereas security glass investments often yield better economic value through enhanced lifespan and safety performance.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Laminated glass offers easier installation for safety screens due to its lightweight nature and single-pane design, reducing labor time and costs. Security glass, often thicker and composed of multiple layers or tempered components, requires specialized mounting systems and skilled handling to ensure proper fit and performance. Maintenance of laminated glass involves routine checks for delamination and surface cracks, while security glass demands inspection for impact resistance integrity and potential shatter risks.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Safety Screen Needs
Laminated glass provides enhanced safety by holding fragments together upon impact, reducing injury risk, while security glass offers superior strength and resistance to forced entry due to its reinforced layers. When choosing the right glass for your safety screen needs, consider factors like impact resistance, durability, and the level of protection required against break-ins or accidents. Prioritize laminated glass for applications emphasizing shatter prevention and security glass for maximum protection in high-risk environments.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Security glass for Safety screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com