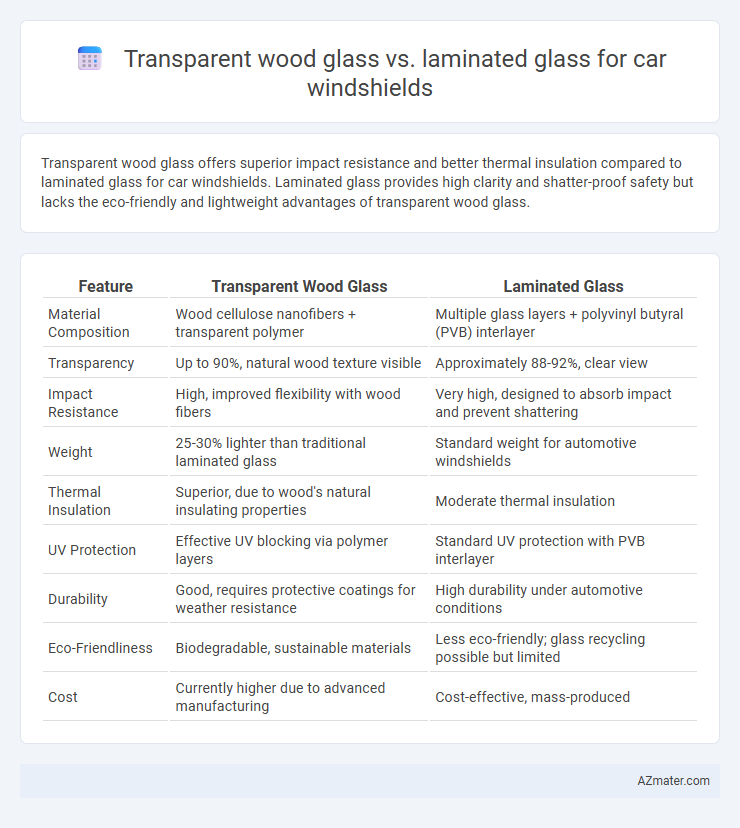
Transparent wood glass offers superior impact resistance and better thermal insulation compared to laminated glass for car windshields. Laminated glass provides high clarity and shatter-proof safety but lacks the eco-friendly and lightweight advantages of transparent wood glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Wood Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood cellulose nanofibers + transparent polymer | Multiple glass layers + polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Transparency | Up to 90%, natural wood texture visible | Approximately 88-92%, clear view |
| Impact Resistance | High, improved flexibility with wood fibers | Very high, designed to absorb impact and prevent shattering |
| Weight | 25-30% lighter than traditional laminated glass | Standard weight for automotive windshields |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior, due to wood's natural insulating properties | Moderate thermal insulation |
| UV Protection | Effective UV blocking via polymer layers | Standard UV protection with PVB interlayer |
| Durability | Good, requires protective coatings for weather resistance | High durability under automotive conditions |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable materials | Less eco-friendly; glass recycling possible but limited |
| Cost | Currently higher due to advanced manufacturing | Cost-effective, mass-produced |
Introduction to Transparent Wood Glass and Laminated Glass
Transparent wood glass, an emerging material combining cellulose nanofibers with polymer resins, offers enhanced strength and light diffusion ideal for automotive applications. Laminated glass, traditionally composed of two glass layers bonded with an interlayer such as polyvinyl butyral (PVB), provides superior impact resistance and safety by preventing shattering in car windshields. Both materials present distinct advantages in durability, clarity, and safety features essential for vehicle windshield performance.
Material Composition and Structure
Transparent wood glass combines cellulose fibers from wood with a polymer matrix, creating a lightweight, shatter-resistant composite with high optical clarity. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded by an interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), offering enhanced impact resistance and preventing shards upon breakage. The structure of transparent wood glass allows for superior energy absorption and sustainability, while laminated glass emphasizes safety through its layered design and proven durability in automotive applications.
Optical Clarity and Transparency Comparison
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced optical clarity by reducing glare and minimizing light distortion compared to laminated glass, which can have slight haze due to interlayer adhesives. The natural cellulose fibers in transparent wood maintain high transparency while providing improved light diffusion, resulting in clearer, more comfortable visibility for drivers. Laminated glass typically achieves transparency through multiple layers of glass and plastic, but may suffer from minor optical imperfections that transparent wood glass can mitigate.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Transparent wood glass exhibits enhanced mechanical strength due to its unique fiber-reinforced structure, offering higher impact resistance and better energy absorption compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass, commonly used in car windshields, provides excellent durability through its multi-layer design that prevents shattering but is more prone to crack propagation under extreme stress. The natural flexibility and fracture toughness of transparent wood glass contribute to longer service life and improved safety performance in automotive applications.
Impact Resistance and Safety Features
Transparent wood glass offers superior impact resistance due to its natural fiber-reinforced composite structure, which absorbs and disperses energy more effectively than traditional laminated glass. Laminated glass, made of two layers of glass with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), provides strong shatter resistance by holding glass fragments together during impact, enhancing passenger safety. While laminated glass is widely used in car windshields for its certified safety standards, transparent wood glass shows promising improvements in reducing crack propagation and increasing durability under high-impact conditions.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection
Transparent wood glass offers superior energy efficiency due to its natural insulating properties, reducing heat transfer and minimizing the need for air conditioning in vehicles. Its cellulose-based structure provides effective UV protection by blocking harmful rays, preventing interior fading and enhancing passenger comfort. In contrast, laminated glass primarily relies on plastic interlayers for UV blocking and offers less thermal insulation, making transparent wood glass a more eco-friendly and energy-saving option for car windshields.
Weight Considerations for Vehicle Design
Transparent wood glass offers a significant weight reduction compared to traditional laminated glass, enhancing fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Its low density and high strength-to-weight ratio contribute to superior impact resistance while minimizing structural load on the car frame. The lighter weight of transparent wood glass enables innovative vehicle design possibilities, promoting better handling and reduced emissions.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing
Transparent wood glass offers potential cost-effectiveness through sustainable raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes compared to laminated glass, which involves multiple layers of glass and plastic interlayers increasing production complexity and cost. Manufacturing transparent wood glass leverages wood cellulose nanofibrils combined with transparent polymers, enabling lower energy consumption and environmental impact than the high-temperature lamination and curing required for laminated glass. However, laminated glass benefits from established production lines, scalability, and regulatory approvals, often leading to broader market availability despite higher material and manufacturing expenses.
Environmental Sustainability and Recyclability
Transparent wood glass offers superior environmental sustainability compared to laminated glass for car windshields due to its renewable cellulose-based composition and lower carbon footprint during production. The biodegradability and ease of recycling transparent wood reduce landfill waste, whereas laminated glass, composed of multiple plastic and glass layers, poses challenges in recycling and contributes to persistent environmental pollution. Adopting transparent wood glass enhances circular economy goals in automotive manufacturing, promoting sustainable resource use and reducing ecological impact.
Future Prospects in Automotive Windshields
Transparent wood glass offers significant potential for future automotive windshields due to its lightweight, high strength, and excellent optical clarity, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and safety. Advances in nanotechnology and cellulose processing are expected to enhance its durability, UV resistance, and impact absorption, positioning it as a sustainable alternative to traditional laminated glass. Continued research on scalability and cost-effectiveness will be crucial for its widespread adoption in next-generation vehicle designs.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs Laminated glass for Car windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com