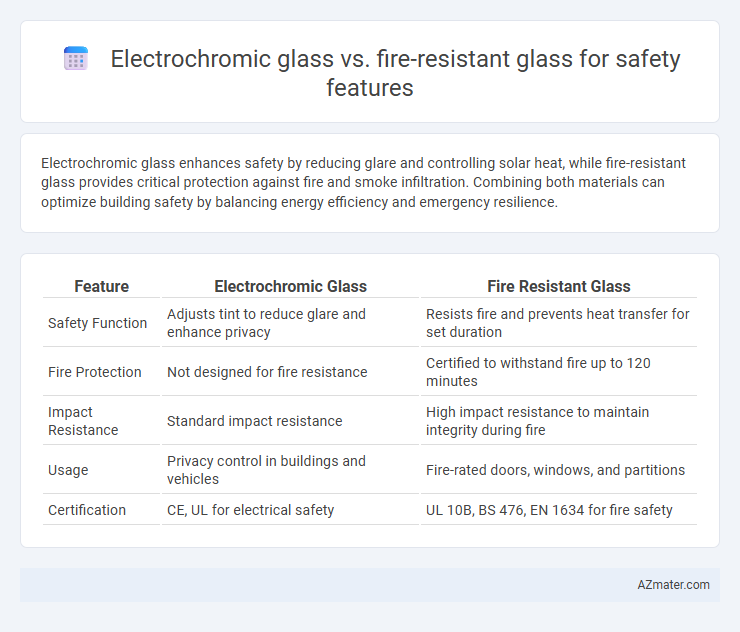
Electrochromic glass enhances safety by reducing glare and controlling solar heat, while fire-resistant glass provides critical protection against fire and smoke infiltration. Combining both materials can optimize building safety by balancing energy efficiency and emergency resilience.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Fire Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Safety Function | Adjusts tint to reduce glare and enhance privacy | Resists fire and prevents heat transfer for set duration |
| Fire Protection | Not designed for fire resistance | Certified to withstand fire up to 120 minutes |
| Impact Resistance | Standard impact resistance | High impact resistance to maintain integrity during fire |
| Usage | Privacy control in buildings and vehicles | Fire-rated doors, windows, and partitions |
| Certification | CE, UL for electrical safety | UL 10B, BS 476, EN 1634 for fire safety |
Introduction to Electrochromic and Fire Resistant Glass
Electrochromic glass enhances safety by dynamically adjusting its transparency to control glare and heat, improving visibility and reducing reliance on blinds or shades. Fire-resistant glass provides critical safety by containing fires, maintaining structural integrity, and preventing the spread of flames and smoke during emergencies. Both technologies serve distinct safety roles, with electrochromic glass focusing on environmental comfort and fire-resistant glass prioritizing fire containment and protection.
How Electrochromic Glass Works
Electrochromic glass enhances safety by dynamically adjusting its transparency through a low-voltage electrical current that alters the oxidation state of its electrochromic layers, thereby controlling light and heat transmission. Unlike fire-resistant glass, which primarily provides passive protection by resisting fire and heat for a specific duration, electrochromic glass actively reduces glare, solar heat gain, and improves occupant comfort, potentially lowering heat-related hazards. This innovative functionality makes electrochromic glass a key component in energy-efficient, safe building designs where automatic light modulation is essential.
Fire Resistant Glass: Key Mechanisms
Fire resistant glass enhances safety by maintaining structural integrity and slowing heat transfer during a fire, using specialized layers that insulate and prevent flames and smoke from spreading. Its core mechanism involves a heat-absorbing gel or intumescent interlayer that swells when exposed to high temperatures, creating a barrier against heat and flames. Unlike electrochromic glass, which primarily offers light control and privacy, fire resistant glass is specifically engineered to meet stringent fire safety standards, making it essential for fire-rated windows and doors.
Comparing Safety Features: Electrochromic vs Fire Resistant Glass
Electrochromic glass offers enhanced safety by controlling glare and reducing UV exposure through adjustable tinting, which helps protect occupants from harmful sun rays and improves visibility in varying light conditions. Fire resistant glass provides critical safety by withstanding high temperatures and preventing the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, thereby allowing more time for evacuation and limiting structural damage. While electrochromic glass improves daily comfort and eye safety, fire resistant glass is essential for life safety in fire emergencies, making each suitable for different safety priorities in building design.
Impact on Building Occupant Safety
Electrochromic glass enhances occupant safety by dynamically controlling glare and heat, reducing eye strain and improving comfort, which indirectly contributes to well-being and alertness. Fire resistant glass provides critical safety by preventing fire spread and maintaining structural integrity during emergencies, offering vital protection and safe evacuation pathways. The choice depends on balancing comfort benefits from electrochromic technology against the essential life-saving barrier afforded by fire resistant glass.
Energy Efficiency and Security Benefits
Electrochromic glass enhances energy efficiency by dynamically controlling solar heat and glare, reducing HVAC loads and improving occupant comfort. Fire-resistant glass provides critical security benefits by withstanding high temperatures and preventing fire spread, ensuring structural integrity and safe evacuation routes. Combining these technologies optimizes building safety while minimizing energy consumption and maximizing protection against fire hazards.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Electrochromic glass must comply with standards such as ANSI Z97.1 for safety glazing and may meet energy efficiency certifications like LEED, ensuring smart shading with safety. Fire-resistant glass is rigorously tested under ASTM E119 and EN 1364-1 standards, providing fire containment and smoke control, often certified by UL for fire ratings from 20 to 120 minutes. Regulatory compliance for fire-resistant glass is critical in building codes to prevent fire spread, whereas electrochromic glass focuses on occupant safety through impact resistance and energy performance certifications.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Electrochromic glass requires precise electrical wiring and controls for installation, often involving integration with building automation systems, while fire resistant glass demands strict adherence to fire safety standards and framing compatibility to ensure its protective integrity. Maintenance of electrochromic glass includes regular checks on electrical components and system calibration, whereas fire resistant glass necessitates periodic inspections for physical damage or seal degradation to maintain its fire-rating effectiveness. Both types require professional servicing, but fire resistant glass often involves less frequent electrical troubleshooting compared to electrochromic glass.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-Term Value
Electrochromic glass generally requires a higher initial investment due to advanced technology and installation complexity, whereas fire resistant glass tends to have a lower upfront cost but may involve higher replacement expenses after exposure to fire. Over the long term, electrochromic glass offers energy savings by reducing HVAC loads and glare, which can offset its initial price and provide enhanced occupant comfort. Fire resistant glass ensures critical safety compliance and durability during fire incidents, potentially reducing damage costs and liability, making it a valuable safety investment despite limited operational savings.
Choosing the Right Glass for Enhanced Safety
Electrochromic glass enhances safety by providing dynamic control over light and glare, reducing heat and UV exposure, which improves occupant comfort and visibility during emergencies. Fire-resistant glass offers critical protection by withstanding high temperatures and preventing the spread of flames and smoke, essential for maintaining structural integrity and safe evacuation. Selecting the right glass requires evaluating safety priorities: electrochromic glass excels in daily comfort and visibility control, while fire-resistant glass is vital for fire containment and life safety compliance.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Fire resistant glass for Safety feature
 azmater.com
azmater.com