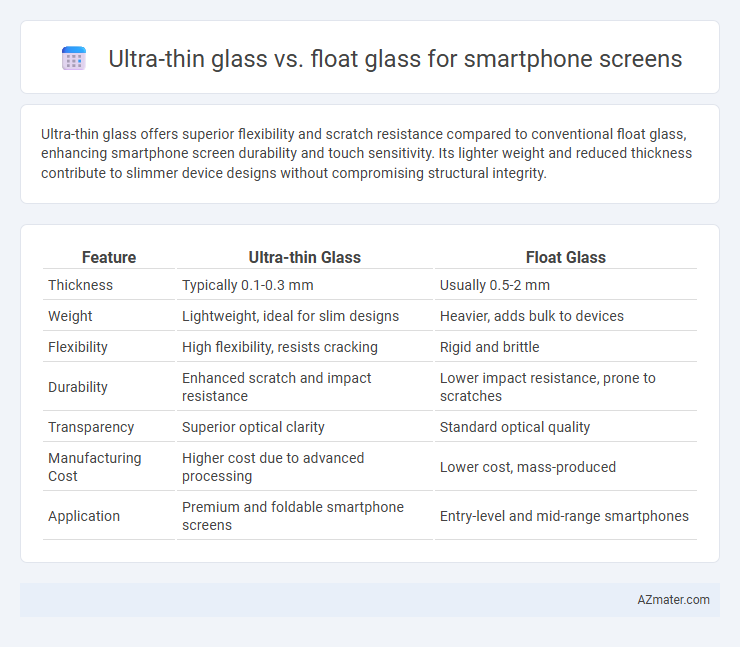
Ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility and scratch resistance compared to conventional float glass, enhancing smartphone screen durability and touch sensitivity. Its lighter weight and reduced thickness contribute to slimmer device designs without compromising structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-thin Glass | Float Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Typically 0.1-0.3 mm | Usually 0.5-2 mm |
| Weight | Lightweight, ideal for slim designs | Heavier, adds bulk to devices |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, resists cracking | Rigid and brittle |
| Durability | Enhanced scratch and impact resistance | Lower impact resistance, prone to scratches |
| Transparency | Superior optical clarity | Standard optical quality |
| Manufacturing Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing | Lower cost, mass-produced |
| Application | Premium and foldable smartphone screens | Entry-level and mid-range smartphones |
Introduction: Ultra-Thin Glass vs Float Glass
Ultra-thin glass offers superior thinness and flexibility compared to standard float glass, making it ideal for modern smartphone screens that demand durability and lightweight design. Float glass, while cost-effective and widely used, lacks the advanced scratch resistance and bendability of ultra-thin glass. The adoption of ultra-thin glass enhances screen sensitivity and resistance to cracks, significantly improving the overall user experience in smartphones.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Ultra-thin glass for smartphone screens is typically made from aluminosilicate glass, which is chemically strengthened through ion exchange, enhancing its durability and flexibility compared to traditional float glass composed primarily of soda-lime silica glass. The manufacturing of ultra-thin glass involves precise thinning processes such as controlled polishing and tempering to achieve thicknesses below 100 microns without compromising structural integrity. In contrast, float glass is produced by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, resulting in thicker, less flexible sheets primarily used for non-mobile screen applications.
Thickness and Flexibility Comparison
Ultra-thin glass (UTG) typically ranges from 30 to 100 micrometers in thickness, significantly thinner than standard float glass, which usually measures around 0.5 to 1 millimeter. The reduced thickness of UTG enhances its flexibility, allowing it to bend and conform to curved smartphone screens without breaking, unlike float glass that remains rigid due to its greater thickness. This flexibility and slim profile make UTG the preferred choice for foldable and curved display smartphones, where durability and seamless design are critical.
Optical Clarity and Display Quality
Ultra-thin glass offers superior optical clarity and enhanced display quality compared to traditional float glass due to its reduced thickness and higher light transmittance, minimizing reflection and distortion. Its lower haze and improved surface flatness enable more vibrant colors and sharper images, crucial for high-resolution smartphone screens. Float glass, being thicker and less refined, often results in slight color shifts and diminished clarity, making ultra-thin glass the preferred choice for premium smartphone displays.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Ultra-thin glass offers superior durability and scratch resistance compared to traditional float glass due to its chemically strengthened surface and reduced thickness, making it less prone to cracking under impact. Float glass, although cost-effective, lacks the robust protective properties of ultra-thin glass, often resulting in easier scratches and lower resistance to drops. Advanced manufacturing techniques in ultra-thin glass enhance its flexibility and toughness, making it the preferred choice for premium smartphone screens.
Impact Resistance and Drop Protection
Ultra-thin glass for smartphone screens offers enhanced impact resistance due to its higher tensile strength and flexibility compared to traditional float glass, which tends to be more rigid and prone to shattering upon impact. The reduced thickness and specialized chemical treatments of ultra-thin glass improve drop protection by absorbing and dissipating shock more effectively. In contrast, float glass, commonly used in older or budget models, lacks these advanced properties, leading to lower durability and a higher likelihood of screen damage from drops.
Weight and Device Ergonomics
Ultra-thin glass significantly reduces the weight of smartphone screens compared to conventional float glass, enhancing overall device ergonomics by making handheld usage more comfortable and less fatiguing. Its superior thinness enables slimmer device profiles without compromising durability, contributing to improved balance and ease of grip. The lighter nature of ultra-thin glass supports extended usage periods and portable convenience, essential factors for modern smartphone design.
Cost Implications and Market Availability
Ultra-thin glass offers superior durability and enhanced touch sensitivity for smartphone screens, but its advanced manufacturing process drives higher production costs compared to conventional float glass. Float glass remains widely available and cost-effective, making it the standard choice for budget and mid-range smartphones despite its lower scratch resistance and optical clarity. Market demand for premium devices is gradually increasing the adoption of ultra-thin glass, allowing manufacturers to scale production and potentially reduce costs over time.
Application in Modern Smartphone Designs
Ultra-thin glass, typically less than 100 microns thick, offers enhanced flexibility and durability, making it ideal for foldable and curved smartphone screens compared to traditional float glass. This advanced material supports higher scratch resistance and improved touch sensitivity, crucial for edge-to-edge displays in modern smartphone designs. Manufacturers increasingly prefer ultra-thin glass to achieve slimmer profiles and more immersive user experiences, outperforming float glass in both weight reduction and mechanical robustness.
Future Trends in Smartphone Screen Technology
Ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility and reduced thickness compared to traditional float glass, enabling more durable, lightweight, and curved smartphone displays. Future trends prioritize Ultra-thin glass for foldable and rollable screens, driven by advancements in chemical strengthening and scratch resistance technologies. As smartphone manufacturers seek seamless integration of touch sensitivity and enhanced visual clarity, Ultra-thin glass is positioned to dominate next-generation screen innovations.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Float glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com