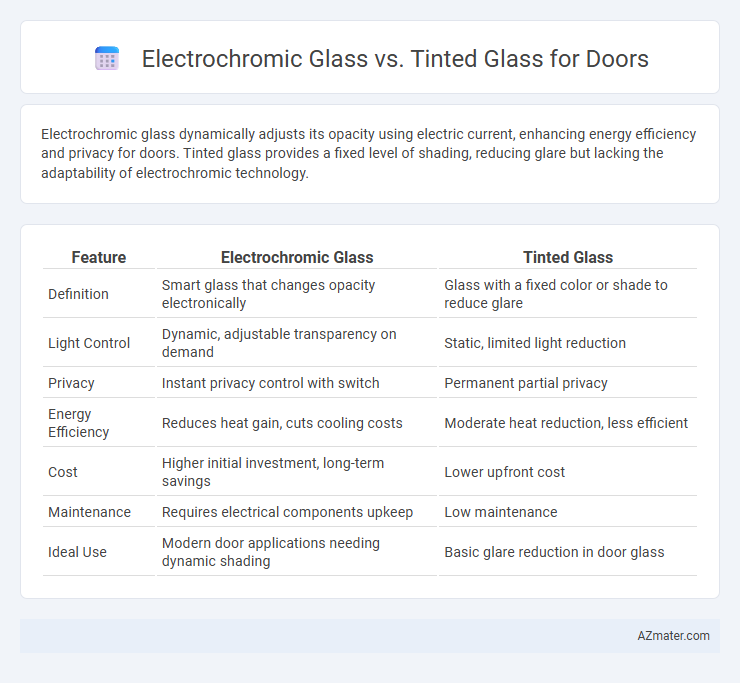
Electrochromic glass dynamically adjusts its opacity using electric current, enhancing energy efficiency and privacy for doors. Tinted glass provides a fixed level of shading, reducing glare but lacking the adaptability of electrochromic technology.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Smart glass that changes opacity electronically | Glass with a fixed color or shade to reduce glare |
| Light Control | Dynamic, adjustable transparency on demand | Static, limited light reduction |
| Privacy | Instant privacy control with switch | Permanent partial privacy |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces heat gain, cuts cooling costs | Moderate heat reduction, less efficient |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, long-term savings | Lower upfront cost |
| Maintenance | Requires electrical components upkeep | Low maintenance |
| Ideal Use | Modern door applications needing dynamic shading | Basic glare reduction in door glass |
Introduction to Electrochromic and Tinted Glass
Electrochromic glass uses a technology that allows its transparency and tint to change dynamically through an applied electrical voltage, offering adjustable privacy and solar control. Tinted glass, on the other hand, contains fixed pigments or films that reduce light transmission and heat gain but do not change once manufactured. For door applications, electrochromic glass provides versatility in light and heat management, while tinted glass offers a consistent, maintenance-free shading solution.
How Electrochromic Glass Works
Electrochromic glass functions through a low-voltage electrical charge that alters its transparency by changing the oxidation state of its conductive layers, allowing precise control over light and heat transmission. Unlike traditional tinted glass, which passively reduces glare and heat by absorbing or reflecting sunlight, electrochromic glass can dynamically switch between clear and tinted states on demand. This technology enhances energy efficiency, privacy, and comfort for doors by optimizing natural light without sacrificing visibility or style.
How Tinted Glass Functions
Tinted glass for doors functions by absorbing and reflecting a portion of sunlight, thereby reducing glare and heat transmission into the interior space. Its color pigmentation is embedded during manufacturing, which filters specific wavelengths of visible and infrared light to improve energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Unlike electrochromic glass, tinted glass provides a fixed level of shading without the ability to change transparency dynamically.
Key Differences Between Electrochromic and Tinted Glass
Electrochromic glass dynamically changes its opacity through an applied electrical voltage, offering adjustable light transmission and enhanced energy efficiency, while tinted glass possesses a fixed shade that reduces glare and heat without control flexibility. Electrochromic glass integrates smart technology for user-controlled privacy and solar heat modulation, whereas tinted glass relies on permanent pigments or films embedded during manufacturing. The key difference lies in electrochromic glass's adaptive functionality versus the static nature of tinted glass, impacting cost, energy savings, and user experience in door applications.
Aesthetic Impact on Door Design
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control, allowing users to switch between transparent and opaque states, significantly enhancing modern door designs with sleek, futuristic aesthetics. Tinted glass provides a static color or shade, contributing consistent privacy and sun protection but limiting design flexibility. The adaptive nature of electrochromic glass creates a visually striking focal point, while tinted glass emphasizes traditional, understated elegance in door applications.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Electrochromic glass offers superior energy efficiency for doors by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and natural light, reducing HVAC load throughout the day. Tinted glass provides fixed shading, limiting visible light and heat but often leading to less optimal indoor temperature regulation and higher energy consumption. Smart electrochromic technology adapts to environmental conditions, resulting in significant energy savings compared to conventional tinted glass.
Privacy and Light Control Features
Electrochromic glass provides dynamic privacy by electronically adjusting its opacity, allowing users to switch between transparent and opaque states for optimal light control and privacy on demand. Tinted glass offers a static solution by reducing light transmission and glare but cannot be altered, limiting flexibility in varying lighting conditions. For door applications requiring adaptable privacy and daylight management, electrochromic glass outperforms tinted glass by enabling customizable transparency and superior control over light intensity.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Electrochromic glass requires professional installation with integrated electrical wiring and control systems, making it more complex than the straightforward fitting process of tinted glass. Maintenance for electrochromic glass involves periodic checks of the electrical components and potential software updates, whereas tinted glass demands minimal upkeep, primarily cleaning to maintain clarity. The higher installation and maintenance complexity of electrochromic glass correspond to its advanced light-adjusting features compared to the fixed shading properties of tinted glass.
Cost Analysis: Electrochromic vs Tinted Glass
Electrochromic glass generally incurs higher upfront costs, ranging from $50 to $120 per square foot, compared to tinted glass which typically costs between $10 to $30 per square foot. While electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control and energy savings through adjustable transparency, tinted glass provides static shading at a fraction of the installation expense. Over a 10- to 15-year period, the energy efficiency benefits and reduced HVAC costs associated with electrochromic glass can offset its initial premium, making it a cost-effective solution for smart building applications.
Which Glass Type Is Best for Doors?
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control and energy efficiency, making it ideal for doors in modern buildings seeking customizable privacy and solar heat management. Tinted glass provides a fixed reduction in glare and UV rays but lacks adaptability to changing light conditions. For doors requiring versatility in transparency, energy savings, and occupant comfort, electrochromic glass is the superior choice.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Tinted glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com