Potash-lime glass offers lower thermal conductivity and superior moisture resistance compared to fiberglass, enhancing insulation durability in humid environments. Fiberglass provides higher tensile strength and flexibility, making it suitable for varied insulation applications requiring structural reinforcement.
Table of Comparison
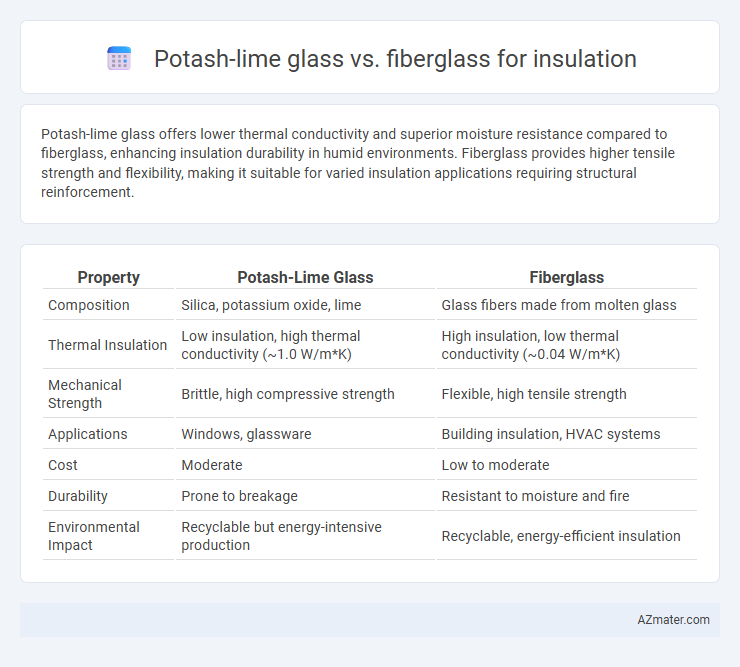
| Property | Potash-Lime Glass | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, potassium oxide, lime | Glass fibers made from molten glass |
| Thermal Insulation | Low insulation, high thermal conductivity (~1.0 W/m*K) | High insulation, low thermal conductivity (~0.04 W/m*K) |
| Mechanical Strength | Brittle, high compressive strength | Flexible, high tensile strength |
| Applications | Windows, glassware | Building insulation, HVAC systems |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Durability | Prone to breakage | Resistant to moisture and fire |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but energy-intensive production | Recyclable, energy-efficient insulation |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Potash-lime glass and fiberglass are both widely used materials in insulation due to their thermal resistance properties. Potash-lime glass, characterized by its chemical composition including potassium oxide, offers moderate thermal insulation and durability, commonly used in windows and structural applications. Fiberglass, composed of fine glass fibers, provides superior thermal insulation, soundproofing, and fire resistance, making it a preferred choice in building insulation and industrial applications.
Overview of Potash-Lime Glass
Potash-lime glass, consisting primarily of silica, potassium oxide, and lime, offers notable thermal stability and chemical resistance. It is widely utilized in insulation due to its effective heat retention properties and durability under varying temperatures. Compared to fiberglass, potash-lime glass provides enhanced moisture resistance but typically lacks the flexibility and lightweight characteristics of fiberglass insulation.
What is Fiberglass Insulation?
Fiberglass insulation consists of fine glass fibers woven into a material designed to reduce heat transfer and enhance energy efficiency. It offers superior thermal resistance compared to potash-lime glass, making it a preferred choice for residential and commercial insulation applications. Fiberglass insulation also provides soundproofing qualities and resists moisture, improving indoor comfort and durability.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Potash-lime glass offers moderate thermal insulation due to its dense composition, resulting in higher thermal conductivity compared to fiberglass. Fiberglass insulation excels with a low thermal conductivity value, typically around 0.04 W/m*K, creating effective resistance against heat transfer. Choosing fiberglass enhances energy efficiency in buildings by providing superior insulation performance over potash-lime glass materials.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Potash-lime glass exhibits lower mechanical strength compared to fiberglass, making fiberglass more suitable for applications requiring high tensile and impact resistance. Fiberglass insulation boasts superior durability and resistance to thermal cycling, moisture, and chemical degradation, enhancing long-term performance in demanding environments. The enhanced toughness of fiberglass results from its reinforced composite structure, which underpins its widespread use in structural insulation and industrial settings.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Potash-lime glass exhibits lower chemical durability and moisture resistance compared to fiberglass, making it more susceptible to degradation in damp environments. Fiberglass insulation offers superior resistance to moisture absorption and chemical corrosion, enhancing its longevity and performance in high-humidity or chemically aggressive settings. This makes fiberglass a preferred choice for insulation in areas prone to moisture exposure and chemical contact.
Fire and Heat Resistance Properties
Potash-lime glass offers moderate fire resistance but tends to soften and deform at temperatures above 500degC, limiting its use in high-heat insulation applications. Fiberglass insulation withstands temperatures up to 650degC without melting or releasing toxic fumes, making it superior for fire-resistant construction. The thermal stability and non-combustible nature of fiberglass ensure enhanced safety and performance in fire-prone environments compared to potash-lime glass.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Potash-lime glass insulation has a lower environmental footprint due to its use of naturally abundant raw materials and higher recyclability compared to fiberglass, which often relies on energy-intensive manufacturing and non-renewable resources. The energy consumption during the production of potash-lime glass is typically less, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainability in construction. Fiberglass insulation, while effective for thermal performance, tends to generate more landfill waste and has a lower potential for reuse, making potash-lime glass a more eco-friendly option for sustainable building projects.
Cost Efficiency and Installation Considerations
Potash-lime glass insulation typically offers lower upfront material costs compared to fiberglass, making it a cost-efficient option for budget-conscious projects. Installation of potash-lime glass requires careful handling due to its brittleness, whereas fiberglass is easier to install with flexible batts or rolls that conform to spaces, reducing labor time and expenses. Long-term cost efficiency favors fiberglass for its superior thermal performance and durability, decreasing energy bills and maintenance needs over time.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Potash-lime glass insulation offers superior thermal resistance and is environmentally friendly due to its recyclable nature, making it ideal for sustainable construction. Fiberglass insulation excels in affordability and ease of installation, with effective soundproofing properties suitable for residential and commercial buildings. Selecting the right material depends on balancing budget constraints, environmental impact, and specific insulation performance requirements.
Infographic: Potash-lime glass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com