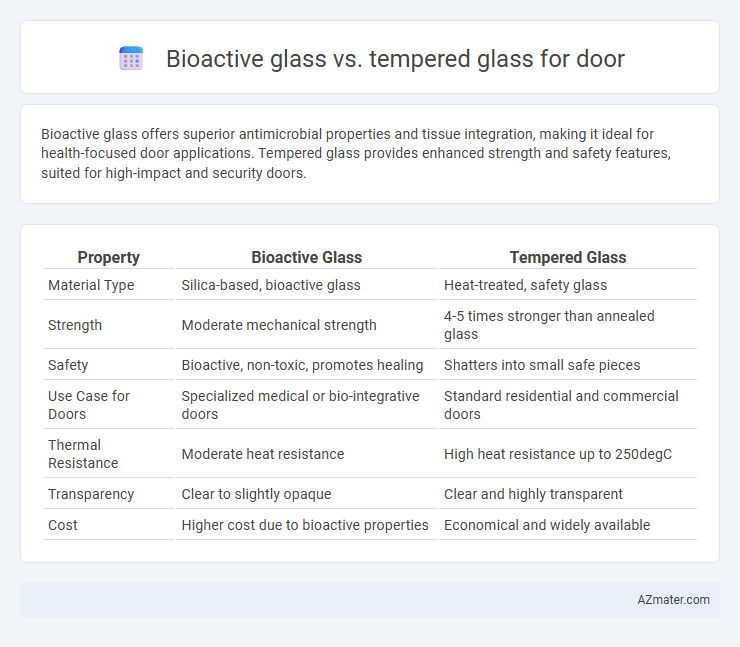
Bioactive glass offers superior antimicrobial properties and tissue integration, making it ideal for health-focused door applications. Tempered glass provides enhanced strength and safety features, suited for high-impact and security doors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioactive Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Silica-based, bioactive glass | Heat-treated, safety glass |
| Strength | Moderate mechanical strength | 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass |
| Safety | Bioactive, non-toxic, promotes healing | Shatters into small safe pieces |
| Use Case for Doors | Specialized medical or bio-integrative doors | Standard residential and commercial doors |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | High heat resistance up to 250degC |
| Transparency | Clear to slightly opaque | Clear and highly transparent |
| Cost | Higher cost due to bioactive properties | Economical and widely available |
Introduction to Bioactive Glass and Tempered Glass
Bioactive glass is a chemically active material that interacts with biological tissues, promoting healing and bonding through the release of ions, making it ideal for medical and specialized applications. Tempered glass undergoes controlled thermal or chemical treatments to enhance its strength and safety, shattering into small, less harmful pieces upon impact, commonly used in door and window installations. Both materials offer unique benefits: bioactive glass for its regenerative properties and tempered glass for its durability and safety in structural applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Bioactive glass used for doors contains silica, calcium oxide, sodium oxide, and phosphorus pentoxide, promoting bioactivity and bonding properties, while tempered glass is primarily soda-lime silica glass subjected to thermal or chemical treatments to increase strength. The manufacturing process of bioactive glass involves melting raw materials at high temperatures followed by controlled cooling to maintain bioactive properties, whereas tempered glass undergoes rapid heating to around 620-650degC and rapid cooling (quenching) to induce compressive stresses on the surface. Bioactive glass's unique composition enables interaction with biological environments, contrasting with tempered glass's focus on enhanced mechanical durability and safety.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Bioactive glass for doors offers superior mechanical strength with enhanced fracture toughness and resistance to crack propagation compared to tempered glass, making it highly durable under stress. Tempered glass, while strong due to its thermal treatment, is more prone to shattering into small pieces upon breakage, whereas bioactive glass maintains structural integrity longer under impact. The enhanced durability of bioactive glass results from its molecular composition that promotes self-healing and corrosion resistance, outperforming tempered glass in high-stress and long-term applications.
Safety Features and Impact Resistance
Bioactive glass offers enhanced safety features due to its ability to bond with biological tissues and self-heal minor scratches, making it highly durable in door applications. Tempered glass provides superior impact resistance by undergoing a thermal or chemical treatment process that increases its strength and causes it to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards upon breakage. Both materials improve door safety, but tempered glass excels in impact resistance, while bioactive glass contributes to long-term durability and injury prevention.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Bioactive glass offers superior aesthetic appeal with its ability to integrate natural elements and luminescent effects, creating visually striking door designs often used in modern, eco-friendly spaces. Tempered glass provides sleek, clean lines and high transparency, ensuring both safety and a minimalist, contemporary look favored in commercial and residential doors. Design flexibility is enhanced with bioactive glass through customizable color and texture options, while tempered glass excels in versatile thicknesses and shapes suitable for frameless or reinforced door styles.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Properties
Bioactive glass enhances energy efficiency in doors through its advanced thermal insulation and ability to reduce heat transfer, thereby maintaining indoor temperature stability. Tempered glass offers strength and safety but generally provides lower insulation performance compared to bioactive glass, leading to increased energy consumption. Selecting bioactive glass can significantly decrease heating and cooling costs by improving overall door thermal resistance and minimizing energy loss.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Bioactive glass for doors offers superior resistance to stains and bacterial growth, significantly reducing the frequency and intensity of cleaning required compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass, while durable against impact, is more prone to showing smudges, fingerprints, and water spots, leading to more frequent maintenance efforts. Choosing bioactive glass enhances hygiene and minimizes upkeep, making it an optimal choice for high-traffic or health-conscious environments.
Cost Comparison and Economic Value
Bioactive glass typically costs more than tempered glass due to its advanced composition and specialized manufacturing process, impacting initial expenditure for door installations. Tempered glass offers lower upfront costs while maintaining strength and safety standards, making it a more economical choice for budget-conscious projects. Evaluating long-term economic value, bioactive glass's potential benefits in durability and antimicrobial properties may justify higher costs in healthcare or specialized environments compared to the cost-effective tempered glass used in conventional settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioactive glass used in doors offers enhanced environmental benefits due to its recyclability and ability to support natural ecosystems through bioactivity, contrasting with tempered glass which, while strong and durable, requires higher energy for production and is less eco-friendly to recycle. Tempered glass production involves significant carbon emissions from its heat treatment process, making it less sustainable compared to bioactive glass that reduces environmental footprint through lower energy use and waste. Bioactive glass's ability to integrate with the environment and promote longevity positions it as a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious door applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Door: Key Takeaways
Bioactive glass offers antimicrobial properties and enhanced durability, making it ideal for high-traffic or healthcare-related door applications where hygiene is critical. Tempered glass provides superior strength and impact resistance, ensuring safety and shatterproof performance suitable for residential and commercial doors. Choosing the right glass depends on prioritizing factors such as sanitation needs, impact resistance, and the specific environmental conditions of the door's location.
Infographic: Bioactive glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com