Prismatic glass enhances privacy and diffuses light through its textured surface, making it ideal for decorative door applications. Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, suitable for high-traffic or safety-critical door installations.
Table of Comparison
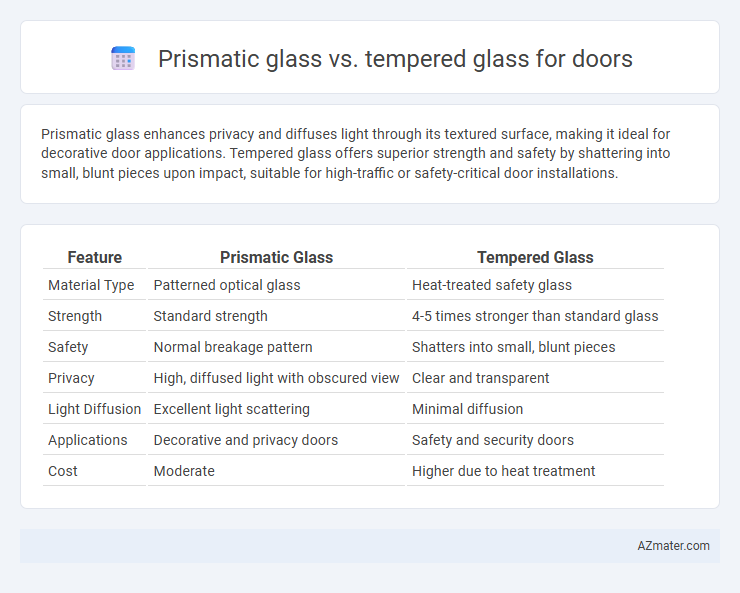
| Feature | Prismatic Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Patterned optical glass | Heat-treated safety glass |
| Strength | Standard strength | 4-5 times stronger than standard glass |
| Safety | Normal breakage pattern | Shatters into small, blunt pieces |
| Privacy | High, diffused light with obscured view | Clear and transparent |
| Light Diffusion | Excellent light scattering | Minimal diffusion |
| Applications | Decorative and privacy doors | Safety and security doors |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to heat treatment |
Introduction: Prismatic Glass vs Tempered Glass for Doors
Prismatic glass offers enhanced light diffusion, creating privacy while maintaining brightness, making it ideal for decorative door panels. Tempered glass provides superior strength and safety, as it shatters into small, blunt pieces upon impact, making it suitable for high-traffic or safety-critical door applications. Choosing between prismatic and tempered glass depends on whether the priority is aesthetic light control or structural durability and safety.
What is Prismatic Glass?
Prismatic glass is designed with a textured surface that refracts light to enhance brightness and privacy while reducing glare, making it ideal for doors in both residential and commercial settings. Unlike tempered glass, which is heat-treated for strength and safety, prismatic glass focuses on optical performance and decorative aesthetics. This glass type improves natural light diffusion without compromising structural integrity, offering unique visual appeal combined with functional transparency.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. When broken, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, reducing the risk of injury, making it ideal for door applications requiring durability and safety. Prismatic glass, by contrast, is designed primarily for light diffusion and aesthetic effects rather than impact resistance.
Visual Appeal and Design Options
Prismatic glass offers unique light diffusion and decorative patterns that enhance visual appeal through intricate textures and color variations, making it ideal for artistic door designs. Tempered glass provides a sleek, clear, and modern aesthetic with superior strength and safety, allowing for minimalist and contemporary door styles. Both glass types support diverse customization, but prismatic glass excels in ornamental features while tempered glass emphasizes durability and transparency.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tempered glass offers superior strength and impact resistance compared to prismatic glass, making it ideal for door applications requiring enhanced safety and durability. While prismatic glass provides decorative light diffusion and moderate strength, tempered glass undergoes a heat treatment process that significantly increases its toughness and shatter resistance. Doors featuring tempered glass can withstand greater force and temperature variations, ensuring long-lasting performance in both residential and commercial settings.
Safety Features and Performance
Prismatic glass enhances safety by diffusing light to reduce glare and improve visibility, minimizing the risk of accidents near doors. Tempered glass offers superior strength, shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, significantly reducing injury hazards. Both materials provide reliable performance; tempered glass excels in impact resistance, while prismatic glass enhances safety through light management.
Privacy Considerations
Prismatic glass offers enhanced privacy by diffusing light and obscuring visibility, making it ideal for door applications where maintaining discretion is essential. Tempered glass, while significantly stronger and safer due to its shatter-resistant properties, tends to be clear or lightly tinted, offering less inherent privacy without additional treatments. Choosing prismatic glass for doors increases privacy without compromising light transmission, whereas tempered glass prioritizes safety with limited privacy benefits unless combined with frosted or laminated layers.
Energy Efficiency and Light Diffusion
Prismatic glass enhances energy efficiency by diffusing natural light evenly, reducing glare and the need for artificial lighting, which lowers electricity usage. Tempered glass, while stronger and safer due to its heat-treated durability, typically offers less light diffusion, allowing more direct sunlight that can increase heat gain and cooling costs. Choosing prismatic glass for doors optimizes daylight penetration and thermal comfort, contributing to sustainable energy management in buildings.
Cost Differences and Installation Factors
Prismatic glass typically costs more than tempered glass due to its specialized light-diffusing properties and intricate manufacturing process, making it a premium choice for doors that require enhanced privacy and aesthetics. Installation of prismatic glass demands precise alignment to preserve its optical effects, which can increase labor costs and time compared to tempered glass known for its straightforward, quicker installation. Tempered glass offers a cost-effective, durable solution with easier handling and faster fitting, making it ideal for budget-conscious projects where safety and strength are prioritized over decorative light diffusion.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Door
Prismatic glass is ideal for doors requiring enhanced privacy and light diffusion, making it perfect for office partitions and interior doors where natural light is desired without clear visibility. Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety, suited for exterior doors and high-traffic areas needing impact resistance and compliance with building codes. Selecting between prismatic and tempered glass depends on balancing privacy, light control, safety requirements, and the door's location within a building.
Infographic: Prismatic glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com