Tempered glass lenses offer enhanced durability and scratch resistance, while optical glass lenses provide superior clarity and color accuracy for high-precision imaging. Choosing between tempered and optical glass depends on the balance of impact resistance versus optical performance required.
Table of Comparison
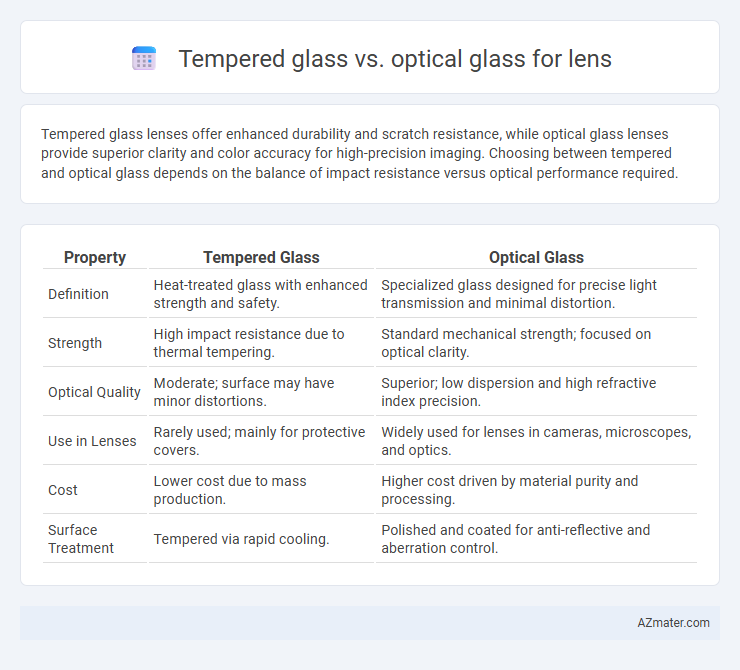
| Property | Tempered Glass | Optical Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heat-treated glass with enhanced strength and safety. | Specialized glass designed for precise light transmission and minimal distortion. |
| Strength | High impact resistance due to thermal tempering. | Standard mechanical strength; focused on optical clarity. |
| Optical Quality | Moderate; surface may have minor distortions. | Superior; low dispersion and high refractive index precision. |
| Use in Lenses | Rarely used; mainly for protective covers. | Widely used for lenses in cameras, microscopes, and optics. |
| Cost | Lower cost due to mass production. | Higher cost driven by material purity and processing. |
| Surface Treatment | Tempered via rapid cooling. | Polished and coated for anti-reflective and aberration control. |
Introduction to Lens Materials
Tempered glass and optical glass are fundamental materials used in lens manufacturing, each offering distinct durability and clarity characteristics essential for precision optics. Optical glass, specifically formulated with controlled refractive indices and minimal impurities, provides superior image quality and light transmission crucial for high-performance lenses. Tempered glass, enhanced through thermal treatment, offers increased strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for lenses subjected to harsh conditions without significantly compromising transparency.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass, making it highly durable and resistant to scratches and impacts. Unlike optical glass, which is specifically engineered for superior light transmission and minimal distortion in lenses, tempered glass is often used as a protective layer over camera lenses to prevent damage. Its enhanced hardness and shatter-resistant properties ensure lens longevity without significantly compromising image clarity.
What is Optical Glass?
Optical glass is a specially formulated material designed to transmit and refract light with high precision, commonly used in camera lenses, microscopes, and telescopes for superior image clarity. Unlike tempered glass, which is heat-treated for durability and impact resistance, optical glass is engineered for optimal optical properties such as low dispersion, high homogeneity, and controlled refractive indices. This makes optical glass essential for high-performance lenses requiring sharp focus and minimal distortion.
Key Differences Between Tempered and Optical Glass
Tempered glass offers enhanced durability and impact resistance due to its heat treatment process, making it ideal for protective coverings rather than precision lenses. Optical glass, specifically designed for lenses, provides superior clarity, minimal distortion, and precise refractive properties essential for high-quality imaging. The key difference lies in tempered glass prioritizing strength and safety, while optical glass prioritizes optical performance and accuracy in visual applications.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Tempered glass in lenses exhibits superior durability due to its enhanced resistance to impact and scratch compared to optical glass, which is more prone to chipping and cracking under stress. Optical glass, while providing higher optical clarity and precision, lacks the structural reinforcement found in tempered glass, making it less ideal for rugged use. The heat-treatment process in tempered glass significantly increases tensile strength, resulting in lenses that withstand daily wear and accidental drops more effectively than conventional optical glass.
Optical Clarity and Performance
Optical glass provides superior optical clarity and performance compared to tempered glass due to its precise refractive index and minimal light distortion, essential for high-quality lenses. Tempered glass, while durable and impact-resistant, often compromises image sharpness and color accuracy because of its lower transparency and higher internal stress. For applications demanding exceptional visual fidelity, such as camera lenses or scientific instruments, optical glass remains the preferred material.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Tempered glass lenses offer superior scratch resistance due to their hardened surface, making them ideal for environments with frequent abrasion risks. Optical glass, while providing exceptional clarity and minimal distortion, typically lacks the enhanced impact resistance found in tempered variants, making it more vulnerable to chipping or cracking under stress. The choice between tempered and optical glass hinges on the balance between durability needs and optical performance requirements.
Cost and Availability
Tempered glass lenses generally offer a lower cost option compared to optical glass due to simpler manufacturing processes and widespread industrial availability. Optical glass lenses provide superior optical clarity and are preferred for high-precision applications but come at a higher price and limited availability from specialized suppliers. The choice between tempered and optical glass lenses depends largely on budget constraints and the required optical performance.
Best Use Cases for Each Material
Tempered glass lenses excel in durability and impact resistance, making them ideal for rugged outdoor activities, sports eyewear, and industrial applications where lens safety is crucial. Optical glass offers superior clarity, precise refractive properties, and minimal distortion, making it the best choice for high-precision optical instruments such as cameras, microscopes, and telescopes. Selecting tempered glass ensures enhanced protection under harsh conditions, whereas optical glass guarantees exceptional image quality in controlled environments.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Lens
Tempered glass offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance, making it ideal for lenses exposed to harsh environments or frequent handling. Optical glass, known for superior light transmission and minimal distortion, is preferred in precision lenses requiring high clarity and accuracy. Choosing the right glass depends on balancing durability needs with optical performance requirements specific to your lens application.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Optical glass for Lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com